Atomic Discoveries Notes
advertisement
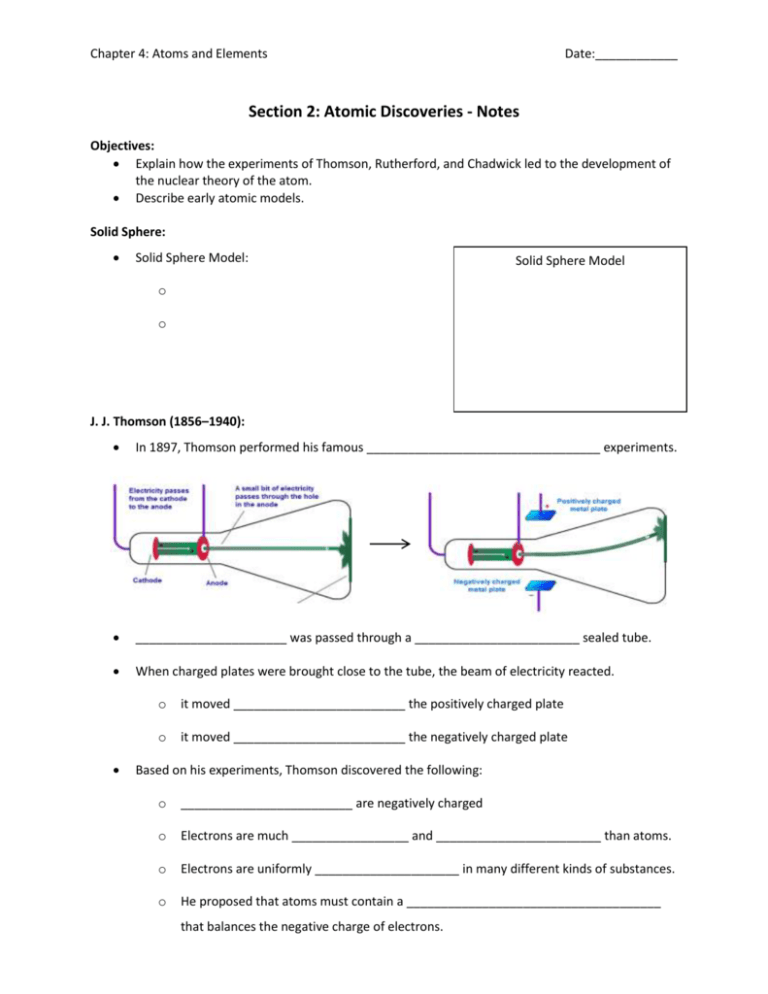
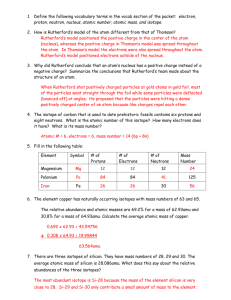
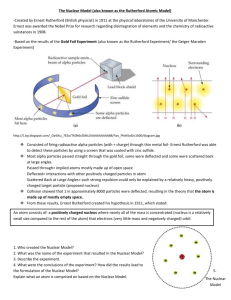
Chapter 4: Atoms and Elements Date:____________ Section 2: Atomic Discoveries - Notes Objectives: Explain how the experiments of Thomson, Rutherford, and Chadwick led to the development of the nuclear theory of the atom. Describe early atomic models. Solid Sphere: Solid Sphere Model: Solid Sphere Model o o J. J. Thomson (1856–1940): In 1897, Thomson performed his famous __________________________________ experiments. ______________________ was passed through a ________________________ sealed tube. When charged plates were brought close to the tube, the beam of electricity reacted. o it moved _________________________ the positively charged plate o it moved _________________________ the negatively charged plate Based on his experiments, Thomson discovered the following: o _________________________ are negatively charged o Electrons are much _________________ and ________________________ than atoms. o Electrons are uniformly _____________________ in many different kinds of substances. o He proposed that atoms must contain a _____________________________________ that balances the negative charge of electrons. Plum Pudding Model Plum Pudding Model o o Ernest Rutherford (1871-1937): In 1909, Rutherford performed his famous _________________________________ experiment. Tiny particles called ____________________________________ were directed at a thin sheet of gold foil. o Most particles passed ___________________________________ the foil, but some were deflected at ___________________________________. Expected result of Rutherford’s gold foil experiment: o If the plum pudding model were correct, the alpha-particles would pass right through the gold foil with _______________________________________. Actual result of Rutherford’s gold foil experiment: o A small number of alpha-particles were _______________________ or ___________________________. Based on his experiments, Rutherford discovered the following: o Most of the atom’s ________________ and all of its positive charge are contained in a small core called the ________________________. o Most of the _______________________ of the atom is ___________________________ through which the tiny, negatively charged electrons are dispersed. o The number of negatively charged electrons outside the nucleus is _________________ to the number of positively charged particles (protons) inside the nucleus, so that the atom is electrically ____________________. Planetary Model: Planetary Model o o James Chadwick (1891-1974): In 1919, Chadwick and his mentor, Rutherford, kept finding that the _______________________ of an atom was larger than the __________________________________ of that atom. Chadwick suggested that there could be an ___________________________________________ in the nucleus that had mass, but no charge. o These particles were called __________________________. Nuclear Model Nuclear Model o o The _______________ nucleus makes up more than ______________ of the mass of the atom o but the nucleus occupies only a small fraction of an atoms ____________________ The electrons are distributed through a much _______________ region but don’t have much _____________. A single grain of sand composed of solid atomic nuclei would have a mass of _______________. o Astronomers believe that ________________________ and _______________________ ________________ are composed of this kind of incredibly dense matter.