CHAPTER 20 Anti Infectives Quiz Yourself 1. Sulfonamide drugs

CHAPTER 20 Anti Infectives
Quiz Yourself
1. Sulfonamide drugs interfere with the manufacture of folic acid that is essential to the metabolism of some bacteria.
2. Some bacteria produce penicillinase, an enzyme that inactivates the penicillin
Molecule by breaking its chemical structure at the site of the beta-lactam ring.
3. [Only need to name four.]
Categories of antibiotic drugs include sulfonamide antiinfective drugs, penicillin antibiotic drugs, cephalosporin antibiotic drugs, aminoglycoside antibiotic drugs, tetracycline antibiotic drugs, carbapenem antibiotic drugs, monobactam antibiotic drugs, quinolone antibiotic drugs, fluoroquinolone antibiotic drugs, and macrolide antibiotic drugs.
4. In 1928, the Scottish bacteriologist, Alexander Fleming, was looking for drugs that would inhibit the growth of the bacterium staphylococcus. He concluded his experiments and went on vacation, after instructing an assistant to wash the culture plates that were soaking in the sink. When Fleming returned from vacation, the plates had not been washed. One culture plate had remained above the water and on it had grown a blue-green mold with a ring around it where the staphylococcus bacteria had been killed. Fleming identified this mold as Penicillium notatum; however, he was unable to extract a drug from this. Later, during World War II, work on penicillin resumed. Two researchers in
England were afraid all of the drug would be destroyed in the bombing of London.
Therefore, they smeared some of the mold inside their coat jackets and brought it to the United States, where penicillin could be produced. A 43-year-old policeman was the first person to be injected with penicillin. He was dying of septicemia. He was given the world’s entire supply of penicillin. He responded well to the treatment, but on the fifth day the supply of penicillin ran out, and he relapsed and died.
Researchers found the strain Penicillium chrysogenum on a moldy cantaloupe in
Peoria, Illinois. It was approximately 20 times more potent than the original mold and could be grown in larger quantities. When the United States entered World War II in
December 1941, the government took immediate control of the supplies and production of penicillin. The first small amounts of commercially produced penicillin became available in 1942.
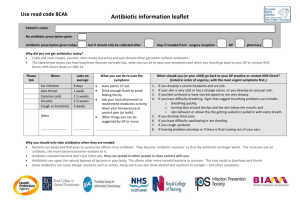
5. Tetracyclines can cause permanent discoloration in the developing teeth if given to a child under eight years of age or to a pregnant woman (it affects the fetus).
6. Ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity are two potentially toxic effects of aminoglycosides.
7. Broad-spectrum antibiotic drugs are those that are effective against both
Grampositive and gram-negative bacteria. The word retrovirus was coined in 1977 and is a shortened form of the phrase reverse transcriptase plus the word virus.
Opportunistic infections are uncommon diseases that have an opportunity to attack the compromised immune systems of patients with HIV. Opportunistic infections include candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, CMV retinitis, histoplasmosis, toxoplasmosis, Salmonella, Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare infection, and
Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia.
8. Cephalosporin antibiotic drugs.
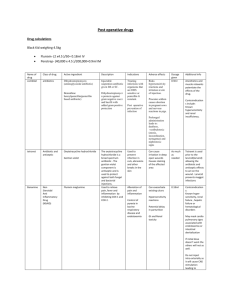
9. Cephalosporin antibiotic drugs are divided into first generation, second generation, and third generation. This designation divides them according to their therapeutic antibiotic properties. First-generation cephalosporin drugs have a fairly broad spectrum of effectiveness against bacteria, but are not very effective against bacteria that produce penicillinase. Second-generation cephalosporin drugs are more effective than first-generation cephalosporin drugs against bacteria that produce penicillinase. They are also effective against more gram-positive bacteria.
Third-generation cephalosporin drugs are the most effective of all the cephalosporin drugs against bacteria that produce penicillinase. Third-generation cephalosporin drugs also show the greatest effectiveness against gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria.
10. Zithromax has a half life of 68 hours. This extended therapeutic effect is good because it makes it possible to take Zithromax just once a day for 5 days to complete treatment, while most other antibiotic drugs have a shorter half life and have to be take two or three times a day for seven days or more.
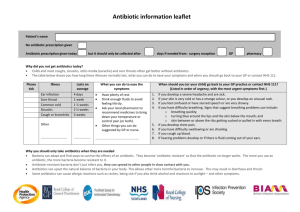
11. Most bacteria have developed resistant strains that are immune to certain antibiotic drugs. This has happened because antibiotic drugs have been so widely prescribed and are often prescribed for conditions that do not warrant antibiotic drug use. Also, antibiotic drugs are given to animals so that they can be housed in crowded conditions that would normally cause disease. The meat from these animals contains traces of antibiotic drugs.
12. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, human immunodeficiency virus, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, methicillin- resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
13. The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) attaches to CD4 receptors on helper T lymphocytes (a specific type of white blood cell in the immune system) and directs the lymphocyte to produce more HIV using the lymphocyte’s own DNA. As the newly produced viruses are released, the lymphocyte is destroyed.
14. Azidothymidine (AZT, zidovudine, Retrovir) was originally synthesized in 1974. It was tested as a treatment for cancer but was not effective. Other uses for it were not investigated. In 1984, although there were only 3,000 reported cases of AIDS in the United States, researchers at the National Cancer Institute, including the co-discoverer of the AIDS virus, Dr. Robert Gallo, approached Burroughs Wellcome drug company to develop a drug to treat AIDS. Burroughs Wellcome tested many different drugs, one of which was AZT. In 1986, clinical testing of AZT was begun using a double-blind study in which severely ill AIDS patients were divided into two groups: One group received AZT while the control group received a placebo. Shortly after the study was begun, it was stopped when it was found that those in the control group had a 40 percent mortality rate while those receiving AZT had only a 6 percent mortality rate. In March 1988, just four months after a new drug application was filed, the FDA approved AZT.
15. A patient’s diagnosis changes from HIV to AIDS when these two indicators are present: CD4 lymphocyte count below 200 cells/mm
3
and the presence of opportunistic infections/diseases.
16. Protease inhibitor drugs inhibit the viral enzyme protease that breaks down certain proteins in the virus so that the virus can reproduce. Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor drugs inhibit reverse transcriptase, an enzyme that the virus needs to reproduce itself. Nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor drugs bind directly to reverse transcriptase and disrupt its activity. Nucleotide analog reverse transcriptase inhibitor drugs inhibit reverse transcriptase; these drugs also become part of the viral DNA chain, which causes it to break. Fusion inhibitor drugs block
HIV when it tries to fuse its viral membrane with the cell membrane of the CD4 lymphocyte.
17. Because HIV continues to mutate, no vaccine has yet been approved by the FDA, although many are in the clinical trials phase.
18. [Only need to name three.]
Opportunistic infections that affect patients with AIDS include candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, CMV retinitis, histoplasmosis, toxoplasmosis, Salmonella,
Mycobacterium aviumintracellulare infection, and Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia.
19. Mycobacterium avium and Mycobacterium intracellulare belong to the same
Category of bacteria as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacterium that causes tuberculosis. The drug rifabutin, used to treat MAC infection, is structurally related to the drugs used to treat tuberculosis. Many antituberculosis drugs are used simultaneously as one of the two drugs needed to treat a MAC infection.
20. Lithium (Lithobid) is used to treat HIV and AIDS, but it is also used to treat manicdepressive disorder, a psychiatric illness.
21. The drug thalidomide was used to treat morning sickness in pregnant women in
Europe and caused the severe birth defect of phocomelia (“seal limbs”) in their babies. It was withdrawn from the market. It would have become an obscure footnote in medical history but, in 1997, it was discovered to be useful in treating cancer, AIDS, and leprosy. Thalidomide is now an official prescription drug used to treat multiple myeloma, leprosy, graft-versus-host disease, and several types of cancers. It is also officially recognized as an orphan drug to treat Crohn’s disease and AIDS wasting syndrome.
22. Each February, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDCP) selects those strains of influenza that are most prevalent in Asia and other parts of the world to include in the flu vaccine that will be offered in the United States the following fall before the start of flu season. Flu viruses mutate constantly and create many new subtypes, and so the influenza vaccine must be reformulated every year.
23. Fungi are related to yeasts, and both of these organisms are treated with many of the same antifungal (or antiyeast) drugs.
24. a. penicillin antibiotic drug b. macrolide antibiotic drug c. cephalosporin antibiotic drug d. cephalosporin antibiotic drug e. fluoroquinolone antibiotic drug f. tetracycline antibiotic drug g. nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor drug h. macrolide antibiotic drug i. antifungal drug
j. quinolone antibiotic drug k. protease inhibitor drug l. antiviral drug for influenza m. drug to treat Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia n. nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor drug o. aminoglycoside antibiotic drug p. nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor drug
Clinical Applications Questions
1. a. amoxicillin and clavulanic acid b. Augmentin
2. a. macrolide antibiotic drug b. The trade names (one is for Ery-Tab and the other is for EryPed). The drug form
(one is delayed-release tablets and the other is an oral suspension). The dose
(one is for 333 mg and the other is for 200 mg/5 mL).
3. a. Zithromax 250 mg b. Cipro 500 mg
4. a. fluconazole b. Diflucan c. antifungal drug d. oral suspension, 10 mg/mL
5. a. ampicillin b. generic name c. penicillin antibiotic drug d. 250 mg, capsules e. Dispense 30. Write on the label: 1 capsule four times a day for urinary infection.
1 refill.
6. a. ritonavir b. Norvir c. protease inhibitor drug d. HIV and AIDS e. oral solution, 80 mg/mL