Curriculum Plan
advertisement
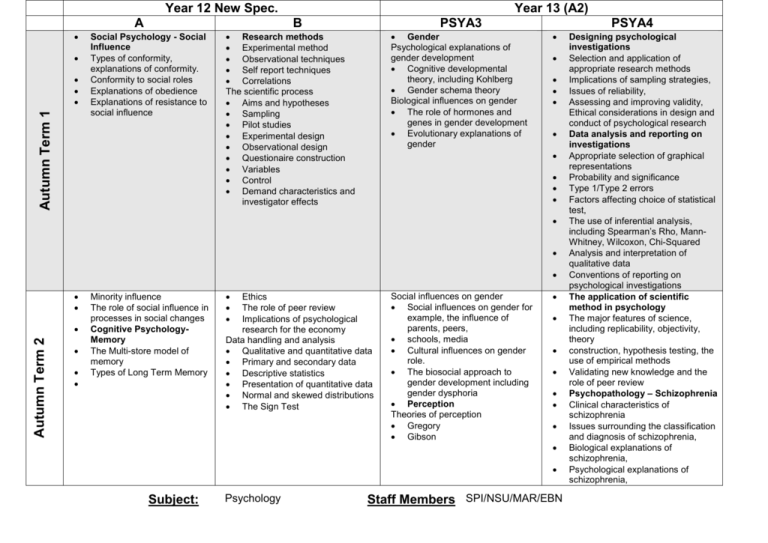
Year 12 New Spec. A Autumn Term 1 Year 13 (A2) B Social Psychology - Social Influence Types of conformity, explanations of conformity. Conformity to social roles Explanations of obedience Explanations of resistance to social influence PSYA3 Research methods Experimental method Observational techniques Self report techniques Correlations The scientific process Aims and hypotheses Sampling Pilot studies Experimental design Observational design Questionaire construction Variables Control Demand characteristics and investigator effects Gender Psychological explanations of gender development Cognitive developmental theory, including Kohlberg Gender schema theory Biological influences on gender The role of hormones and genes in gender development Evolutionary explanations of gender PSYA4 Autumn Term 2 Minority influence The role of social influence in processes in social changes Cognitive PsychologyMemory The Multi-store model of memory Types of Long Term Memory Ethics The role of peer review Implications of psychological research for the economy Data handling and analysis Qualitative and quantitative data Primary and secondary data Descriptive statistics Presentation of quantitative data Normal and skewed distributions The Sign Test Social influences on gender Social influences on gender for example, the influence of parents, peers, schools, media Cultural influences on gender role. The biosocial approach to gender development including gender dysphoria Perception Theories of perception Gregory Gibson Subject: Psychology Staff Members SPI/NSU/MAR/EBN Designing psychological investigations Selection and application of appropriate research methods Implications of sampling strategies, Issues of reliability, Assessing and improving validity, Ethical considerations in design and conduct of psychological research Data analysis and reporting on investigations Appropriate selection of graphical representations Probability and significance Type 1/Type 2 errors Factors affecting choice of statistical test, The use of inferential analysis, including Spearman’s Rho, MannWhitney, Wilcoxon, Chi-Squared Analysis and interpretation of qualitative data Conventions of reporting on psychological investigations The application of scientific method in psychology The major features of science, including replicability, objectivity, theory construction, hypothesis testing, the use of empirical methods Validating new knowledge and the role of peer review Psychopathology – Schizophrenia Clinical characteristics of schizophrenia Issues surrounding the classification and diagnosis of schizophrenia, Biological explanations of schizophrenia, Psychological explanations of schizophrenia, Summer Term 1 Spring Term 2 Spring Term 1 Summer Term 2 . • The Working Memory Model Explanations for forgetting Factors affecting the accuracy of eyewitness testimony Improving the accuracy of eyewitness testimony Developmental Psychology – attachment Caregiver-infant interactions in humans Approaches in Psychology The Learning Theory Approaches The Cognitive Approach The Biological Approach The Psychodynamic Approach The Humanistic Approach Comparison of Approaches Animal studies of attachment Explanations of attachment Ainsworth’s ‘The Strange Situation’ Bowlby’s theory of maternal deprivation The influence of early attachment on childhood and adult relationships . Research Project Psychopathology Definitions of abnormality Behavioural, emotional and cognitive characteristics of phobias, depression and OCD The behavioural approach to phobias The cognitive approach to depression The biological approach to OCD Research Project Mocks Development of perception Developmental of Perceptual abilities Perceptual development Face recognition Bruce and Young’s theory Explanations of prosopagnosia Biological therapies for schizophrenia, Psychological therapies for schizophrenia, for example, Biological rhythms and sleep Biological rhythms Circadian, infradian, and ultradian rhthyms, including the role of endogenous pacemakers and of exogenous zeitgebers in the control of circadian rhythms Disruption of biological rhythms, for example shift work, jet lag Sleep The nature of sleep Functions of sleep, Disorders of sleep Explanations for sleep disorders, Mocks Media psychology Media influences on social behaviour Explanations of media influences on pro- and anti-social behaviour The positive and negative effects of computers and video games on behaviour. Revision and Exam preparation N/A Media and persuasion The application of Hovland-Yale and Elaboration Likelihood models in explaining the persuasive effects of media Explanations for the persuasiveness of television advertising The psychology of ‘celebrity’ The attraction of ‘celebrity’, including social psychological and evolutionary explanations Research into intense fandom, including, celebrity worship and celebrity stalking. Consolidation Revision of all topics. Exam preparation. N/A







