6.EE.1 Lesson Expressions with Exponents
advertisement

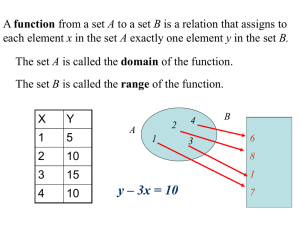
Lesson Title: _6.EE.1 Expressions with Exponents________ Date: _____________ Teacher(s): ____________________ Course: __Common Core 6_________ Start/end times: ________________ Lesson Objective(s): What mathematical skill(s) and understanding(s) will be developed? Apply and extend previous understandings of arithmetic to algebraic expressions. 6.EE.1 Write and evaluate numerical expressions involving whole-number exponents. Which Mathematical Practices do you expect students to engage in during the lesson? MP4: Model with mathematics. MP8: Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. Lesson Launch Notes: Exactly how will you use the first five minutes of the lesson? Have student desks set up in groups of 3 or 4 for today’s lesson. 1. Pose this problem to the class and have them use the prior knowledge of order of operations and integers to find the solution individually. 3 2 2 2 2 2 4 2 2. Have students share solutions with the other members of their group. Groups should compare and contrast answers and approaches for solving. Students should be able to defend the method they used to solve the expression and groups should be able to agree upon a final solution. 3. Have a student from each group put the answer on the board. 4. Discuss student answers and address any misconceptions that came up in the solving process (have members of groups share these with the class). Lesson Closure Notes: Exactly what summary activity, questions, and discussion will close the lesson and provide a foreshadowing of tomorrow? List the questions. Come back to new vocabulary at the end of the class period and have students review it and then add these words to a word wall for the unit. Why do people use exponents? What do they mean? When evaluating expressions, why do we evaluate exponents before we add and subtract? What exponent is described by each of the following words? Square? Cube? Why is something raised to the second power referred to as being “squared”? What about “cubed”? Lesson Tasks, Problems, and Activities (attach resource sheets): What specific activities, investigations, problems, questions, or tasks will students be working on during the lesson? Be sure to indicate strategic connections to appropriate mathematical practices. 1. Discuss Exponential Notation: Highlight the part of the numeric expression in the warm-up problem that has the same number being multiplied by itself five times: 2 2 2 2 2 . Say, “Writing repeated multiplication like this uses a lot of paper. Because of this, people decided to come up with a shorthand way of writing repeated 5 multiplication, which was to write an expression with an exponent. So, 2 2 2 2 2 is written as 2 and can be read as ‘two raised to the fifth power.’ The parts of this power are as follows: 2 is the base, 5 is the 5 exponent, and 2 is called a power. The base is the number that is being multiplied by itself repeatedly. The exponent is the number of times that the base is being multiplied by itself. The power is the exponential notation 5 5 of 2 2 2 2 2 which is 2 .” Emphasize that 2 2 2 2 2 2 . 2. Have the groups write some examples of repeated multiplication in exponential notation (1 per group) and record examples on the board. Discuss each example and have students determine whether or not each is written correctly in exponential notation. (Include examples of cubes and squares and introduce this vocabulary as well as examples with exponents higher than 3.) Lesson Title: _6.EE.1 Expressions with Exponents________ Date: _____________ Teacher(s): ____________________ Course: __Common Core 6_________ Start/end times: ________________ 3. Mini Task: Exploring Squares: Present the following problem to the class: Minia knows that square animal pens are the most economical for the amount of space they provide. Can you provide a table for Minia that shows the areas of square pens that have between 4 meters and 10 meters of fence on each side? (Elementary and Middle School Mathematics: Teaching Developmentally Seventh Edition (p. 474), Van de Walle). (Examples of Student Work are available. You may wish to provide students with the table as a potential resource. You may also provide cm graph paper for students to draw the animal pens, using the scale 1 cm = 1 m.) (Students should engage in MP4: Modeling with mathematics.) 2 4. When students finish, ask what they notice about the equations and areas of each pen. Reinforce that 4 means 2 you have a 4 by 4 square with an area of 4 16 . 5. During this discussion be sure students are conferring with their classmates about the connection between the square shape, the area of that square, and the exponent known as ‘squared’. Ask students how other areas can be reasoning) represented. (Check for evidence of MP8: Look for and express regularity and repeated such as 4 3 . Ask students how this expression is similar and different from 6. Present students with other powers, the area expressions. What could this expression mean? How would a solution be determined? (Check for evidence of MP8: Look for and express regularity and repeated reasoning) 7. Activity: Evaluate Numeric Expressions with Exponents. Create a bingo game where students write a multiplication problem in exponential form or take a problem in exponential form and write it as a multiplication problem. This will emphasize the idea that the two different forms represent the same number. (i.e., 2 2 2 2 2 2 5 ). Distribute supplies for bingo and explain the rules to the students. 8. Display the lesson launch problem again, and ask them to rewrite the problem using what they just learned about 5 5 exponents. Students should replace 2 2 2 2 2 with 2 . Say, “If we want to solve 3 2 4 2 using 5 the order of operations, when do you think we need to evaluate the 2 ?” Students should make the connection that exponents must be evaluated before adding and subtracting because they are multiplication. An exponent applies to its immediate base. Say, “How are the problems below different?” Display: 3 Example 1: 2 5 Example 2: 2 5 Do a few examples with the students to solidify understanding. Use whiteboards so you can readily see student work/answers and address any misconceptions. 9. Activity: Order of Operations with Exponents. Create an Around the World Game in which students evaluate expressions that involve addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, parentheses, and exponents. a. Using the city signs attached here, design a problem to post at each city’s location. b. Have students solve the problem and write the answer on their passports (also attached here) in the appropriate place. Students can start anywhere. c. Students must solve the problem, have you check the work, and have you stamp their passport before they are allowed to move on to a new problem. d. Have students turn in the passports at the end of class. Students should be able to complete and have stamped at least 6 of the 12 problems by the end of the activity. 10. Extension Task: The Painted Cube Problem (see Elementary and Middle School Mathematics: Teaching Developmentally Seventh Edition (p. 475), Van de Walle) 3 Evidence of Success: What exactly do I expect students to be able to do by the end of the lesson, and how will I measure student mastery? That is, deliberate consideration of what performances will convince you (and any outside observer) that your students have developed a deepened (and conceptual) understanding. Students will express repeated multiplication using exponents and vice versa, evaluate expressions in exponential form, and evaluate numeric expressions involving exponents using the order of operations. Student mastery will be measured by class discussion, teacher monitoring student work, and through the Around the World game. Lesson Title: _6.EE.1 Expressions with Exponents________ Date: _____________ Teacher(s): ____________________ Course: __Common Core 6_________ Start/end times: ________________ Notes and Nuances: Vocabulary, connections, anticipated misconceptions (and how they will be addressed), etc. Vocabulary: Numeric expression, Repeated multiplication, Power, Exponent, Base, Squared, Cubed Connections: Students will continue to use skills for evaluating numeric expressions using the order of operations. Students will continue to apply knowledge of operations with whole numbers. 3 Common Mistakes: Students often will evaluate 2 as 2 3 instead of 2 2 2 . Typical Misconceptions: Students often get confused by the vocabulary, specifically mixing up when to use “power” versus “exponent.” Students may have trouble understanding which base the exponent applies to. Resources: What materials or resources are essential for students to successfully complete the lesson tasks or activities? Homework: Exactly what follow-up homework tasks, problems, and/or exercises will be assigned upon the completion of the lesson? Options include: Glencoe Mathematics Applications and Connections Course 1 (p. 30) Birthday Problem (attached below) Glencoe Mathematics Applications and Connections Course 2 (p. 19) Copy of table for Exploring Squares (optional; Elementary and Middle School Mathematics: Teaching Developmentally Seventh Edition on page 474.) Cm graph paper Bingo game boards (blank)-1per student Bingo problems Bingo answers (to display for students to fill in boards) Whiteboards-1 per student Dry erase markers-1per student Around the World problems (display around the room) Around the World passport-1 per student Stamp and stamp pad (for Around the World game) Lesson Reflections: How do you know that you were effective? What questions, connected to the lesson objectives and evidence of success, will you use to reflect on the effectiveness of this lesson? Were students able to evaluate expressions with whole number powers? Were students able to understand why powers should be evaluated before adding and subtracting in expressions? If students are struggling with order of operations, what will I do tomorrow to address these needs? Are students understanding and using the vocabulary associated with this lesson? How can I reinforce vocabulary usage throughout teaching? Lesson Title: _6.EE.1 Expressions with Exponents________ Date: _____________ Teacher(s): ____________________ Course: __Common Core 6_________ Start/end times: ________________ Exploring Squares: Example of Student Work Side Length Pen Picture Equation 444 4 meters Area 2 16m 2 4m 4m 5 meters 5 5 52 25m 2 5m 5m 6 meters 6 6 62 36m 2 6m 6m 7 meters 7 7 72 49m 2 7m 7m 8 meters 8 8 82 64m 2 8m 8m 9 meters 9 9 92 81m 2 9m 9m 10 meters 10 m 10 10 10 2 10 m 100m 2 Lesson Title: _6.EE.1 Expressions with Exponents________ Date: _____________ Teacher(s): ____________________ Course: __Common Core 6_________ Start/end times: ________________ Your Birthday is a Math Problem! Investigating Order of Operations Project You will be creating a math problem where the solution is your birthday (month and day only). For instance, Luigi was born on January 28th (1/28). He could create the following math problem: 10 2 7(2 2) 10 2 7(4) 100 7(4) 100 28 128 The problem must be turned in on HALF a sheet of paper. It must have each of the following: Parentheses Exponents Three other operations The answer MUST be your birthday. It must be neat! You must show your work. It must have your name. TOTAL: points points points points points points points points You are welcome to decorate them however you like, but I must be able to read the problem, the work, and the answer. NOTE: If your birthday is also on January 28th, you must come up with a different problem than Luigi’s above! Rough draft: Lesson Title: _6.EE.1 Expressions with Exponents________ Date: _____________ Teacher(s): ____________________ Course: __Common Core 6_________ Start/end times: ________________ Passport for Around the World 1. Paris Name: Date: Block: 2. London 3. Dublin 4. Grand Canyon 5. New York 6. Niagara Falls 7. Costa Rica Lesson Title: _6.EE.1 Expressions with Exponents________ Date: _____________ Teacher(s): ____________________ Course: __Common Core 6_________ Start/end times: ________________ 8. Egypt 9. Beijing 10. Puerto Rico 11. Chicago 12. San Francisco Lesson Title: _6.EE.1 Expressions with Exponents________ Date: _____________ Teacher(s): ____________________ Course: __Common Core 6_________ Start/end times: ________________ You did it!!! Lesson Title: _6.EE.1 Expressions with Exponents________ Date: _____________ Teacher(s): ____________________ Course: __Common Core 6_________ Start/end times: ________________ Order of Operations with Exponents Around the World Lesson Title: _6.EE.1 Expressions with Exponents________ Date: _____________ Teacher(s): ____________________ Course: __Common Core 6_________ Start/end times: ________________ Paris Lesson Title: _6.EE.1 Expressions with Exponents________ Date: _____________ Teacher(s): ____________________ Course: __Common Core 6_________ Start/end times: ________________ London Lesson Title: _6.EE.1 Expressions with Exponents________ Date: _____________ Teacher(s): ____________________ Course: __Common Core 6_________ Start/end times: ________________ Dublin Lesson Title: _6.EE.1 Expressions with Exponents________ Date: _____________ Teacher(s): ____________________ Course: __Common Core 6_________ Start/end times: ________________ Grand Canyon Lesson Title: _6.EE.1 Expressions with Exponents________ Date: _____________ Teacher(s): ____________________ Course: __Common Core 6_________ Start/end times: ________________ New York Lesson Title: _6.EE.1 Expressions with Exponents________ Date: _____________ Teacher(s): ____________________ Course: __Common Core 6_________ Start/end times: ________________ Niagara Falls Lesson Title: _6.EE.1 Expressions with Exponents________ Date: _____________ Teacher(s): ____________________ Course: __Common Core 6_________ Start/end times: ________________ Costa Rica Lesson Title: _6.EE.1 Expressions with Exponents________ Date: _____________ Teacher(s): ____________________ Course: __Common Core 6_________ Start/end times: ________________ Egypt Lesson Title: _6.EE.1 Expressions with Exponents________ Date: _____________ Teacher(s): ____________________ Course: __Common Core 6_________ Start/end times: ________________ Beijing Lesson Title: _6.EE.1 Expressions with Exponents________ Date: _____________ Teacher(s): ____________________ Course: __Common Core 6_________ Start/end times: ________________ Puerto Rico Lesson Title: _6.EE.1 Expressions with Exponents________ Date: _____________ Teacher(s): ____________________ Course: __Common Core 6_________ Start/end times: ________________ Chicago Lesson Title: _6.EE.1 Expressions with Exponents________ Date: _____________ Teacher(s): ____________________ Course: __Common Core 6_________ Start/end times: ________________ San Francisco