Learners Analysis
advertisement

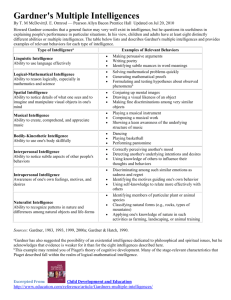
Learner Analysis Trellis Buckles Target Audience Learners for the project were selected from At-Risk Students in an alternative school K-12 environment. Due to disciplinary reasons, all students were expelled from their home schools by the Disciplinary Tribunal Committee and referred to an alternative school as a disciplinary consequence for behavior correction. Students were assigned one to two semesters depending on the infraction violation via the Student Code of Conduct guidelines. The student demographic range from elementary, middle school, and high school students; however, 4th through 12th graders thus far. Learners chosen for this assignment were placed in the following categories: one elementary 5th grader; three 6th, 7th, 8th middle school students; and four 9th, 10th, 11th, 12th high school students. In connecting the learning styles with the students, the students’ first name will only be mention in this analysis; due to, privacy and confidentiality laws prohibiting full disclosure without parental consent. The students are Leigh-5th grade; Kim-6th grade; Catherine-7th grade; Anna-8th grade; Shannon-9th grade; Jarvis-10th grade; Josh 11th grade; and Travis-12th grade. The students’ ages range between 9 and 17. For gender, four female and four males were used in the analysis. One student was visual impaired and one hearing impaired. There were 7 African American students and 1 Hispanic student. All students noted English as their natural language with the exception of the 1 student fluent in Spanish. Gardner’s Multiple Intelligence Howard Gardner, psychologist and developer of the Multiple Intelligence Theory, noted that students think and learn in various ways. Gardner identified seven Intelligence associated with learners’ cognitive ability. According to Smith (2008), Gardner characterized students as Logical-Mathematical learner, Verbal-Linguistic learners, Visual-Spatial learners, Body-Kinesthetic learners, Musical-Rhythmic learners, Interpersonal learners, and Intrapersonal learners. The Intelligence rarely operate independently noted Gardner. Verbal-Linguistic Intelligence is the ability to use words and language. Logical-Mathematical Intelligence is the capacity for inductive and deductive thinking and reasoning; as well as the ability to recognize patterns. Visual-Spatial Intelligence is the ability to visualize objects and spatial dimensions, thus, creating and internal images and pictures. Body-Kinesthetic Intelligence is the ability to control the body and physical motion. Musical-Rhythmic Intelligence recognize tonal patterns and sounds, thereby, sensitive to rhythms and beats. Interpersonal Intelligence is the guided by the ability to communications and form relationships. Last, Intrapersonal Intelligence are spiritual, self-reflection, and awareness learners. In assessing the students, the learning styles varied; however, occasionally one dominated the other. According to the Gardner’s Multiple Intelligence Theory, the students were identified by the following learning styles: Leigh (logical-mathematical intelligence); Catherine (musical-rhythmic intelligence); Anna (visual-spatial & logical-mathematical intelligence); Josh (visual-spatial intelligence); Jarvis (verbal-linguistic & interpersonal intelligence); Shannon(logical-mathematical & verbal-linguistic intelligence); Travis (interpersonal intelligence); and Kim (logical-mathematical intelligence). Special Needs In the student learning analysis, the students Anna and Josh were identified as receiving special services. One student had been diagnosed with Asperger Syndrome and the other as intellectual disabled. Anna is currently going through the Individual Education Plan (IEP); however, Josh has had one since grade school. Asperger Syndrome According to the Autism Society, Asperger Syndrome (AS) is a severe developmental disorder characterized by major difficulties in social interaction, and restricted and unusual patterns of interest and behavior. In an instructional environment, it is suggested that students with Asperger be taught socialization and vocation skills noted below: *Socialization skills: Emphasis should be placed on skills that correspond to relative strengths for the individual as well as skills that may be viewed as central for the person’s future vocational life, such as, writing skills, computer skills, and science *Vocational skills: Suggests that students learn how to use the library, access data bases and the Internet Intellectual Disability The American Association on Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities (AAIDD) defines intellectual disability as synonymous with the term ‘mental retardation.’ Intellectual disability is a disability that involves significant limitations both in intellectual functioning and in adaptive behavior, thereby, covering many everyday social and practical skills. AAIDD identifies the essential developmental skills for those with disability as: *Conceptual skills: Literacy; self-direction; and concepts of number, money, and time *Social skills: Interpersonal skills, social responsibility, self-esteem, gullibility, naïveté social problem solving, following rules, obeying laws, and avoiding being victimized *Practical skills: activities of daily living (personal care), occupational skills, use of money, safety, health care, travel/transportation, schedules/routines, and use of the telephone As Instructional designers scurry around trying to identify various ways to address student’s learner styles, many professionals note that it is just as challenging addressing the needs of students with disabilities. Using technology with students with disabilities is highly recommended according to Technology Teacher, Diggs (2000). Diggs notes that at-risk students use technology to interact with their peers and it assists with academic success. There are numerous agencies and organizations that provide guidelines and identify statues to ensure equal treatment for students with disabilities, such as, the Office For Civil Rights, American With Disabilities, The US Department of Education, and ARC to name a few. Cultural/Ethnic Background Students observed for the assessment were identified into two main groups; however, several sub-categories were noted. The Ethnic groups were African American and Hispanic. In determining learning styles and academic success, culture and ethnic differences influences students’ achievement. Currently 95% of the students enrolled in the alternative program of African American, 4.5% Hispanic, and .5 White. The male to female ratio is 5:1. Of the Hispanic students, less than half are fluent in English; however, many students with English as their native language demonstrate broken dialect as well. Often there exist barriers in the educational arena between students from various cultural and ethnic background and teachers; thus, interfering with the instructional connections and transferring of material. Mora, 2002, suggests the importance of using multicultural literature to teach reading. According Professor Mora, multicultural literature reflects culture diversity within the community and within the classroom. Also, it acts as a bridge in connecting students’ real-life experiences and academic learning. The Institute for the Study of Social Change, (1991) noted in literature that students of various culture back expressed that there exist subtle discrimination in the educational arena; thus, maintaining the barriers between students. According to Davis, (1993) there are no guidelines to address this problem; however, being thoughtful and sensitive might help the problem. Davis suggests the strategies noted to assist with diversifying an educational environment: *Recognize any biases or stereotypes you may have absorbed *Treat each student as an individual, and respect each student for who he or she is *Rectify any language patterns or case examples that exclude or demean any groups *Do your best to be sensitive to terminology *Get a sense of how students feel about the cultural climate in your classroom What Motivate Students John Keller divides motivation strategies to engage students into four categories: attention, relevance, confidence, and satisfaction. Keller suggests the follows: Attention *Perceptual arousal assists with gaining and maintaining student’s attention via novels *Inquiry arousal stimulate information-seeking by having learners generate questions/solve problems *Variability maintains student interest by varying the element of instruction Relevance *Familiarity adapts instruction by using concrete language and examples *Goal Orientation provides statements or examples instructions *Motive Matching using teaching strategies that match the motive profiles of the students Confidence *Expect success by making learner aware of performance requirements and evaluation criteria *Challenge Setting by providing multiple achievement levels *Attribution Molding allows feedback that supports student’s ability and efforts Satisfaction *Natural Consequences provides opportunities to use new skills in a simulated setting *Positive Consequences provides feedback and reinforcements that assist w behavior *Equity maintain consistent standards and consequences for accomplishing the task