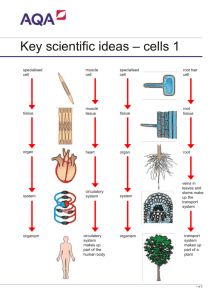
Unit 3 Outcomes ANSWERS – Cells are Organized into Systems
advertisement

Name _________________________ Period _____ Unit 3 Outcomes ANSWERS – Cells are Organized into Systems Please be aware that you will need to apply the information below. Don’t just memorize! 1. What are the five levels of organizations beginning at the cellular level and moving up to the entire organism? What is a simple definition of each level. 1. Cells - The smallest living part of an organism. 2. Tissues - Tissues are large groups of cells all doing the same job. 3. Organs - Organs are groups of tissues that work together to do a job. 4. Organ systems - A group of organs that work together to perform a major function in the plant or animal. 5. Organisms - An individual animal, plant, or single-celled life form 2. What are the functions of the skeletal system? 1) Provides shape and support. 2) Enables you to move. 3) Protects your organs. 4) Produces blood cells. 5) Stores minerals until your body needs them. a. How does this system help the organism survive? We would not be alive without blood. If organs weren’t protected they would become damaged and we could die from internal bleeding. Die of starvation without anything to attach muscles to to get food. Bones would break without calcium. You’d be a blob. b. What kinds of specialized cells and/or tissues help make this system work? Cell – Bone cells, cartilage cells, blood cells, adipose (fat) cells, neurons (nerve cells) Tissue –cartilage, connective tissues, epithelial tissues, blood-forming tissues, adipose and nervous tissue 3. What are the functions of the muscular system? 1. Move the skeleton (with the skeletal system) 2. Movement inside of internal organs 3. Maintains your posture and body position 4. Generation of body heat a. How does this system help the organism survive? Food and blood would not be able to move through our body without our muscular system so we would die due to lack of oxygen and nutrients. We would also freeze to death. Bones wouldn’t be held together. Without the diaphragm we couldn’t breathe. Muscles protect bones so they don’t break easily. b. What kinds of specialized cells and/or tissues help make this system work? Cells – muscle cells Tissue – smooth muscle tissue, cardiac muscle tissue, skeletal muscle tissue 4. What are the functions of the digestive system? 1. Digestion – breaking down food to release nutrients 2. Absorption of nutrients 3. Elimination of wastes a. How does this system help the organism survive? We would die if we could not absorb nutrients. If we couldn’t get rid of feces we would poison ourselves from the inside or rupture internally and bleed to death. b. What kinds of specialized cells and/or tissues help make this system work? Cells – enzyme secreting cells, bile secreting cells Tissues – smooth muscle tissue, nervous tissue, connective tissue 5. What are the functions of the excretory system? Eliminate or get rid of waste! a. How does this system help the organism survive? If we couldn’t get rid of waste we would poison ourselves from the inside. Water in our lungs would drown us, salts would poison us, and uric acid would poison us. Plants wouldn’t get carbon dioxide. No sweat = overheating. b. What kinds of specialized cells and/or tissues help make this system work? Cells – pore cells, gland cells, duct cells Tissues – smooth muscle tissue, epithelial tissue 6. What are the functions of the circulatory system? 1) Deliver food and oxygen to cells 2) Remove waste products 3) Aid in disease prevention a. How does this system help the organism survive? We would not survive and die due to bacteria and infections without white blood cells, we would suffocate from the inside without oxygen delivered to our cells and we would be poisoned by our own wastes. Glucose couldn’t get to our mitochondria to make ATP. b. What kinds of specialized cells and/or tissues help make this system work? Cells – red and white blood cells, platelets, heart cells Tissues – cardiac muscle tissue, epithelial tissue (blood vessels), smooth muscle tissue (blood vessels) 7. What are the functions of the respiratory system? To supply oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide and water. a. How does this system help the organism survive? We would suffocate without oxygen going to our cells and die of carbon dioxide poisoning. We would drown by not ridding our lungs of water. b. What kinds of specialized cells and/or tissues help make this system work? Cells – Epithelial cells, nerve cells, muscle cells Tissues – Epithelial tissues, nerve tissues, muscle tissues, connective tissues 8. What are the functions of the nervous system? 1. Receives information about what is happening both inside and outside your body. 2. Directs the way our body responds to the information received. 3. Helps maintain homeostasis by sending instructions to the rest of the body, making it respond. a. How does this system help the organism survive? None of our organ systems would operate without our nervous system. We could also be burned to death of similar fate if we couldn’t use our senses to react to negative stimuli. Every system in our body would shut down and not work. b. What kinds of specialized cells and/or tissues help make this system work? Cells – neurons Tissues – nerve, blood, and connective tissues 9. Describe the interactions of all the above systems to perform a basic movement such as bending the elbow. Your brain sends a message to your muscles to contract and bend your arm. The muscles are attached to the skeleton which moves the arm. 10. What is the function(s) of the root system in plants? Anchorage and support, absorbing nutrients, storing nutrients a. How does this system help the organism survive? Without water and nutrients the plant would shrivel and die. The plant would blow away. b. What kinds of specialized cells help make this system work? Cell = Plant cell Tissue (vascular) = xylem, phloem 11. What is the function of the stem system in plants? Carries nutrients, and water and the products of photosynthesis (glucose and oxygen) between the plant’s roots and leaves. Provides support for the plant. Helps store water in some plants. a. How does this system help the organism survive? Without the stem system, the plant wouldn’t get water, nutrients, glucose and oxygen where it was needed. It would not be able to stand up. In some plants without water storage it would become dehydrated and die. b. What kinds of specialized cells help make this system work? Cell = Plant cell Tissue (vascular) = xylem, phloem 12. What is the function of the leaf system in plants? 1. Making food through photosynthesis. 2. Exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide through stomata. 3. Evaporation of water on leaf surface and through stomata. a. How does this system help the organism survive? The plant (and humans) would have no energy to function without the products of photosynthesis and the exchange of gasses. Water would accumulate in and on the plant weighing it down. b. What kinds of specialized cells help make this system work? Cell = Plant cell Tissue = epidermal tissue 13. Define homeostastis. Homeostasis is the process by which an organism’s internal (inside) environment is kept stable in spite of changes in the external (outside) environment. It maintains BALANCE or EQUILIBRIUM! Examples are: maintaining our body temperature at 98.6, shivering to warm up, sweating to cool down, feeling hungry to get food for energy, etc. 14. Are there any systems that are not required for the survival of the organism and species? No, each system has specific jobs that need to be carried out for our survival. The nervous system leads them all and helps keep them functioning smoothly. 15. What animal system(s) is the plant root system most similar to? Explain how they are similar and how they are different. Our skeletal and digestive systems because we also need support (skeletal) and we need to absorb nutrients (digestive). The plant’s root system does not make blood cells or allow it to move like our skeletal system. It also does not eliminate waste like our digestive system. 16. What animal system(s) is the plant stem system most similar to? Explain how they are similar and how they are different. Our circulatory system is most like the stem system. The xylem and phloem are like our blood vessels and move (transport) nutrients and waste throughout both our bodies. The plant’s stem system does not fight disease like our circulatory system. 17. What animal system(s) is the plant leaf system most similar to? Explain how they are similar and how they are different. The leaf system is most like our respiratory system. We also exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide through our alveoli and they do the same through their stomata. Both systems also release water as waste. We do NOT make food in our respiratory system or in any other system.