7 th Grade Vocab
advertisement

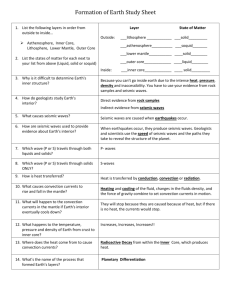
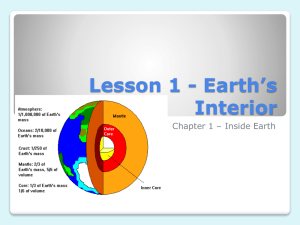
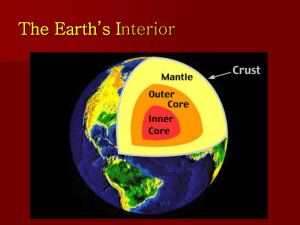
7th Grade Vocab Section 2: Earth Matters Atmosphere: The Various Layers of Air that surround Earth. The densest atmospheric layers are closer to Earth, and the least dense layers are farther away from the Earth. Crust: The solid outer layer of Earth where life is found. This is the thinnest layer of the earth Lithosphere: The lower layer of Earth’s crust in addition to the upper layer of the Earth’s Mantle, composed of brittle/rigid/solid materials Mantle: A semi-solid layer of Earth that takes up the most volume of Earth. This layer is found directly below the Earth’s crust Asthenosphere: A layer of Earth that is composed of molten upper mantle material that can “flow.” Mesosphere: A layer of Earth that is located under the crust, lithosphere, and asthenosphere, but above the outer core. Mostly considered “inner mantle” Outer Core: A liquid layer of Earth found near the center. It is between the Mantle and the Inner Core. Inner Core: A solid layer in the center of the Earth made of metal. It is the densest layer of the Earth Mixture: A combination or blend of two or more substances that have not chemically combined. Each substance maintains its own identity. Particle: A small piece of matter. Sorting: The process that separates particles based on differences of density and/or particle size. Seismic Waves: The way energy travels from the point of an earthquake Primary Waves (P-Waves): the fastest-travelling seismic waves; they can pass through solids, liquids, and gases (waves move parallel) Secondary Waves (S-Waves): the second fastest-travelling seismic waves; they can pass through solids waves move perpendicular) Continental Crust: composed of mafic magma that erupts on the seafloor to create basalt lava, which flows or cools deeper down to create the intrusive igneous rock gabbro Oceanic Crust: composed of many different types of igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks Archimedes’ Principle: If an object has a greater density than the water, it sinks. If an object has a lesser density than the water, it floats. If an object has an equal density as the water, it will neither sink nor float Convection: Heat is transferred through rapid collisions of atoms, which can only happen if the material is solid. Heat flows from warmer to cooler places until all are the same temperature Conduction: If a material is able to move, even if it moves very slowly, convection currents can form, wherein particles of heat move up and particles that have cooled off move down 7th Grade Vocab Section 2: Earth Matters Atmosphere: Crust: Lithosphere: Mantle: Asthenosphere: Mesosphere: Outer Core: Inner Core: Mixture: Particle: Sorting: Seismic Waves: Primary Waves (P-Waves): Secondary Waves (S-Waves): Continental Crust: Oceanic Crust: Archimedes’ Principle: Convection: Conduction: