mec12800-sup-0006-TableS2
advertisement
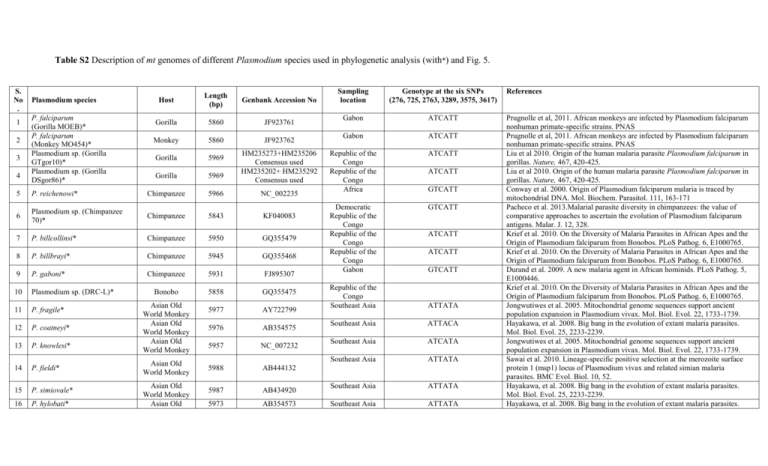
Table S2 Description of mt genomes of different Plasmodium species used in phylogenetic analysis (with*) and Fig. 5. S. No . 1 2 3 4 Plasmodium species P. falciparum (Gorilla MOEB)* P. falciparum (Monkey MO454)* Plasmodium sp. (Gorilla GTgor10)* Plasmodium sp. (Gorilla DSgor86)* Host Length (bp) Genbank Accession No Gorilla 5860 JF923761 Monkey 5860 JF923762 Gorilla 5969 Gorilla 5969 HM235273+HM235206 Consensus used HM235202+ HM235292 Consensus used 5 P. reichenowi* Chimpanzee 5966 NC_002235 6 Plasmodium sp. (Chimpanzee 70)* Chimpanzee 5843 KF040083 7 P. billcollinsi* Chimpanzee 5950 GQ355479 8 P. billbrayi* Chimpanzee 5945 GQ355468 9 P. gaboni* Chimpanzee 5931 FJ895307 10 Plasmodium sp. (DRC-L)* Bonobo 5858 GQ355475 11 P. fragile* 5977 AY722799 12 P. coatneyi* 5976 AB354575 13 P. knowlesi* 5957 NC_007232 14 P. fieldi* 5988 AB444132 15 P. simiovale* 5987 AB434920 16 P. hylobati* 5973 AB354573 Asian Old World Monkey Asian Old World Monkey Asian Old World Monkey Asian Old World Monkey Asian Old World Monkey Asian Old Sampling location Genotype at the six SNPs (276, 725, 2763, 3289, 3575, 3617) Gabon ATCATT Gabon ATCATT Republic of the Congo Republic of the Congo Africa ATCATT Democratic Republic of the Congo Republic of the Congo Republic of the Congo Gabon GTCATT ATCATT GTCATT ATCATT ATCATT GTCATT Republic of the Congo Southeast Asia ATTATA Southeast Asia ATTACA Southeast Asia ATCATA Southeast Asia ATTATA Southeast Asia ATTATA Southeast Asia ATTATA References Prugnolle et al, 2011. African monkeys are infected by Plasmodium falciparum nonhuman primate-specific strains. PNAS Prugnolle et al, 2011. African monkeys are infected by Plasmodium falciparum nonhuman primate-specific strains. PNAS Liu et al 2010. Origin of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum in gorillas. Nature, 467, 420-425. Liu et al 2010. Origin of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum in gorillas. Nature, 467, 420-425. Conway et al. 2000. Origin of Plasmodium falciparum malaria is traced by mitochondrial DNA. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 111, 163-171 Pacheco et al. 2013.Malarial parasite diversity in chimpanzees: the value of comparative approaches to ascertain the evolution of Plasmodium falciparum antigens. Malar. J. 12, 328. Krief et al. 2010. On the Diversity of Malaria Parasites in African Apes and the Origin of Plasmodium falciparum from Bonobos. PLoS Pathog. 6, E1000765. Krief et al. 2010. On the Diversity of Malaria Parasites in African Apes and the Origin of Plasmodium falciparum from Bonobos. PLoS Pathog. 6, E1000765. Durand et al. 2009. A new malaria agent in African hominids. PLoS Pathog. 5, E1000446. Krief et al. 2010. On the Diversity of Malaria Parasites in African Apes and the Origin of Plasmodium falciparum from Bonobos. PLoS Pathog. 6, E1000765. Jongwutiwes et al. 2005. Mitochondrial genome sequences support ancient population expansion in Plasmodium vivax. Mol. Biol. Evol. 22, 1733-1739. Hayakawa, et al. 2008. Big bang in the evolution of extant malaria parasites. Mol. Biol. Evol. 25, 2233-2239. Jongwutiwes et al. 2005. Mitochondrial genome sequences support ancient population expansion in Plasmodium vivax. Mol. Biol. Evol. 22, 1733-1739. Sawai et al. 2010. Lineage-specific positive selection at the merozoite surface protein 1 (msp1) locus of Plasmodium vivax and related simian malaria parasites. BMC Evol. Biol. 10, 52. Hayakawa, et al. 2008. Big bang in the evolution of extant malaria parasites. Mol. Biol. Evol. 25, 2233-2239. Hayakawa, et al. 2008. Big bang in the evolution of extant malaria parasites. 17 P. inui* 18 P. cynomolgi* 19 P. vivax* 20 P. gonderi* 21 Plasmodium sp. (Mandrill)* World Monkey Asian Old World Monkey Asian Old World Monkey Human African Old World Monkey African Old World Monkey 5972 AB354572 5884 AY800108 5990 AY598140 5900 AY800111 5896 AY800112 22 P. malariae* Human 5969 AB354570 23 P. ovale* Human 5855 HQ712053 24 P. gallinaceum* Bird 6003 NC_008288 25 P. juxtanucleare* Bird 6014 NC_008279 26 P. falciparum Human 5949 27 P. falciparum* Human 5967 28 29 30 P. falciparum (SUR1)* P. falciparum (SUR2)* P. falciparum (SUR6)* Human Human Human 5967 5967 5967 AY282924-AY282927, AY282929, AY282931-AY282982, AY282984-AY283006, AY283008-AY283019; AJ276844-AJ276847 KJ569459- KJ569462, KJ569464- KJ569478, KJ569481- KJ569483, KJ569485- KJ569487, KJ569489-KJ569502 KJ569479 KJ569480 KJ569484 Southeast Asia ATTATA Southeast Asia ATTATA Tropical, subtropical, and temperate regions Central Africa ATTATA ATCATA Central Africa ATCATA Tropical, subtropical, and temperate regions Tropical and subtropical regions Tropical and subtropical regions Tropical and subtropical regions Africa, South America, Asia and Papua new guinea ATTATA Mol. Biol. Evol. 25, 2233-2239. Hayakawa, et al. 2008. Big bang in the evolution of extant malaria parasites. Mol. Biol. Evol. 25, 2233-2239. Mu et al. 2005. Host switch leads to emergence of Plasmodium vivax malaria in humans. Mol. Biol. Evol. 22, 1686-1693. Jongwutiwes et al. 2005. Mitochondrial genome sequences support ancient population expansion in Plasmodium vivax. Mol. Biol. Evol. 22, 1733-1739. Mu et al. 2005. Host switch leads to emergence of Plasmodium vivax malaria in humans. Mol. Biol. Evol. 22, 1686-1693. Mu et al. 2005. Host switch leads to emergence of Plasmodium vivax malaria in humans. Mol. Biol. Evol. 22, 1686-1693. Hayakawa, et al. 2008. Big bang in the evolution of extant malaria parasites. Mol. Biol. Evol. 25, 2233-2239. ATTATA Pacheco et al. 2011. Timing the origin of human malarias: the lemur puzzle. BMC Evol. Biol. 11, 299. ATCATA Omori et al. 2007. Complete nucleotide sequences of the mitochondrial genomes of two avian malaria protozoa, Plasmodium gallinaceum and Plasmodium juxtanucleare. Parasitol. Res. 100, 661-664. Omori et al. 2007. Complete nucleotide sequences of the mitochondrial genomes of two avian malaria protozoa, Plasmodium gallinaceum and Plasmodium juxtanucleare. Parasitol. Res. 100, 661-664. Conway et al. 2000. Origin of Plasmodium falciparum malaria is traced by mitochondrial DNA. Mol. Biochem Parasitol. 111, 163-171. Joy et al. 2003. Early origin and recent expansion of Plasmodium falciparum. Science, 300, 318-321. ATCATT GCCGCA India GCCGCA This study India India India ATTGCA ATTGCA ATTGCA This study This study This study 31 32 33 34 35 31 P. falciparum (SUR10)* P. falciparum (SON8)* P. fragile (Pfragile1) P. fragile (Pfragile2) P. fragile (Pfragile3) P. coatneyi (Pcoatneyi2) Human Human 5967 5967 Monkey 1663 partial Monkey 1663 partial Monkey 1663 partial Monkey 1440 partial KJ569488 KJ569463 KJ668850+ KJ668851+ KJ668852+ HG969418 Consensus used KJ668853+ KJ668854+ KJ668855+ HG969419 Consensus used KJ668856+ KJ668857+ KJ668858+ HG969420 Consensus used KJ668847+ KJ668848+ KJ668849+ HG969417 Consensus used India India India ATTGCA ATTGCA ATTATA This study This study This study India ATTATA This study India ATTATA This study India ATTACA This study