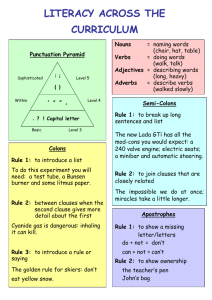
Yr 7 grammar planning grid Spring term
advertisement

Year 7 Grammar lessons: Spring term L1: What is a simple sentence? Why are simple sentences used? (Revision) L4: What is a main clause? What is a subordinate clause? What is a complex sentence with embedded clauses? LO L1: What is a simple sentence? Why are simple sentences used? Homework Students choose one picture to construct a paragraph using simple sentences for effect. L2: What is a compound sentence? L5: What is a complex sentence? What is a subordinating conjunction? Starter Students copy date and title Do it now task! Vocabulary test L3: To be able to identify and use commas within a list L6: Grammar checkpoint Introduction Development Recap definition of Explain to a simple sentence. students that being able to Students identify identify a simple the subject and sentence is good verb in a range of but being able to simple sentences. comment on its Feedback. effect is important. Read an extract from ‘Wonder’. Students identify simple sentences from within the passage. Feedback. Students use a visual stimulus to describe a character in a particular situation using simple Read through first passage from ‘Stormcatchers’. Explain that simple sentences have been used here to create tension. Model the first example before students explore three further sentences, explaining how they help to create Plenary What is a subject? What is a verb? What is a simple sentence? Why are simple sentences used? sentences. Feedback. tension. Feedback. Introduce students to text and how simple sentences have been used for emotive impact. Students explore three simple sentences and their emotive impact before considering their overall impact. Feedback. Complete a class reading of an information text and the use of simple sentences to convey information. Students identify five simple sentences and the information that is being conveyed. Feedback. L2: What is a compound sentence? Students re-draft paragraph from 1st homework to incorporate compound sentences. Students copy date and title Recap: What is a simple sentence? Do it now task! Vocabulary test Read through definition and example of a compound sentence. Introduce students to three different co-ordinating conjunctions with a general overview of their purpose: Compound Students explore a sentences using range of ‘and’ to express compound similar ideas. sentences, identifying the 2 Compound simple sentences, sentences using the subject, the ‘but’ to express verb and the contrasting ideas. linking conjunction. Compound Feedback. sentences using ‘so’ to express the consequence of one action on another. Students read through a passage and identify the compound sentences before exploring what the co-ordinating Show students a selection of sentences with one of three coordinating conjunctions at the end. Students finish the sentences, ensuring the relationship between the two simple sentences is as it should be. Feedback. Plenary: How does a compound sentence differ from a simple sentence? Why do we use the coordinating conjuctions ‘and’, ‘but’ and ‘so’? conjunction tells them. Feedback. sentences. L3: To be able to identify and use commas to separate items in a list. Students insert commas into a number of sentences. Students construct three sentences using commas in a list to describe three of the characters from Wonder. SAMLearning: simple and compound sentences Students copy date and title Do it now task! Vocabulary test Recap questions: What is a subject? What is a verb? What is a simple sentence? How does a compound sentence differ from a simple sentence? Feedback responses. Show students a Plenary question: picture stimulus. Comma focus in Students create today’s lesson. sentences containing commas in a list to describe different features of the picture. Feedback. Students identify simple and compound sentences from within a passage. Extending: Students identify the effect of these sentences. Students construct a descriptive paragraph of writing using commas in a list but simple and compound sentences as well, using the picture stimulus. Recap commas and the multiple purposes that commas serve. Recap commas to Students selfassess their work, identifying in the margin where they have used the separate items in a list. Students identify where the commas should go in a number of sentences. Feedback. L4: What is a main clause? What is a subordinate clause? What is a complex sentence with embedded clauses? Students add in the commas to the complex sentences before identifying the main and the subordinate clauses. Students then redraft their paragraph incorporating complex sentences with embedded clauses. Students copy date and title Do it now task! Vocabulary test Recap questions: What is a simple sentence? What is a compound sentence? above sentence structures. Feedback, examples of students’ work. Students explore a grid of clauses. Students identify which of the clauses are main and which of the Introduce complex clauses are sentences with an subordinate. embedded clause. Model example. Students then use the clauses to Students identify form complex the main and sentences with subordinate embedded clauses in a clauses. number of complex Feedback sentences. students’ Feedback. responses. Students re-draft complex sentences with Students read through a passage and identify the simple, compound and complex sentences with embedded clauses. Students find at least one example of each and explain how they know it is the particular sentence type. E.g. simple sentence – one subject and one verb used for ___ effect. embedded clauses, inserting the commas in the appropriate places. Feedback. L5: What is a complex sentence? What is a subordinating conjunction? Students write up paragraph describing one of three pictures, ensuring paragraph incorporates: Simple sentences for effect Compound sentences Commas in a list Commas with embedded clauses Commas using subordinating conjunctions. Students copy date and title Do it now task! Vocabulary test Recap questions: What is a subject? What is a verb? What is a simple sentence? What is a compound sentence? What is a main clause? What is a subordinate clause? Where do the commas in a complex sentence with embedded clauses go? Show students a visual stimulus taken from The Fault in Our Stars. In pairs, students construct complex sentences that begin with the subordinating conjunctions on the page. Students then continue to work in pairs or groups of four on crafting a Show students description using two complex the complex sentences – one sentences with with an embedded subordinating clause and one conjunctions but, if using a they wish to subordinating extend conjunction. themselves, with simple, Students share their descriptive paragraphs, orally talking through their selfassessment of structures. Students identify main and subordinate clause in a number of sentences. Students also identify the subordinating conjunction. Feedback. L6: Grammar check. compound, complex with embedded clauses and commas in a list. Students selfassess their sentence usage in the margin. Students re-draft complex sentences so that they begin with the subordinating conjunction and a comma is inserted correctly. Feedback. Grammar checkpoint to assess their understanding of unit and previous unit.