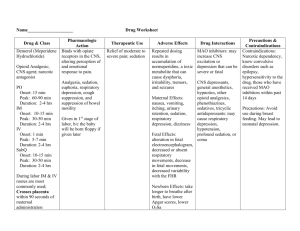
Patients medical history is reviewed prior to administering drugs and
advertisement

Patients medical history is reviewed prior to administering drugs and changes may be made on an individual basis, Sedation or “Premix” given prior to anesthetic helps relax the animal. Acepromazine is used to facilitate restraint of patients. It has anti emetic, anti spasmodic and hypothermic properties. Adverse and Common Side effects- Following side effects have been noted with use of acepromazine: constipation, paradoxical aggression, sinus bradycardia, depression of my contractility, hypotenison, collapse, and prolongation of pseudocyesis. Acepromazine lowers the seizure threshold and should not be used in animals with known seizure activity. It should not be given to animals with tetanus. Prolonged effects (even at low doses) may be seen in older animals. Giant breeds, including Greyhounds, appear quite sensitive to clinical effects of the drug, while terrier breeds seem more resistant. Boxers are predisposed to the hypotensive and bradycardic effects of the drug. Concurrent administration of atropine can counter the bradycardia. Drug Interactions- Acepromazine is contraindicated in animals with strychnine or organophosphate poisoning and should not be given to animals who have had succinylcholine or other cholinesterase inhibitors. Concurrent anestheic or narcotic preparations may exacerbate CNS depression. Kaolin pectate or bismuth subsalicilate and antacids decrease the oral absorption of acepromazine. Concurrent administration of acepromazine with propanolol may increase serum levels of both. Phenytoin activity may be decreased. If used with epinephrine, could cause profound vasodilation and tachycardia. Other CNS depressants may enhance hypotension and respiratory depression. Barbituate drugs increase the metabolism of phenothiazines and may reduce their effects. Barbituate anesthetics may increase excitation (tremor, involuntary muscle movements) and hypotension. In humans, there has been the unexplained possibility of sudden death when used concurrently with phenylpropanolamine. Hydromorphone- Special Risk Patients: In general, opioids should be given with caution, with a reduction in initial dose in the elderly or debilitated, those with severe impairment of hepatic, pulmonary or renal function, myxedema or hypothyroidism, Addison’s disease, CNS depression or coma, elevated intracranial pressure, prostatic hypertrophy or urethral stricture. Contraindications: Not for patients with known hypersensitivity to the drug, patients with respiratory depression in the absence of resuscitative equipment, patients with severe CNS depression and patients in status asthmaticus. Adverse Reactionssimilar to other opioid analgesics and include respiratory depression and apnea. To a lesser degree, circulatory depression, respiratory arrest, shock and cardiac arrest have been reported. The more frequently observed side effects of hydromorphone include constipation, dizziness, sedation, feeling faint, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite and weakness. Drug Interactions- Concurrent use of CNS depressants, including sedatives and hypnotics, general anesthetics, phenothiazines or tranquilizers may increase CNS depression, respiratory depression and hypnotic effects. Profound sedation or coma may occur. Anticholinergics and anti diarrheals could increase chance of constipation. Antihypertensive agents have their effects potentiated by opioids. Thiopental is an ultra short acting barbiturate anesthetic primarily used an an induction agent before additional anesthtetics or for very short procedures. Adverse and Common Side Effects- if given perivascularly, can cause irritation and sloughing of tissues. Respiratory depression is common after bolus administration. Other side effects may include myocardial depression, arrhythmia, hypotension, and hypothermia. At sedative doses, barbiturates have a wide margin of safety with few side effects. Use with caution in animals with pre-existing arrhythmias, renal or hepatic disease and hypoalbuminemia or acidosis. Lack of body fat can predispose to prolonged recovery. Greyhounds and other sight hounds metabolize thiobarbiturates very slowly. Obese animals are at risk of relative drug overdose. The very old and the very young at increased risk for barbiturate effects. Hypothyroidism may predispose to sensitivity. Thiobarbiturates may induce anaphylactic reactions and can occur without prior exposure to this drug. Drug Interactions- metabolic acidosis, hypoalbuminemia, renal or hepatic disease, administration of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory, certain sulphonamides, glucose, and atropine augment the anesthetic effect of barbiturates and can potentiate toxicity. Any CNS depressant enhances the response to barbiturates. Isoflurane- is an inhalant anesthetic. It is well tolerated in debilitated patients and those with hepatic or renal impairment. Adverse and Common Side Effects- dose-dependant cardiac and respiratory depression occurs. Hypotension, respiratory depression, arrhythmias, nausea, vomiting and post operative ileus have been reported. MetacamA non-steroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID) given post operatively for pain. Contraindications- Should not be administered if gastric or intestinal bleeding is suspected, if there is evidence of cardiac, hepatic or renal disease or evidence of hemorrhagic disorders or individual sensitivity to the product. Do not administer concurrently with other steroidal or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAIDS). Safety has not been established for breeding, lactating or pregnant animals. Particular care must be taken with regards to dosing in cats. Cats have been shown to be much more sensitive to NSAIDs than dogs. Repeat dosing of the inject able form in cats should NOT be undertaken and has been associated with acute renal failure and death. Repeat usage of the label dose of the oral form is appropriate, but also with caution and should be discontinued if any signs of decreased appetite or gastrointestinal upset are noted and your veterinarian should be contacted immediately. Adverse Effectsbased on case reports, the most important body systems affected, in order, are the GI tract (vomiting, diarrhea, ulceration, inappetance), central nervous system/behaviour (ataxia, seizures, blindness, depression, hyperactivity, trembling), renal (elevated creatinine and BUN, acute kidney failure) and dermatological system (itchiness, eczema, focal hairloss, hot spots). Acute allergic reactions/anaphylaxis have also been reported. In rare cases, side effects have been severe enough to cause death.