File
advertisement

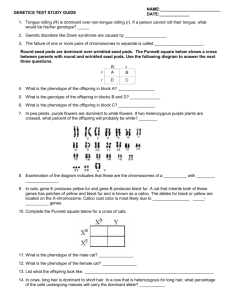
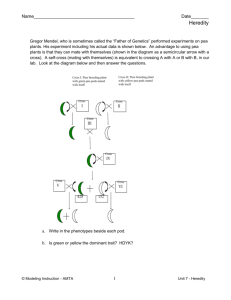
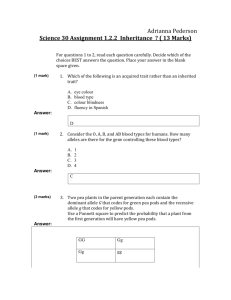
Name__________________________________ Date_____________ Period_____ Using Punnett Squares to Predict the Outcomes of Crosses A completed punnett square gives the probable outcome of a genetic cross. However, actual results may vary from the probable results, especially if only a few offspring are considered. Monohybrid Crosses: Crosses that involve one trait, such as seed color, are called monohybrid crosses. In this activity we will use some of the traits Mendel observed in pea plants. The traits and alleles are shown in the chart below: Trait Pod shape Pod color Flower position Plant height Dominant Allele Inflated (I) Green (G) Axial (A) Tall (T) Recessive Allele Constricted (i) Yellow (g) Terminal (a) Short (t) Example Problem: A plant that is heterozygous for green pods is crossed with a plant that has yellow pods. What are the possible genotypic and phenotypic ratios of the offspring resulting from this cross? Step 1: Determine the correct letter to represent the alleles in the cross. In this case, the letters are G (green pods), and g (yellow pods). This can be found in the table above. Step 2: Write the genotypes of the parents. Since the plant with green pods is heterozygous, its genotype must be Gg. We know that yellow pods is the recessive trait, therefore the genotype must be gg. This must be true because the recessive trait is only expressed if both alleles are recessive. The cross is therefore Gg x gg Step 3: Determine the possible gametes that the parents can produce from their genotypes. The two alleles of a trait are segregated during meiosis to form gametes. Thus the green pod parent (Gg) will produce gametes with G and g. The yellow pod parent (gg) will produce gametes with only g. G g Step 4: Enter the possible gametes at the top and side of the punnett square. Step 5: Complete the punnett square by writing the alleles from the parents in the appropriate boxes to represent possible offspring. Step 6: Determine the genotypes and phenotype of the possible offspring. g g g g G g Gg gg Gg gg Since green pods (G) is dominant over yellow pods (g), offspring that have G in their genotypes will have green pods. Only plants with gg will have yellow pods. In this example, 2 out of 4 will have green pods (Gg) and 2 out of 4 will have yellow pods (gg). 0 out of 4 will have green pods and be homozygous (GG). Name__________________________________ Date_____________ Period_____ Using Punnett Squares to Predict the Outcomes of Crosses Step 7: Using the results from step 6, determine the genotypic and phenotypic ratios. We have 0 (GG), 2 (Gg), and 2 (gg); therefore the genotypic ratio is 0:2:2 or 1:1. We have 2 green pod offspring possible, and 2 yellow pod offspring possible; therefore the phenotypic ratio is 2:2 or 1:1 Practice Problems: For each of the following problems, draw a punnett square in the space provided and indicate the phenotypic and genotypic ratios. 1. Ii x II Genotypic Ratio: Phenotypic Ratio: 2. Aa x aa Genotypic Ratio: Phenotypic Ratio: 3. Tt x Tt Genotypic Ratio: Phenotypic Ratio: 4. Cross two pea plants that are heterozygous for green pod color. Genotypic Ratio: Phenotypic Ratio: Name__________________________________ Date_____________ Period_____ Using Punnett Squares to Predict the Outcomes of Crosses 5. Cross a plant that is heterozygous for axial flowers with a plant that has terminal flowers. Genotypic Ratio: Phenotypic Ratio: 6. Cross a homozygous tall pea plant with a short pea plant. Genotypic Ratio: Phenotypic Ratio: 7. Cross a plant that is heterozygous for inflated pods with a plat that has constricted pods. Genotypic Ratio: Phenotypic Ratio: 8. When a tall pea plant is crossed with a short plant, some of the offspring are short. What are the genotypes of the parents, and the possible offspring? What would be the possible phenotypic ratio of the offspring? What are the genotypes of the parent plants? ______x______ Genotypic Ratio: Phenotypic Ratio: 9. Three fourths of the plants produced by a cross between two unknown pea plants have axial flowers and one fourth have terminal flowers. What are the genotypes of the parent plants? What are the genotypes of the parent plants? ______x______ 10. What cross would result in ½ of the offspring having green pods and ½ of the offspring having yellow pods? What are the genotypes of the parent plants? ______x______