GCSE PHYSICS UNIT 1 Revision and Exam Practice
advertisement

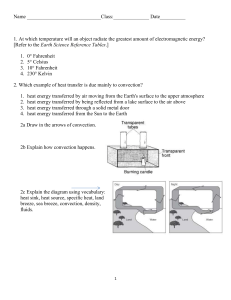
GCSE PHYSICS UNIT 1 Revision and Exam Practice EXAM: THURSDAY 12TH JUNE 2014 In this booklet you will find all the points and subject content needed to revise for Physics Unit 1. You will find multiple questions throughout the booklet to test your understanding of a certain topic. There are no answers. You should know if it is right or wrong! Name:………………………………………………… Set…………………………………………….. AQA GCSE PHYSICS REVISION NOTES/EXAM PRACTICE EXAM: THURSDAY 12TH JUNE 2014 P1.1.1 INFARED RADIATION All objects EMIT and ABSORB infrared radiation The hotter the obect, the more infrared radiation it emits (gives off) Dark/Matte surfaces are good absorbers of infrared radiation however they are bad REFLECTORS of radiation. Light and shiny surfaces are good reflectors of infrared radiation but BAD absorbers. GCSE Exam Question A man drinks tea on a daily basis, he drinks out of a white cup. Explain why having a black mug helps the tea stay warmer for longer (2 marks) ……………………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………………….. P1.1.2- Kinetic Theory Kinetic theory is used to explain the different states of matter The particles of solids, liquids and gases have different amounts of energy. We can make a substance change between each of these by heating or cooling them. In a SOLID, the particles vibrate around fixed positions so the solid has a FIXED shape. In a LIQUID, the particles are in contact with each other but can move about at random. They don’t have a fixed shape and can fit the shape of their container In a GAS,the particles are usually far apart and move at random much faster. NO FIXED SHAPE AND CAN FLOW. GCSE EXAM QUESTION (4 MARKS) Diagram 1 Diagram 1 shows the arrangement of particles of a solid 7a) One kilogram of gas has a much larger volume than 1 kilogram of a solid Use kinetic theory to explain why …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………........................................................................ P1.1.3 Energy Transfer by heating Conduction Conduction occurs mainly in solids. Most liquids and gases are poor conductors When 1 end of a solid is heated, the particles of the end gain KINETIC energy and vibrate more. The energy is then passed to the neighbouring particles and this way the enerfy is transferred by the solid. This process occurs in metals. Metals are EXCELLENT conductors. Metals have FREE ELECTRONS. When metals are heated their free electrons gain kinetic energy and move through the metal. They transfer their energy by colliding with other particles Poor conductors are called insulators. Materials like wool and fibre glass are good insualtors because they contain trapped air. GCSE QUESTION Explain why saucepans are much more common with plastic handles than metal handles. (3 marks) …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… P1.1.4- Convection Convection occurs in fluids (liquids and gases). When a fluid is heated, it expands. The fluid then becomes less dense and rises. The warm fluid is replaced by cooler/denser fluid. Rule for Convection Convection occurs when the more energetic particles move from the hotter region to the cooler region and take their heat energy with them The resulting CONVECTION CURRENTS transfer energy throughout the fluid. Basically, convection currents are currents that result from convection. The convection currents can be on a very small scale, such as heating water in a beaker, or on a very large scale such as heating the air above on land and sea. DON’T FORGET!! CONVECTION DOES NOT OCCUR IN SOLIDS!!! GCSE EXAM QUESTION In terms of the particle arrangements of solids and liquids explain why convection CANNOT occur in solids. (4marks) .................................................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................................................. .................................................................................................................................................................. P1.1.5- Evaporation and Condensation Evaporation is the change of a liquid into a gas Condensation is the change of a gas into a liquid Particles in a liquid have different levels of energy Evaporation occurs when the highest kinetic energy level particles escape from the surface of the liquid, allowing the liquid to turn into a gas Factors that affect the rate of evaporation Increasing the surface area of the liquid Increasing temperature of the liquid Creating a draught of air across the liquids surface Condensation is when a gas turns into a liquid. This may take place on cold surfaces such as windows and mirrors The rate of condensation is affected by: surface area and reducing the surface temperature Question What effect would decreasing the surface area of a liquid have on its rate of evaporation? …………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………… P1.7 Energy Transfer by Design The greater the temperature difference between an object and its surroundings, the greater the rate at which that energy is transferred. The rate at which energy is transferred also depends on: The materials that the object is in contact with The objects shape The objects surface area Sometimes we want to maximise the rate of energy transfer to keep things cool. To do this we may use things that: 1. Are good conductors 2. Are painted dull black 3. Have the air flow around them maximised Question Why does painting an object dull black maximise the rate of energy transfer? ………………………………………………………………………………........ .................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................... Sometimes we need to minimise the rate of energy transfer in order for us to keep things warm. In order to do this, we need to minimise the rate of energy transfer by conduction, convection and radiation We may use things that: are good insulators, are white and shiny, prevent convection currents by trapping air in small pockets GCSE Exam Question 6 Marks *In this question you will be assessed on using good english, organising information clearly and using specialist terms where appropriate. The Diagram shows the structure of a vacuum flask *Describe as fully as you can how the design of a vacuum flask keeps liquid inside hot …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………… 6 mark questions There will be at least 1 6 mark question in the Physics paper. You need to have a coherent understanding on how the examiners mark these six mark questions so you can confidently tackle them in the exam. The 6 mark question you encountered on the above page is from the June 2013 paper. Here is the mark scheme for it. Have a go at marking it yourself! 1) First of all, the examiners will place your mark into a band. Level 1 Level 2 or Level 3. They will look for spelling mistakes, punctuation and how well you convey your answer. 2) Then they will look for scientific points to back up your answer. Here are some scientific points you could of used in your reponse. Responses to 6 mark questions should be a mini essay type so you are able to convey all the necessary information and scientific points the question asks you. The Classic Artic Fox In your physics papers and many in the past, examiners have threw in question of the artic fox. Questions to do with the artic fox are normally ones like: “Describe adaptations of the artic fox which reduce heat loss” Adaptations of the Arctic Fox Past Exam Question –June 2013 P1.1.8 Specific Heat Capacity When we heat a substance, we transfer energy to it so the overall temperature is increased. The specific heat capacity is the amount of this energy required to raise the temperature of 1 kilogram of the substance by 1°C. Different substances have different specific heat capacities. The greater the SHC, the more energy required for each degree temperature change The greater the mass of a substance being heated the more enrgy required for each degree temperature change. If we had a 2kg piece of copper we would need to transfer twice the energy needed to raise the temperature of 1kg of copper bu the same amount. Practice Question 1) The Specific Heat Capacity of water is 4200J/kg°C . How much energy is needed to raise the temperature of 2kg of water by 1°C. ………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………. PAST EXAMINATION QUESTION Heating and Insulating buildings This topic is a ‘How Science Works’ topic therefore it has something to do with the Social/Economic/Environment. Most people would like to minimise the rate of energy transfer out of their homes to reduce fuel bills. (Economic/Environmental, less money spent, less CO₂ emissions.) Ways of insulating homes Fibre glass loft insulation to reduce enrgy loss via conduction Cavity wall insulation that traps air in small pockets to reduce energy transfer by convection. Double glazing windows to reduce energy transfer by conduction through windows Draught Proofing to reduce enrgy transfer by convection Aluminium Foil behind radiators to reflect escaping heat back into the room. U Values U Values measure how effective an insulator is. The lower the U Value, better the insulator. The U Value measures how much energy per second passes through it. Bump up your grade by being able to look at a table of U Values to see which is a better insulator. Using the table, which is the best insulator and why? ..................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................... Solar heating panels contain water that is heated by radiation from the sun. This water may then be used to heat buildings or provide domestic/home use hot water. Solar heating panels are cheap to run because they do not use fuel. This is environmetnally beneficial as it does not produce Carbon Dioxide emissions which is a common cause of global warming. However they are expensive to buy and install and the water is not heated at night. Opininated Questions Opinionated questions ask your opinion of something as long as you can justify them with valid scientific points. Exam Question Why do you think the copper pipes that contain the water in a solar heating panel are often painted black? ………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………… ……..………………………………………………………………… ……………..……………………………………………………….. P1.2-Energy and Efficiency Forms of Energy C-Chemical(Nuclear) H-Heat E-Elastic Potential Electrical Kinetic Y S-Sound Light A Gravitational Potential Energy can be transferred from one form to another by different processes. Any object above the ground has gravitational potential energy for example someone standing on a chair has gravitational potential energy. When energy is transferred from one form to another, there is only a percentage of useful energy, there is usually more wasted. For example, the whole purpose of a light bulb is to convert electrical energy into light energy however some light bulbs only produce 10% useful light energy and 90% wasted heat energy which disspiateds into the surroundings. List of Energy Transfers between Devices Electrical devices convert ELECTRICAL ENERGY into SOUND/LIGHT/HEAT, and there is obviously going to be wasted heat . Televisions convert electrical energy to LIGHT & SOUND Water can produce electricity. Water falls from the sky, converting potential energy to kinetic energy. This energy is then used to rotate the turbine of a generator to produce electricity. In this process, the potential energy of water in a dam can be turned into kinetic energy which can then become electric energy. When playing pool, the cue ball is shot at a stationary 8 ball. The cue ball has energy. When the cue ball hits the 8 ball, the energy transfers from the cue ball to the 8 ball, sending the 8 ball into motion. The cue ball loses energy because the energy it had has been transferred to the 8 ball, so the cue ball slows down. Kelly ran across the room and bumped into her brother, pushing him to the floor. The kinetic energy she possessed because of her movement was transferred to her brother, causing him to move. When a moving car hits a parked car and causes the parked car to move, energy is transferred from the moving car to the parked car. When playing the lawn game bocce ball, a small ball is thrown with the intention of hitting larger balls and causing them to move. When a larger ball moves because it was hit by the small ball, energy is transferred from the small ball to the larger one. When you push a book across the table, the energy from your moving arm is transferred from your body to the book, causing the book to move. A cat sitting on the highest branch of a tree has what is known as potential energy. If he falls off the branch and falls to the ground, his potential energy is now being converted into kinetic energy. When kicking a football that is sitting on the ground, energy is transferred from the kicker’s body to the ball, setting it in motion. Sam was rearranging furniture, and needed help to push the heavy sofa. His brother came over, and together they were able to lift the sofa onto sliders. This made it easy to push the sofa across the room. When Sam and his brother pushed the sofa and it slid across the wood floor, energy was transferred from the men to the piece of furniture. A fly ball hits a window in a house, shattering the glass. The energy from the ball was transferred to the glass, making it shatter into pieces and fly in various directions. Two football players collided on the field, and both went flying backwards. Energy was transferred from each player to the other, sending them in the opposite direction from which they had been running. Claire threw the ball and it hit her mother’s vase, knocking it over. Energy was transferred from the moving ball to the stationary vase, causing the vase to move. Fingers hitting piano keys transfer energy from the player’s hand to the keys. Billy hit the punching bag, transferring energy from his arm to the stationary bag. The dog ran in into the Christmas tree and knocked it over. Energy was transferred from the moving dog to the stationary tree, causing the tree to move. When the car hit the road sign, the sign fell over. Energy was transferred from the moving car to the stationary sign, causing the sign to move. No energy was lost in the transfer. Potential energy of oil or gas is changed into energy to heat a building. When a bowling ball knocks over pins that had been standing still, energy is transferred from the ball to the pins. No energy is lost. Beth hit the wall so hard that she put a hole in it. Energy was transferred from Beth’s body to the drywall, causing it to move. When the car hit the curb it broke apart. Energy from the moving car was transferred to the non-moving cement, causing it to move. P1.2.2- The Conservation of Energy As you should know energy CAN NOT BE CREATED OR DESTROYED only transferred. This means that the total amount of energy is always the same. This is called the ruel of the CONSERVATION OF ENERGY and it applies to ALL energy transferrs. P1.2.3- Useful Energy A machine is something that transfers energy from one place to another The energy we get out of a machine consists of : Useful energy which is transferred to the place we want and in the form we want it Wasted energy energy that is not usefully transferred or we do not need. Energy is often wasted in a machine because of friction of the moving parts of a machine. This friction/energy warms up the machine and the surroundings. Question Why should we talk about energy being wasted and not lost? …………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………… P1.2.4- Energy and Efficiency Energy is measured in J (JOULES) and this applied to all forms of energy The energy that is supplied to a machine is often called the input energy, from the conservation of energy we know that: Input energy=useful energy transferred+energy wasted The less energy wasted makes a device/machine more efficient We can calculate the efficiency of any appliance that supplies energy Formula for efficiency EFFICIENCY= USEFUL ENERGY TRANSFERRED TOTAL ENERGY SUPPLIED (X100%) Practice Question In a light bulb for every 25 joules of energy that are supplied to the bulb, 5 joules are usefully transferred into light energy. Calculate the efficiency of the bulb 5j useful 25j 20j useful ……………………………………… ……………………………………… ……………………………………… ……………………………………… ……………………………………… ……………………………………… …………………………………… The efficiency can either be left as a fraction or be turned into a percentage by multiplying it by 100. No appliance except an electric heater can be 100% efficient. This is because all the electric energy transferred into the device is transferred as heat to the surroundings. SANKEY DIAGRAMS Sankey diagrams illustrate how much input energy is transformed into different types of energy The wider the arrow the more energy it shows So the width of the arrow shows the amount of energy An exam question may ask you to calculate energies using the sankey diagram In order for us to work this out, each square in an arrow is worth 1 joule of energy. So if an arrow is 8 squares wide, it is worth 8 joules of energy. Electrical Appliances Electrical Appliances transfer electrical energy into whatever form of energy we want. Common electrical appliances include: Lamps- to produce light Speakers to produce sound Televisions to produce light and sound energy Kettles- to produce heat energy Many appliances transfer energy by heating such as a kettle which transfers electrical enrgy into sound and heat energy. Heat energy is the useful however the sound is the wasted. Appliances should be designed to waste as little energy as possible. P1.3.2- Electrical Power The rate at which energy is transferred is known as the POWER of the appliance The unit of power is WATTS (W). An appliance with a power of 1 watt transfers 1 joule of electrical enerrgy to other forms of energy every second A watt is too small of a unit to be useful so power may also be given in kilowatts (kW) 1 kW = 1000w Power is given by the equation p=E/T P=power in watts (w) E= energy in joules (j) T= Time taken (in seconds) for the energy to be transferred Power is the energy per second transferred or supplied. Equation EFFICIENCY=USEFUL POWER OUT TOTAL POWER IN (X100%) Practice Question An electric motor transfers 48 kJ of electrical energy into kinetic energy in 2 minutes. What is the useful power output of the motor? ………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………… P1.3.3- Using Electrical Energy Companies that supply mains electricity charge customers for the amount of electrical energy used. Because of the large numbers involved, the joule j. The amount of energy used is measured in killowat hours (kWh) A killowatt hour is the amount of energy that is transferred by a one-killowatt aappliance for an hour The amount of energy transferred to a mains appliance can be found using this equation: E=pxt E= is the energy transferred in killowatt hours, kWh P= Power of the appliance T= time taken (hours) for the energy to be transferred The electricity meter in a house records the number of kWh of energy used. If the previous meter reading is subtracted from the current reading, the electrical energy used between the readings can be calculated. The cost of electrical energy supplied is found using this equation Question P1.3.4- Cost Effectivness Matters! (HSW) In order to compare the cost effectivness of different appliances we must consider a number of different costs These include: The cost of buying the appliance. The cost of installing the appliance The running costs The maintenance costs Environmental costs The interest charged on a loan to buy the appliance Many households want to reduce their energy bills. In order for them to do this, they need to buy new more efficient appliances. They could also install materials designed to reduce energy wastage. PAYBACK time is the time it takes for an appliance or installation to pay for itself interms of energy savings. REDUCING HEAT LOSS FROM THE HOME HEAT EXCHANGER A heat exchanger costs £1000 to install The annual savings are £100 What is the payback time? Easy way to do this is to divide the cost of installation by the annual savings £1000 /£100= 10 P1.4- Fuel for electricity The most common way of generating electricity is by burning fossil fuels. Generation electricity by nuclear power for example produces a lot of energy however one day they will eventually run out and they also produce greenhouse gases which are harmful to the envrionment. Non renewable energy resources Coal Oil Natural gas Nuclear fuels All non renewable energy resources will eventually run out They all harm the environment However they give us the most out of our energy. Energy sources can be used to heat water in power stations (Most fossil fuels (coal,oil and gas) work in the same way. DISADVANTAGES OF FOSSIL FUELS (coal) 1) Fossil fuels are limited resources therefore they will eventually run out, forcing us to use renewable enrgy resources 2) When fossil fuels are burnt to produce energy, they release carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide and other green house gases which contribute to global warming 3) S0₂ causes acid rain, which could potentially ruin building structures 4) S0₂ poses a risk for breathing/living creatures NUCLEAR POWER The main nuclear powers that we use are uranium and plutonium. Unlike coal, they aren’t burnt to produce energy, they instead undergo nuclear fission reactions. This is where the nuclei atoms are split to produce their energy therefore they do not release greenhouse gases such as Carbon Dioxide The rest of the process of generating electricity is then identical to the process using fossil fuels. The heat energy is used to boil water. The kinetic energy in the expanding steam spins turbines, which then drive generators to produce electricity Advantages Unlike fossil fuels, they do not release the harmful greenhosue gases such as carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide They produce A LOT of energy Disadvantages They are non renewable therfore they will eventually run out If there is an accident, lots of radioactive material could be released into the environment, posing a serious cancerous risk from all of the radiation. This will cause massive disruption as the radioactive material would have to be kept underground a stored for 1000’s of years for it to become unreactive *As fossil fuels are running out at a rapid pace, we need to start using a range of renewable ways to produce our energy which will aslo help to conserve the environment Wind Power Wind is produced due to GIANT convection currents in the atmosphere of the Earth, which are driven by heat energy from the Sun. The KINETIC ENERGY in the wind is a renewable energy resource Have a go at describing the ADVANTAGES and DISADVANTAGES yourself! Advantages Disadvantages Biofuels Biofuels such as ethanol and biodiesel are used mainly for transport needs. Ethanol is produced by the sugar cane when being used as a bio fuel. Advantages They are renewable which means they will never run out They are carbon neutral Tidal Waves Disadvantages They produce CO₂ when burnt There is a chance of crop failure therefore it is an unreliable way of renewable energy