Unit 3
advertisement
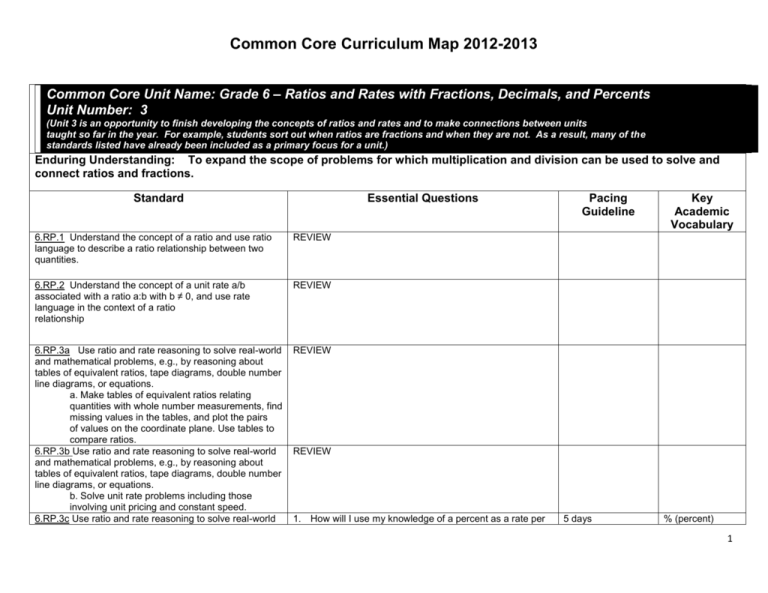
Common Core Curriculum Map 2012-2013 Common Core Unit Name: Grade 6 – Ratios and Rates with Fractions, Decimals, and Percents Unit Number: 3 (Unit 3 is an opportunity to finish developing the concepts of ratios and rates and to make connections between units taught so far in the year. For example, students sort out when ratios are fractions and when they are not. As a result, many of the standards listed have already been included as a primary focus for a unit.) Enduring Understanding: To expand the scope of problems for which multiplication and division can be used to solve and connect ratios and fractions. Standard Essential Questions 6.RP.1 Understand the concept of a ratio and use ratio language to describe a ratio relationship between two quantities. REVIEW 6.RP.2 Understand the concept of a unit rate a/b associated with a ratio a:b with b ≠ 0, and use rate language in the context of a ratio relationship REVIEW 6.RP.3a Use ratio and rate reasoning to solve real-world and mathematical problems, e.g., by reasoning about tables of equivalent ratios, tape diagrams, double number line diagrams, or equations. a. Make tables of equivalent ratios relating quantities with whole number measurements, find missing values in the tables, and plot the pairs of values on the coordinate plane. Use tables to compare ratios. 6.RP.3b Use ratio and rate reasoning to solve real-world and mathematical problems, e.g., by reasoning about tables of equivalent ratios, tape diagrams, double number line diagrams, or equations. b. Solve unit rate problems including those involving unit pricing and constant speed. 6.RP.3c Use ratio and rate reasoning to solve real-world REVIEW Pacing Guideline Key Academic Vocabulary REVIEW 1. How will I use my knowledge of a percent as a rate per 5 days % (percent) 1 Common Core Curriculum Map 2012-2013 and mathematical problems, e.g., by reasoning about tables of equivalent ratios, tape diagrams, double number line diagrams, or equations. c. Find a percent of a quantity as a rate per 100 (e.g., 30% of a quantity means 30/100 times the quantity); solve problems involving finding the whole, given a part and the percent 6.RP.3d Use ratio and rate reasoning to solve real-world and mathematical problems, e.g., by reasoning about tables of equivalent ratios, tape diagrams, double number line diagrams, or equations. d. Use ratio reasoning to convert measurement units; manipulate and transform units appropriately when multiplying or dividing quantities. 6.EE.6 Use variables to represent numbers and write expressions when solving a real-world or mathematical problem; understand that a variable can represent an unknown number, or, depending on the purpose at hand, any number in a specified set. Represent and analyze quantitative relationships between dependent and independent variables. 6.EE.7 Solve real-world and mathematical problems by writing and solving equations of the form x + p = q and px = q for cases in which p, q and x are all nonnegative rational numbers. 100 to find the percent of a known quantity? 2. How will I represent percents using tools such as tables of equivalent ratios, tape diagrams, double line diagrams, and equations? 3. How will I establish connections between tools that allow for extended reasoning and synthesis of the concept of ratios and rates (e.g., How do tape diagrams and double number lines show rate reasoning given the same context? 1. How will I use measurement units to employ ratio reasoning (e.g., If 3 feet is equal to a yard, then 6 feet is equal to 2 yards)? 2. How will I use tools such as tables of equivalent ratios, tape diagrams, double number line diagrams, and equations to help scaffold understanding for converting measurement units? 3. How will I establish connections between tools to allow for extended reasoning and synthesis of the concept 4. of ratios and rates (e.g., How do tape diagrams and double number lines show rate reasoning given the same context)? REVIEW 5 days 1. Convert 2. 10n (power of 10 notation REVIEW 2 Common Core Curriculum Map 2012-2013 6.EE.9 Use variables to represent two quantities in a realworld problem that change in relationship to one another; write an equation to express one quantity, thought of as the dependent variable, in terms of the other quantity, thought of as the independent variable. Analyze the relationship between the dependent and independent variables using graphs and tables, and relate these to the equation. Suggested Resources by Unit REVIEW Location of these resources 3