Computer Generations: History & Evolution of Technology
advertisement

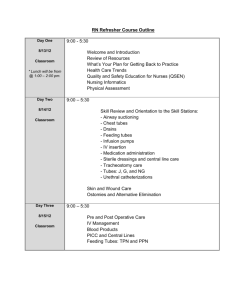
www.W3studentnotes.com GENERATIONS OF COMPUTER Generation means one step walk in hardware technology. But now a days, it has them standard to induce both hardware and software which together walk up man in trial computer system. There is no clear cut separating line between the Generations. Two generations may overlap each other in their technologies. With each new generation the circuitry has gotten smaller and more advanced than previous generations before it. As a result of this the speed, power and memory of computers has proportionally increased. (1) First Generation (1942-1955)- Vacuum Tubes The first generation computers used Vacuum Tubes as the main electronic component. These computers were physically large size with limited memory. The vacuum tubes consumed a large amount of electricity, produce large amount of heat were relatively unreliable. ENIAC, EDVAC, UNIVAC, IBM-650 are some example of first generation computer. Features of First Generation (a) Electronic circuit used vacuum tubes. (b) Punched card used for feeding information. (c) Punched card and paper used for getting results. (d) Slow input/output operation. (e) Limited programming capabilities. (2) Second Generation (1959-1965)-Transistor The second generation used Transistor in the place of Vacuum Tubes. Transistor were made from materials called semi conductors principally silicon and germanium. In these computer magnetic core was used as internal storage. IBM 1400 series and 7000 series are examples of second generation computers. Features of Second Generation (a) Electronic circuitry used transistor. (b) Secondary storage on tapes. (c) Greater reliability and speed. (d) Faster than first generation. (e) Development of magnetic disk storage. (3) Third Generation (1965-1974)-IC Integrated Circuit on chips (ICs) was used to store data and process instruction in the third generation computers. These computers could handle more than one operation simultaneously. IBM 380 series and ICL 1900 series are examples of third generation computer. Features of Third Generations (a) Electronic circuitry used Integrated Circuits. (b) Monitor and Keyboard were used for input and output. (c) Magnetic disk used for external storage. (d) Better storage devices. (e) Concepts of multiprogramming were used. (4) Fourth Generation (1974-1991)-Microprocessor In the fourth generation, Large Scale Integration and Very Large Scale Integration were Chips which packed about 50,000 Transistor in a single chip are used as the Primary Storage Medium and provided fast processing speed with more reliability. The IBM 370 and HP 3000 are examples of these computers. Satinder Singh M.Sc(IT), MCA Amandeep Singh B.Sc(IT), M.Sc(IT) www.W3studentnotes.com Features of Fourth Generation (a) Introduction to Microprocessor. (b) Disk memory become very large. (c) Large Scale and Very Large Scale Integration Circuits. (d) Semi conductor primary storage. (e) Very reliable. (5) Fifth Generation (Present)-Artificial Intelligence Exact time of fifth generation cannot be specified but it has been started near 1990. This generation name mainly emphasis in the field of Parallel Processing and Artificial Intelligence. This generation computers are termed as thinking computers that are capable of making reasoning and relational judgment. The main aim of this generation is to make computers intelligent like human being. Super computer and Robot are the result of this generation. Satinder Singh M.Sc(IT), MCA Amandeep Singh B.Sc(IT), M.Sc(IT)