Y9 Physics Keyword List
advertisement
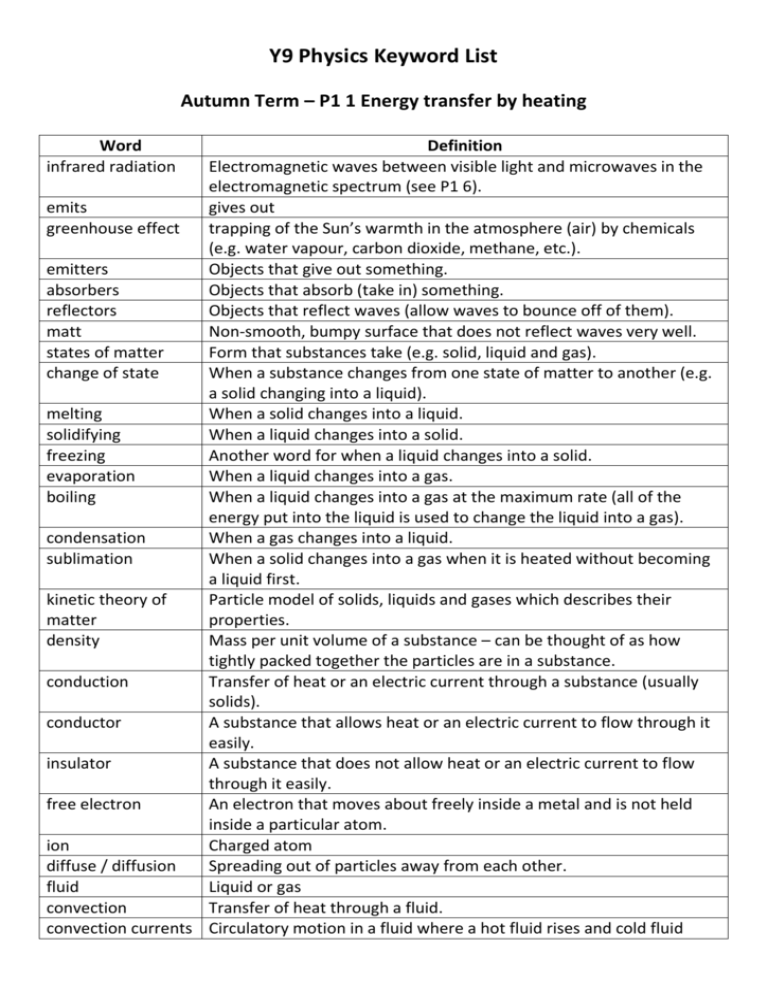
Y9 Physics Keyword List Autumn Term – P1 1 Energy transfer by heating Word infrared radiation Definition Electromagnetic waves between visible light and microwaves in the electromagnetic spectrum (see P1 6). emits gives out greenhouse effect trapping of the Sun’s warmth in the atmosphere (air) by chemicals (e.g. water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, etc.). emitters Objects that give out something. absorbers Objects that absorb (take in) something. reflectors Objects that reflect waves (allow waves to bounce off of them). matt Non-smooth, bumpy surface that does not reflect waves very well. states of matter Form that substances take (e.g. solid, liquid and gas). change of state When a substance changes from one state of matter to another (e.g. a solid changing into a liquid). melting When a solid changes into a liquid. solidifying When a liquid changes into a solid. freezing Another word for when a liquid changes into a solid. evaporation When a liquid changes into a gas. boiling When a liquid changes into a gas at the maximum rate (all of the energy put into the liquid is used to change the liquid into a gas). condensation When a gas changes into a liquid. sublimation When a solid changes into a gas when it is heated without becoming a liquid first. kinetic theory of Particle model of solids, liquids and gases which describes their matter properties. density Mass per unit volume of a substance – can be thought of as how tightly packed together the particles are in a substance. conduction Transfer of heat or an electric current through a substance (usually solids). conductor A substance that allows heat or an electric current to flow through it easily. insulator A substance that does not allow heat or an electric current to flow through it easily. free electron An electron that moves about freely inside a metal and is not held inside a particular atom. ion Charged atom diffuse / diffusion Spreading out of particles away from each other. fluid Liquid or gas convection Transfer of heat through a fluid. convection currents Circulatory motion in a fluid where a hot fluid rises and cold fluid moves in to fill its place. air conditioning unit A system for controlling the temperature of air in a room or vehicle. energy transfer Movement of energy from one object to another. payback time Time it takes to save back the money spent on something. U-values Energy per second that passes through 1 m2 of a material when the temperature difference between its two surfaces is 1 ˚C. mass How much matter (‘stuff’) there is in an object – measured in kilograms. specific heat Energy needed by 1 kg of a substance to increase its temperature by capacity 1 ˚C. storage heaters An electric heater that gains heat in water or bricks over night when electricity is cheaper and then releases the energy during the day. Spring Term – P1 5 Waves and P1 6 Electromagnetic Waves Word mechanical waves electromagnetic waves sound waves transverse waves longitudinal waves compressions rarefactions plane mirror ray diagram reflection image normal angle of incidence angle of reflection virtual image Definition Vibration that travels through a substance. Electric and magnetic disturbances that transfer energy from one place to another. Vibrations that pass through a substance and can be detected as sound. Waves in which the vibrations are perpendicular (at 90˚) to the direction energy is transferred. Waves in which the vibrations are parallel to (in the same direction as) the direction energy is transferred. Parts of a longitudinal wave which are squeezed together, so that they have a higher density. Parts of a longitudinal wave which are stretched or spread apart, so that they have a lower density. Flat mirror Diagram drawn to show the direction a wave travels in (usually drawn for light rays). When a wave bounces off of the surface of a substance. A copy of an object formed by a mirror or lens. Straight line through a surface or boundary perpendicular (at 90˚) to the surface or boundary. Angle between the incident ray (approaching a mirror) and the normal. Angle between the reflected ray (moving away from a mirror) and the normal. An image, seen in a lens or mirror, from which light rays appear to come from. A virtual image cannot be projected onto a screen and light rays never meet at its position. real image An image formed where light rays meet. A real image can be projected onto a screen. refraction The change in direction of a wave when it passes across a boundary between two substances (e.g. when light passes from air into glass). boundary The surface between one substance and another. prism A glass or transparent object, usually triangular in shape, that can be used to split white light into its different colours. total internal When light travelling towards a boundary between a more dense and reflection a less dense substance (e.g. glass to air) is completely reflected back in to the denser substance (e.g. the glass). diffraction The spreading of waves when they pass through a gap or around the edges of an obstacle which has a similar size as the wavelength of the waves. crests Peaks of a transverse wave. troughs Bottom most parts of a transverse wave. amplitude The height of a wave crest or a wave trough of a transverse wave from the rest position. In a longitudinal wave, this is the maximum distance moved by an oscillating object from its equilibrium position. wavelength The distance from one wave crest to the next wave crest (along the waves). frequency The number of wave crests passing a fixed point every second. Hertz (Hz) Unit of frequency speed How fast an object is travelling white light Light that is made of all the colours of the visible spectrum. electromagnetic List of electromagnetic waves which shows the different types of spectrum electromagnetic waves as their wavelength changes. microwaves Electromagnetic waves with a wavelength between approximately 1 mm and 10 cm. radio waves Electromagnetic waves with a wavelength longer than about 10 cm. These are electromagnetic waves with the lowest energy. Bluetooth Short range radio wave connections which are used to transfer information. Satellite Object in orbit around a planet. Around Earth, some artificial satellites are used for microwave communications. visible light Electromagnetic waves that can be seen by the human eye. infrared radiation Electromagnetic waves between visible light and microwaves in the electromagnetic spectrum. optical fibre Thin glass fibre used to send signals. ultraviolet radiation Electromagnetic waves between visible light and X-rays in the electromagnetic spectrum. X-rays Electromagnetic waves between ultra violet and gamma rays in the electromagnetic spectrum. They are commonly used for medical imaging. gamma radiation Electromagnetic waves with the shortest wavelengths and the echo vacuum pitch resonates Doppler effect red-shift blue-shift galaxy universe Big Bang theory cosmic microwave background radiation Big Yawn Big Crunch highest energy in the electromagnetic spectrum. Reflection of a sound wave – when a sound wave bounces off of a surface. An area or space which is entirely empty and contains no matter. How high a sound wave sounds – it is directly related to its frequency. When sound vibrations build up in a musical instrument and cause the sound from the instrument to become much louder. The change of wavelength (and frequency) of the waves from a moving source due to the movement of the source towards or away from the observer. Increase in the wavelength of electromagnetic waves emitted by a star or galaxy due to its motion away from us. The faster the speed of the star or galaxy, the greater the red-shift. Decrease in the wavelength of electromagnetic waves emitted by a star or galaxy due to its motion towards us. The faster the speed of the star or galaxy, the greater the blue-shift. Collection of billions of stars. All existing matter and space The theory that the universe was created in a massive explosion (the Big Bang) and that the universe has been expanding ever since. Electromagnetic radiation that has been travelling through space ever since it was created shortly after the Big Bang. The radiation was emitted as gamma radiation, but has been red-shifted to microwaves. The theory that if the density of the universe is less than a certain amount, it will expand forever. The theory that if the density of the universe is more than a certain amount, it will stop expanding and reverse, moving back inwards. Summer Term – P1 2 Using energy Word energy transfer chemical energy kinetic energy gravitational potential energy elastic potential energy electrical energy sound energy light energy conservation of energy pendulum machine useful energy wasted energy dissipated weight newtons (N) joules (J) Sankey diagram input energy efficiency Definition Movement of energy from one object to another. Energy of an object due to chemical reactions in it. For example chemical energy is stored in batteries and food. Energy of a moving object due to its motion. Energy of an object due to its position in a gravitational field. Energy stored in an elastic object when work is done to change its shape. E.g. energy stored in a stretch elastic band. Energy transferred by the movement of electrical energy. Energy transferred by sound waves. Energy transferred by visible waves. Law that energy cannot be created or destroyed. A mass attached to the end of a rod or string. When moved from their still position they swing from side to side, and are used in some clocks. Device or object used to do something useful. Energy transferred to where it is wanted in the form it is wanted. Energy that is not usefully transferred. Energy is spread out to the surroundings, usually in the form of heat. The force of gravity on an object. The unit of weight. The unit of energy. A diagram to show how energy is transferred in a particular situation Energy put into a system or device. Useful energy transferred by a device divided by the total energy supplied to the device. It is a measure of how good a device is at transferring energy usefully.







