Psychopharmacology * Nuts and Bolts
advertisement

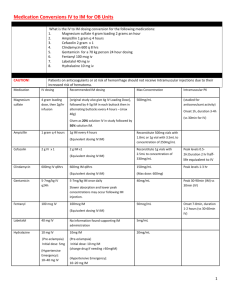
Psychopharmacology – Nuts and Bolts Medications and Things to Know: - Always think DRUGS – in ANY DDx, could it be an adverse effect, side effect, drug-drug interaction, overdose or noncompliance - Pregnancy - there are basically no psychotropic drugs that are rated better than Class C - Off label use of medications is very common in psychiatry ANTIDEPRESSANTS - Overall, most of these medications have the same efficacy for treating depression, the main difference is side effects - Most antidepressants take a minimum of 2-4 wks to have initial efficacy; a trial of 6-8 wks at a therapeutic dose would be considered an adequate trial for most - Any Antidepressant may induce a manic state in pts with a predisposition (they would not require a prior diagnosis of Bipolar disorder as this may be the sentinel event) - There may be an inc risk for suicidal ideation in any pts taking an antidepressant Tricyclics Imipramine (used to treat enuresis) Amitriptyline Doxepin Nortriptyline Clomipramine Desipramine MoA - inhibition of serotonin and NE uptake Indications – Depression, dysthymia, OCD, panic d/o, PTSD, chronic pain (TCA>> SSRI) Side Effects - Anticholinergic (dry eye, mouth, constip, urinary retention, blurred vision, AMS (inc risk in elderly 2/2 muscarinic blockade) - Histaminic – sedation, wt gain - Alpha -1 adernergic blockade - orthostatic hypotension, falls - Possilbe EKG changes, arrhythmias (prolonged QY and PR, AV block) * In OVERDOSE=widened QRS Pearls - Cheap but dirty - Require diet modification to avoid HTN crisis (avoid tyramine containing foods) - Cannot be combined with other antidepressants (risk of serotonin syndrome) or sympathomimetic drugs; avoid with cough syrup or Demerol - SERIOUS RISK IN OD SSRIs Flouxetine (Prozac) 20-80mg daily dosing range Sertraline (Zoloft) 50-200mg/day Paroxetine (Paxil) 20-80mg/day Citalopram (Celexa) 20-60mg/day Fluvoxamine (Luvox) 50-300mg/day Escitalopram (Lexapro) 10-30mg/day MoA – blocks reuptake of serotonin at the presynaptic nerve terminals Indications – depression, panic d/o, OCD (typically dose upper limits), bulimia, pain d/o, GAD, social phobia, PTSD, PMDD ; in elderely, pts with panic d/o and in children start at doses ½ the nl starting dose or less Side Effects (SSRIs) - GI upset, HA, insomnia, sexual dysfcn - Hypernatremia in the elderly - Prozac/Zoloft tend to be more activating - Paxil tends to be more sedating - Lovox tends to have more drug-drug interactions Pearls - Typically fewer side effects and very safe - Risk of serotonin syndrome when used with other serotonin meds (SSRIS, TCAs, MAOS, demerol, St. John’s Wart) - Serotonin Syndrome – may present as a delirium (AMS, restless, shivering, VS abnl 2/2 autonomic instability (inc HR,BP,temp), hyperreflexia – may lead to shock, coma, death – A MEDICAL EMERGENCY - Discontinuation syndrome – common, particularly if taper too quickly, esp with shorter acting agents (does not happen with Prozac 2/2 long ½ life) – presents as flu-like symptoms (GI upset, sleep disturbance, mood chngs, dizziness, lethargy – resolve when restart med Other Antidepressants Venlafaxine (Effexor) dosing range 75-375mg/day - Blocks reuptake of Serotonin and Norepinephrine - May elevate BP Duloxetine (Cymbalta) dosing range 60-120mg/day - Blocks serotonin and NE transporters; metabolized through CYP2D6 pathway – sig drug interactions - Indications include depression and chronic pain d/o (fibromyalgia as well) - Newer and very expensive Buproprion (Wellbutrin, Zyban) dosing range 75-400mg/day - Increased dopamine activity - Indications include MDD, dysthymia, Bipolar depression, ADHD (at low doses), used for smoking cessation - Contraindications for use include h/o sz d/o, head trauma or anorexia/bulimia - No sig sexual side effects - NOT effective for anxiety; can actually worsen anxiety/agitation Mirtazipine (Remeron) dosing range 7.5-45mg/day - Alpha 2 adernergic antagonist, enhances noradnergic and serotenergic - Sedation and wt gain are sig side effects; often used in depression for those with insomnia and poor appetite; no sig sexual side effects - Effective in combo with SSRI for augmenting treatment of depression Desyrel (Trazodone) dosing range 25-600mg - MoA includes primary inhibition of presynaptic serotonin reuptake with possible mild postsynaptic sertonertic antagonism. Does of AEs 2/2 to histaminic, anticholinergic and alpha-1 blockades - Used most commonly as a sleep aid rather than as antidepressant - Effective at low doses (25mg – 200mg) for sleep, requires higher dosing for antidepressant properties (200600mg) - PRIAPRISM in 1/6000 pts Nefazodone (Serzone) - Is an analog of Trazodone - Sedating, less sexual side effects - Many drug-drug interactions 2/2 p450 inhibition by a metabolite - Inc risk of hepatic failure MOOD STABILIZERS Lithium MoA – unclear; second messenger system effect – effect on circadian rhythms and augments serotonin fnc. Renally cleared and can cause sig renal impairment (esp if dehydration, use of NSAIDS, thiazide diuretics and in elderly Indications – BPAD, Schizoaffective d/o, augmentation for depression, mood lability Side effects - GI upset, fatigue, fine tremor, confusion - Toxicity – AMS, N/V, slurred speech, course tremor, ataxia - Cardiac conduction problems – 1st degree block, slowed sinus node, PVCs - Renal impairment (DI, rare nephritic syndrome) - Hypothyroidism in 5% Pearls - Pregnancy Class D – EBSTEIN’s Anomely – ht defect at tricuspid valve; avoid in 1st Trimester - Requires blood level monitoring, has narrow therapeutic window (0.8-1.2); dialysis rec for levels greater than 4.0 - Steady state takes 5 days - LETHAL in OD Valproic Acid (Depakote) MoA – unknown; ? if changes metabolism of GABA Indications – BPAD (esp for rapid cycling mania), Schizoaffective d/o, aggression, impulse control probs Side effects - N/V; sedation, tremor, wt gain - Blood abnormalities (thrombocytopenia) - Liver dysfcn (rare hepatotoxicity) and very rare Hemorrhagic pancreatitis Pearls - Metabolized by liver, via P450 pathway – multitude of drug-drug interactions - PREGNANCY CLASS D – 2/2 neural tube defects - Requires blood level monitoring, but wide therapeutic window - Steady state reached in 3 days Carbamazapine (Tegretol) - Less effective, not as widely used - Serious side effects include blook abnl (aplastic anemia, agranulocytosis); severe rash - Preg Class D - Can be risky in OD, particularly 2/2 other drug-drug interactions Lamotrigine (Lamictal) - Used for Bipolar depression, not for manic state; commonly used for augmentation of antidepressant medications - 10% incidence of rash, cases of Stevens-Johnson have occurred, particularly when dosed to high too fast - Requires slow titration to get to effective dosing (start at 25mg and inc by 25mg every 2 wks; target range is ~200mg) Other Mood Stabilizers include other anticonvulsants (Gabapentin, Topiramate) but overall less effective and poor outcome data ANTI-PSYCHOTICS - Typical and Atypicals are equally effective (CATIE trial) for treatment of symptoms. Primary difference is side effect profiles and new agents tend to be better tolerated - Although some effect may seen within hours of dosing, real antipsychotic effects can take 3-6 wks to materialize as meds reach a steady state - Extrapyramidal Side Effects (EPS) o Parkinsonism – shuffled gait, rigidity, masked facies, drooling, tremor o Acute Dystonia – slow/sustained muscle contractions (neck, lock jaw, eyes); Rx with Cogentin or Benadryl IM – scary but reversible o Akathesia – inner restlessness, need to pace/rock; Rx with Inderal or BZDs o Tardive Dyskinesia – often longterm, may be irreversible – abnl, invol mvmt of face, limbs, trunk. Rx but stopping agent and changing to new antipsychotic med - Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS) – potentially lethal reaction to antipsychotic meds, rapid onset. Presentation may consist of elevated temp, muscle rigidity, VS instability, AMS. Medical emergency – requires urgent intervention and possible ICU admission, Rx w/ d/c of antipsychotic, IVF, and possibly bromocriptine/dantrolene Traditional Neuroleptics (Typicals, 1st Generation) Haloperidol (Haldol) 5-20mg/day dosing range High Potency Trifluoperazine (Stelazine) 5-20mg/day High Potency Fluphenazine (Prolixin) 10-20mg/day High Potency Thiothixene (Navane) 5-20mg/day High Potency Pimozide (Orap) 1-10mg/day High Potency Molindone (Moban) Loxapine (Loxitane) Perphenizine (Trilafon) 50-100mg/day 50-100mg/day 4-40mg/day Mid Potency Mid Potency Mid Potency Mesoridazine (Serentil) Chlopromazine (Thorazine) Thioridizine (Mellaril) 50-400mg/day 200-800mg/day 200-800mg/day Low Potency Low Potency Low Potency MoA – Dopamine D2 receptor Antagonism (High, Mid, Low potencies depend on binding affinity) Lower potency typically require higher dosing to elicit antipsychotic effect Indications – Schizophrenia, psychosis 2/2 primary mood d/o/dementia/delirium, schizoaffective d/o, severe agitation, tics Side Effects - Lower potency agents have more troublesome side effects 2/2 greater antagonism of cholinergic, adrenergic and histaminergic receptors - High potency agents have more frequent EPS effects 2/2 potent antagonism of dopa receptors - Wt gain, sexual dysfcn, orthostatic hypotension, decreased sz threshold - Prolonged QTc – risk of Torsades Pearls - Compliance is a HUGE issue and can be rare at times. Haldol and Prolixin come in injectable depot forms (req q monthly dosing once at steady state) Atypical Antipsychotics (new generation) Clozapine (Clozaril) Olanzapine (Zyprexa) Risperidone (Risperdal) Aripiprazole (Abilify) Quetiapine (Seroquel) Ziprasidone (Geodone) 400-600mg/day 5-20mg/day 1-6mg/day 10-30mg/day 200-800mg/day 80-160mg/day Check blood levels MoA – Prominent antagonism at Serotonin 2A receptor as well as Dopamine D2 blockade; less action on nigrostriatal pathway (where EPS Symptoms are thought to originate) Indications – same as above Side Effects - Clozapine – Agranulocytosis in 1-2%, requires CBCs weekly while starting, monthly forever; lowers sz threshold. Myocarditis. Commonly causes tachycardia, hypotension, drooling - Common SEs for all include metabolic syndrome (wt gain, hypercholesterol, DM); sedation, orthostatic hypotension - EPS lower frequency; inc frequency in pts who are neuroleptic niave - TD much less incidence, but may still occur - Cardiac side effects, QTc prolongation; independent cardiovasc risk for all taking atyipcals (inc risk of ischemic stroke) – despite length of time taking - Risperdal has risk of elevated prolactin (amenorrhea, gynecomastia, galactorrhea and impotence) Pearls - Risperdal comes in long acting injectable - Abilify, Geodone, Zyprexa come in short acting injectable (often used in acute settings) - Abilify, Risperdal, Zyprexa all come in dissolvable tablet formulation (helpful for noncompliance) - Have benefit in treating particularly negative symptoms and most have mood stabilization properities (Seroquel, Abilify and Geodone have FDA approval as primary agents for BPAD manic/mixed state) - Clozaril is the go to agent for treatment refractory schizophrenia ANTIPARKINSONIAN DRUGS Benztropine (Cogentin) Trihexyphenidyl (Artane) Biperiden (Akineton) MoA – Anticholinergic effect, restores ACh/Dopa balance Indications – treatment of EPS side effects assoc w/ antipsychotic drugs Side Effects - Dry mouth, blurred vision, constipation, confusion/AMS, delirium Pearls - Artane has euphorigenic properties and is at risk of being abused - Amantadine is an alternative treatment (mech is a dopa agonist) ANTI-ANXIETY MEDICATIONS SSRIs – see above Benzodiazepines *these are controlled substances Clonazepam (Klonopin) 18-50hr ½ life Alprazolam (Xanax) 6-12hr ½ life Lorazepam (Ativan) 10-20hr ½ life Diazepam (Valium) 20-100hr ½ life Chlordiazepoxide (Librium) 5/30hr ½ life Clorazepate (Tranxene) 36-200hr ½ life MoA (BZDS) – work at GABA receptor (like EtOH) to cause CNS depression Indications – panic d/o, severe anxiety, agitation, agitated depression, social phobia, akathesia, insomnia, acute EtOH withdrawal. Often used for initial treatment of anxiety until SSRI therapeutic Side Effects - Sedation, drowsiness, dizziness (Feelings of being intoxicated) - Delirium, Respiratory suppression - Dependence formation (physiological as well as psychological); AKA can develop tolerance Pearls - Just as EtOH, physical dependence can lead to withdrawal syndrome upon abrupt cessation as well as risk of seizure, coma and death - Caution in gero population, metabolites can often build up excessively with significantly prolonged ½ lives and dangerous blood levels – recommend minimal use to avoidance - Can be lethal in OD Buspirone (BuSpar) not a controlled substance - Mild effect for GAD; may be used for augmentation of antidepressant treatment - Common SEs HA, N/V, dizziness - No risk of dependence or developing tolerance - Safe in OD Hydroxyzine (Vistaril, Atarax) not a controlled substance - MoA – antihistaminic (used for treatment of anxiety as well as purities) - Likely deliriogenic in elderly 2/2 anticholinergic properties SUBSTANCE ABUSE Disulfuram (Antabuse) - Req pt to be strongly motivated, only by taking than causes severe rxn if EtOH ingested (N/V) - Contraindicated if pt with liver dis Naltrexone (Revia) - Dec craving by targeting “pleasure pathway” in brain - Often pts will dec but not completely abstain from use Methadone – controlled substance - Rx of heroin dependence Buprenorphine (Suboxone) – controlled substance - Tx opioid dependence DEMENTIA Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors (used to treat mild-moderate dementia of Alzheimer’s type) Donepezil (Aricept) – reversible, selective inhib o Decreases breakdown of Acetylcholine in brain ( inhibits acetylcholinesterase) o More specific and less GI side effects Rivastigmine (Exelon) – reversible, selective inhib o also available as a patch Galantamine (Reminyl) – reversible, competitive inhib NMDA Antagonist (used to treat moderate to severe dementia of Alzheimer’s type) Memantine (Namenda)- noncompetitive NMDA antagonist, reduces glutamate mediated excitotoxicity Vitamin E – antioxidant, thought to prevent cell death HYPNOTICS Benzodiazepines Zolpidem (Ambien) Zaleplon (Sonata) Eszopiclone (Lunseta) Desyrel (Trazodone) ADHD MEDICATIONS Stimulants - All work equally well, but individuals may differ in response - Quick onset of action and effect (same day is possible) - May require multiple daily doses - All stimulants are controlled substances - FDA Approval – Adderall and Dexedrine for age 3 and up; all other stimulants for age 6 and up Methylphenidate o Short Acting forms (Ritalin, Methylin, Focalin) o Long-Acting forms (Ritalin LA and SR, Metadate ER and CD, Methylin ER, Focalin XR, Concerta, Daytrana Patch) Amphetamines o Short-Acting forms (Adderall, Dexedrine, Dextrostat, Desoxyn) o Long-Acting forms (Adderall XR, Dexedrine Spansule, Vyvanse) Atomoxetine (Strattera) - MoA more like antidepressant than stimulant - Gen considered 2nd line; recommendation would be to try 3 separate stimulant trials prior to starting - Consider 1st line when h/o substance abuse, h/o anxiety or parents requesting non-controlled substance - FDA approved from age 6 and above - May take weeks to be effective, requires daily use and strict compliance - Same black box warnings as antidepressants Non-FDA Approved – 2nd to 3rd line agents Buproprion Modafanil (used for treatment of narcolepsy) Clonidine (antihypertensive; also used in children for treatment of aggression/agitation) Amantadine (treatment for influenza, MoA – dopamine agonist)