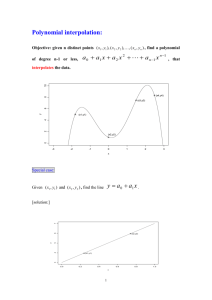
Math Special Topics A Mapping
advertisement

RCSHS Math Special Topics A Unit One Length of Unit Four Weeks Core Content/POS Linear Relations and Functions Key Concepts/Skills/Guiding Questions Terms: A-CED 1 A-CED 2 A-REI 3 F-IF 1 F-IF 2 F-IF 3 F-IF 4 F-IF 5 F-IF 7 F-LE 1 F-EL 5 Rowan County Senior High School 2012-2013 2012-2013 Abscissa, absolute value function, boundary, coinciding lines, composite, composition of functions, constant function, domain, family of graphs, function, function notation, greatest integer function, half plane, iterate, iteration, linear equation, linear function, linear inequality, ordinate, parallel lines, perpendicular lines, piecewise function, pointslope form, range, relation, slope, slope-intercept form, standard form, step function, vertical line test, x-intercept, y-intercept, zero of a function, best-fit line, correlation coefficient, goodness of fit, model, pearson-product moment correlation, prediction equation, regression line, scatter plot Unit Learning Targets Students will be able to: I can determine whether a given relation is a function I can identify the domain and range of a relation or function I can evaluate functions I can perform operations with functions I can find composite functions I can iterate functions using real numbers I can graph linear equations I can find the x- and y-intercepts of a line I can find the slope of a line through two points I can find zeros of linear functions I can investigate the effect of changing the value of m or b in y = mx + b I can write linear equations I can write equations of parallel and perpendicular lines I can draw and analyze scatter plots I can write a prediction equation and draw best-fit lines I can use a graphing calculator to compute correlation coefficients to determine goodness of fit I can solve problems using prediction equation models I can graph linear inequalities Activities/Assessments/ Resources Pre-test Intentional Review with Bell Ringers Word Wall Think-Pair Share Anticipation Guides Admit/exit slips Jigsaw Double entry organizer Note-taking Guide Win-plot TI-84 graphing calculator Power point presentations Infinite Algebra1 & 2 Infinite Geometry Kahn Academy Edmodo Quality Core Discovery Education Brightstorm.com/math/algebra-2/ Inquiry-based activities Post-test Page 1 RCSHS Math Special Topics A Unit Two Length of Unit Four Weeks 2012-2013 Systems of Linear Equations, Inequalities, and Matrices Core Content/POS A.CED.1 A.CED.2 A.CED.3 VM.7 VM.9 VM.10 VM.11 VM.12 Key Concepts/Skills/Guiding Questions Terms: Additive identity matrix, column matrix, consistent, dependent, determinant, dilation, dimensions, element, elimination method, equal matrices, identity matrix for multiplication, image, inconsistent, independent, infeasible, inverse matrix, m x n matrix, matrix, minor, nth order, ordered triple, polygonal convex set, pre-image, reflection, reflection matrix, rotation, rotation matrix, row matrix, scalar, solution, square matrix, substitution method, system of equations, system of linear inequalities, transformation, translation, translation matrix, vertex matrix, vertex theorem, zero matrix, linear programming, constraints, unbounded. Unit Learning Targets Students will be able to: Rowan County Senior High School 2012-2013 I can solve systems of equations graphically. I can solve systems of equations algebraically. I can solve systems of equations involving three variables algebraically. I can model data using matrices. I can add, subtract, and multiply matrices. I can use matrices to determine the coordinates of polygons under a given transformation. I can evaluate determinants. I can find inverses of matrices. I can solve systems of equations by using inverses of matrices I can graph systems of inequalities. I can find the maximum or minimum value of a function defined for a polygonal convex set. I can use linear programming procedures to solve Activities/Assessments/ Resources Pre-test Intentional Review with Bell Ringers Word Wall Think-Pair Share Anticipation Guides Admit/exit slips Jigsaw Double entry organizer Note-taking Guide Win-plot TI-84 graphing calculator Power point presentations Infinite Algebra1 & 2 Infinite Geometry Kahn Academy Edmodo Quality Core Discovery Education Brightstorm.com/math/algebra-2/ Inquiry-based activities Post-test Page 2 RCSHS Math Special Topics A Unit Three Length of Unit Four Weeks Core Content/POS Functions 9-12.IF.7 F.IF.4 F.IF.5 applications. I can recognize situations where exactly one solution to a linear programming application may not exist. Functions and Their Graphs Key Concepts/Skills/Guiding Questions Terms: Evaluate, function, domain, input, equation, parent function, transformation, slope, x-intercept, y-intercept, linear function, coordinate plane, vertex, quadratic function, maximum, minimum, square root function, cube root function, piecewise function, step function, absolute value function, factor, polynomial, polynomial function, end behavior, turning point, zero, multiplicity, rational function, removable discontinuity, nonremovable discontinuity, vertical asymptote, horizontal asymptote, exponential function, logarithmic form, exponential form, logarithmic function, trigonometric function, period, midline, amplitude. Unit Learning Targets Students will be able to: I can explain that the parent function for quadratic functions is the parabola f(x) = x2. I can identify whether the vertex of a quadratic will be a minimum or maximum by looking at the equation. I can find the y-intercept of a quadratic by substituting 0 for x and evaluating. I can graph a quadratic using evaluated points. I can use technology to graph a quadratic and to find precise values for the x-intercept(s) and the maximum or minimum. Rowan County Senior High School 2012-2013 2012-2013 Activities/Assessments/ Resources Pre-test Intentional Review with Bell Ringers Word Wall Think-Pair Share Anticipation Guides Admit/exit slips Jigsaw Double entry organizer Note-taking Guide Win-plot TI-84 graphing calculator Power point presentations Infinite Algebra1 & 2 Infinite Geometry Kahn Academy Edmodo Quality Core Discovery Education Brightstorm.com/math/algebra-2/ Inquiry-based activities Post-test Page 3 RCSHS Math Special Topics A Rowan County Senior High School 2012-2013 2012-2013 I can explain that the parent function for the square root functions is the function f(x) = √x. I can sketch graph a square root function by hand using convenient values of x an inputs. I can use technology to graph square root functions and find the intercepts. I can explain that the parent function for cube root functions is the function f(x) = 3√x. I can sketch graph a cube root function by hand using convenient values of x as inputs. I can use technology to graph cube root functions and find the intercepts. I can define piecewise functions as functions that have different rules for evaluation depending on the value of the input. I can identify which evaluation rule to use for a specific value of x. I can represent a piecewise function with a table or graph by evaluating several values of x. I can explain that the parent function for absolute value functions is f(x) = |𝑥|. I can explain why absolute value is considered a composite function. I can identify whether the vertex of an absolute value will be a minimum or maximum by looking at the equation. I can find the y-intercept of an absolute value by substituting 0 for x and evaluating. I can use calculated values while looking for a minimum or maximum to decide if the quadratic has x-intercepts. I can graph an absolute value using evaluated points. I can use technology to graph an absolute value and to find precise values for the x-intercepts and the maximum or minimum. I can graph a step function by substituting values for x and plotting the points. I can define a polynomial. I can identify the degree of a polynomial. I can determine the x-intercepts of a polynomial when looking at a graph of the function. Page 4 RCSHS Math Special Topics A Rowan County Senior High School 2012-2013 2012-2013 I can determine the end behavior of a polynomial by looking at the degree and leading coefficient of the equation. I can use technology to graph a polynomial and to find precise values for the x-intercept(s) and the maximums and minimum (turning points). I can define rational functions as the ratio of two polynomials. I can state the end behavior of a rational function by interpreting the graph. I can determine if a rational function has a horizontal asymptote and find the asymptote. I can use technology to graph rational functions and to find precise values for the x-intercepts, and the maximums and minimum (turning points). I can explain that the parent function for exponentials is f(x) = bx. I can determine the domain, range, and end behavior (horizontal asymptote) of an exponential function when looking at its graph. I can classify exponential functions in function notation as growth or decay. I can graph exponential functions. Page 5