Computer Lab Research – Earth`s Interior http://ansatte.uit.no
advertisement

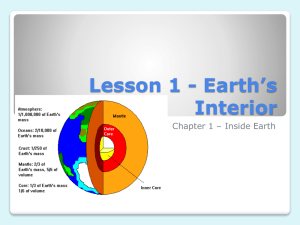
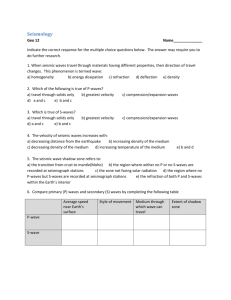
Computer Lab Research – Earth’s Interior http://ansatte.uit.no/kku000/webgeology/ Introduction: 1. How far is it to the center of the earth? How far have we drilled? (6000km, 15km) Exploring: 2. How do we study the interior of the earth? (seismic waves) 3. The velocity of a seismic wave depends on the _________________ it passes through. (density) 4. How do we determine the depth of a layer reflecting seismic waves to the surface? (travel time) 5. Only high energy seismic waves can travel far into the earth. Name two sources for high energy seismic waves. 6. Two important seismic waves are P-waves and S-waves. How do S-waves prove that the outer core of the earth is liquid? Structure of Earth: 7. Name the four major layers. 8. Describe the two types of crust. (oceanic- basalt and gabbro; continental – granite) 9. What is special about the area of the upper mantle known as the asthenosphere? 10. If we add substantial weight to an area of the crust, we will cause the crust to ___________________. How could such weight be added in nature? 11. If we remove substantial weight to an area of the crust, we will cause the crust to _______________. How could such weight be removed in nature? 12. Describe the composition and nature of the outer and inner cores. Internal Heat: 13. What is responsible for most of the heat transfer from the hot core to the surface of the earth? 14. Heat transfer from the earth’s interior to the surface drives the movement of the plates. This movement of plates (plate tectonics) is responsible for such well known geological processes as (name 4)_____. (earthquakes, volcanoes, mountain building, erosion) Earth’s Magnetic Field: 15. What is the cause of the earth’s magnetic field? Use the following site for this worksheet: http://ansatte.uit.no/kku000/webgeology/ The Earth’s Interior Introduction: 1. How far is it to the center of the earth? How far have we drilled? Exploring: 2. How do we study the interior of the earth? 3. The velocity of a seismic wave depends on the _________________ it passes through. 4. How do we determine the depth of a layer reflecting seismic waves to the surface? 5. Only high energy seismic waves can travel far into the earth. Name two sources for high energy seismic waves. 6. Two important seismic waves are P-waves and S-waves. How do S-waves prove that the outer core of the earth is liquid? Structure of Earth: 7. Name the four major layers. 8. Describe the two types of crust. 9. What is special about the area of the upper mantle known as the asthenosphere? 10. If we add substantial weight to an area of the crust, we will cause the crust to ___________________. How could such weight be added in nature? 11. If we remove substantial weight to an area of the crust, we will cause the crust to _______________. How could such weight be removed in nature? 12. Describe the composition and nature of the outer and inner cores. Internal Heat: 13. What is responsible for most of the heat transfer from the hot core to the surface of the earth? 14. Heat transfer from the earth’s interior to the surface drives the movement of the plates. This movement of plates (plate tectonics) is responsible for such well known geological processes as (name 4)_____. Earth’s Magnetic Field: 15. What is the cause of the earth’s magnetic field? The Earth’s Interior Introduction: 1. How far is it to the center of the earth? How far have we drilled? Exploring: 2. How do we study the interior of the earth? 3. The velocity of a seismic wave depends on the _________________ it passes through. 4. How do we determine the depth of a layer reflecting seismic waves to the surface? 5. Only high energy seismic waves can travel far into the earth. Name two sources for high energy seismic waves. 6. Two important seismic waves are P-waves and S-waves. How do S-waves prove that the outer core of the earth is liquid? Structure of Earth: 7. Name the four major layers. 8. Describe the two types of crust. 9. What is special about the area of the upper mantle known as the asthenosphere? 10. If we add substantial weight to an area of the crust, we will cause the crust to ___________________. How could such weight be added in nature? 11. If we remove substantial weight to an area of the crust, we will cause the crust to _______________. How could such weight be removed in nature? 12. Describe the composition and nature of the outer and inner cores. Internal Heat: 13. What is responsible for most of the heat transfer from the hot core to the surface of the earth? 14. Heat transfer from the earth’s interior to the surface drives the movement of the plates. This movement of plates (plate tectonics) is responsible for such well known geological processes as (name 4)_____. Earth’s Magnetic Field: 15. What is the cause of the earth’s magnetic field? The Earth’s Interior Introduction: 1. How far is it to the center of the earth? How far have we drilled? Exploring: 2. How do we study the interior of the earth? 3. The velocity of a seismic wave depends on the _________________ it passes through. 4. How do we determine the depth of a layer reflecting seismic waves to the surface? 5. Only high energy seismic waves can travel far into the earth. Name two sources for high energy seismic waves. 6. Two important seismic waves are P-waves and S-waves. How do S-waves prove that the outer core of the earth is liquid? Structure of Earth: 7. Name the four major layers. 8. Describe the two types of crust. 9. What is special about the area of the upper mantle known as the asthenosphere? 10. If we add substantial weight to an area of the crust, we will cause the crust to ___________________. How could such weight be added in nature? 11. If we remove substantial weight to an area of the crust, we will cause the crust to _______________. How could such weight be removed in nature? 12. Describe the composition and nature of the outer and inner cores. Internal Heat: 13. What is responsible for most of the heat transfer from the hot core to the surface of the earth? 14. Heat transfer from the earth’s interior to the surface drives the movement of the plates. This movement of plates (plate tectonics) is responsible for such well known geological processes as (name 4)_____. Earth’s Magnetic Field: 15. What is the cause of the earth’s magnetic field?