Honors Algebra 2 Glencoe McGraw
advertisement

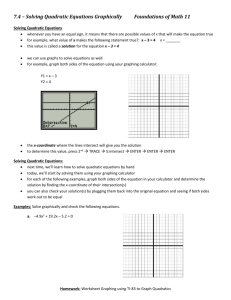
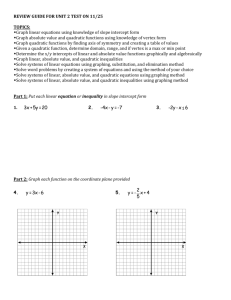
Honors Algebra 2 Glencoe McGraw-Hill 2010 OBJECTIVES CHAPTER 1 Equations and Inequalities 1.01(a) Use the order of operations to evaluate expressions. 1.01(b) Use formulas. 1.02(a) Classify real numbers as rational, irrational, whole, integer, natural. 1.02(b) Identify the properties of real numbers. 1.02(c) Use the properties of real numbers to evaluate expressions. 1.03(a) Translate verbal expressions into algebraic expression/equations & vice versa. 1.03(b) Solve equations using the Properties of Equality. 1.03(c) Solve literal equations for a specified variable. 1.04(a) Evaluate expressions involving absolute values. 1.04(b) Solve absolute value equations. 1.05(a) Solve one-step inequalities. 1.05(b) Solve multi-step inequalities. 1.06(a) Solve compound inequalities. 1.06(b) Solve absolute value inequalities. CHAPTER 2 Linear Relations and Functions 2.01(a) Distinguish between relations & functions. 2.01(b) Identify one-to-one and onto functions. 2.01(c) Distinguish between a discrete and a continuous relation. 2.01(d) Specify the domain and range of a relation or function including from a graph. 2.02(a) Identify a linear function. 2.02(b) Convert linear equations to standard form. 2.02(c) Use intercepts to graph a line. 2.03(a) Find the rate of change given a real-world situation. 2.03(b) Find the slope of a line given 2 points on the line. 2.03(c) Find the slope of a line using a graph. 2.04(a) Write the equation of a line given the slope and one point on the line. 2.04(b) Write the equation of a line parallel or perpendicular to a given line. 2.04(c) Write the equation of a line given two points on the line. 2.05(a) Use graphing calculator technology to create a scatterplot of given data points. 2.05(b) Use graphing calculator technology to determine the equation of the least squares line. 2.05(c) Use graphing calculator technology to determine the correlation coefficient and be able to explain the relevance of this number. 2.05(d) Use linear regression to predict unknown data. 2.08(a) Graph linear inequalities CHAPTER 3 Systems of Equations and Inequalities 3.01(a) Solve systems of linear equations by graphing (both manually & using graphing calculator). 3.01(b) Classify systems of linear equations as inconsistent, consistent dependent, or consistent independent. 3.02(a) Solve systems of linear equations by the substitution method. 3.02(b) Solve systems of linear equations by the addition/elimination method. 3.02(c) Solve real-world problems by setting up and solving a system of linear equations. 3.03(a) Solve systems of linear inequalities by graphing (both manually & using graphing calculator). 3.03(b) Determine the coordinates of the vertices of the region formed by the graph of a system of inequalities. 3.04(a) Find the maximum and minimum values of a function over a feasible region. 3.04(b) Solve real-world optimization problems using linear programming. 3.05(a) Solve systems of linear equations in three variables. 3.05(b) Solve real-world problems using systems of linear equations in three variables. CHAPTER 5 Quadratic Functions and Relations 5.01(a) Graph a quadratic function using a table of values. 5.01(b) Find the y-intercept, equation of the axis of symmetry & the x-coordinate of the vertex. Use this information to graph the parabola. 5.01(c) Identify if a quadratic function has a maximum or minimum and be able to state that value. 5.01(d) State the domain and range of a given quadratic function. 5.01(e) Solve real-world problems by writing and solving a quadratic equation. 5.02(a) Solve quadratic equations by graphing (both manually and using a graphing calculator). 5.02(b) State the number of solutions for a quadratic given its graph. 5.02(c) State the solution or estimate of non-integer solutions of a quadratic function. 5.03(a) Factor various types of polynomials: GCF, difference of two squares, perfect square trinomials, ordinary trinomials, sums & differences of two cubes. 5.03(b) Factor completely including factoring by grouping. 5.03(c) Write a quadratic equation in standard form given its roots. 5.03(d) Solve real-world problems by writing the appropriate quadratic equation and solving by factoring. 5.04(a) Perform operations with pure imaginary numbers. 5.04(b) Perform operations with complex numbers. 5.05(a) Solve quadratic equations by using the Square Root Property. 5.05(b) Solve quadratic equations by completing the square (CTS). 5.06(a) Solve quadratic equations by using the Quadratic Formula (QF). 5.06(b) Use the discriminant to determine the number and type of roots of a quadratic equation. 5.06(c) Set up and solve a quadratic equation for a real-world situation. 5.07(a) Write the Vertex form of a quadratic equation given the standard form equation. 5.07(b) Write the Vertex form of a quadratic equation given the vertex & 1 point on the parabola. 5.07(c) Graph a parabola based on the vertex form, the axis of symmetry, and reflection points. 5.07(d) Understand from the vertex form of a quadratic equation the impact of a, h, & k on the appearance of the graph.