nitrogencycle (1) - Presentation High School
advertisement

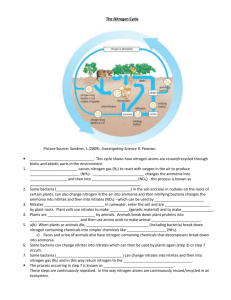
5th grade topic 1 What are the different ways humans impact the nitrogen cycle – examples – fertilization and burning of fuels o Productivity – humans use nitrogen-containing fertilizers to enhance productivity of plants, for example. Even if a plant has unlimited amounts of other resources, it’s productivity is limited by nitrogen levels, and farmers are attempting to control that o Plant species diversity – plant species are adapted to function under a nitrogen constraint, and an overabundance of nitrogen benefits plant species that are evolved to take full advantage of higher nitrogen levels. These genetically gifted plant variations out compete the other variations, and biodiversity decreases. o Increased levels of nitrogen also cause acidification of aquatic systems and adverse effects on fish o Increased levels of nitrogen also causes eutrophication, causing a decrease in levels of oxygen in aquatic ecosystems. th 5 grade topic 2 – how is nitrogen lost from the cycle Denitrification o Bacteria changes nitrate in the soil to atmospheric nitrogen, which joins the atmosphere. Volatilization o Turns urea fertilizers and manures on the soil surface into gases that also join the atmosphere Runoff o The nitrogen in fertilizers and manure and the nitrogen in the soil is carried into our rivers and streams — a concern for water quality. Leaching o Nitrates are carried so deep into the soil that plants can no longer use them o Produces a dual concern — for lost fertility and for water quality, as nitrates enter the groundwater and the wells that provide our drinking water. 4th grade topic 3 What is the role of animals in the nitrogen cycle Animals consume nitrogen when they consume plants or other animals. The nitrogen circulate in their bodies and assists with bodily functions. When animals produce nitrogen rich waste or die, bacteria decompose the waste and release it into the atmosphere, where the free nitrogen reenters the cycle. th 4 grade topic 4 What is the process when nitrogen in the air becomes a part of biological matter through the actions of bacteria and algae o Nitrogen fixation – free pure nitrogen is very inert an nonreactive and must be combined with other elements into usable compounds o Nitrogen fixing bacteria and algae convert pure nitrogen into ammonia, which is absorbed by plants o Bacteria of the genus rhizobium also live inside nodules inside plant roots and secret nitrogen compounds in exchange from nourishment from the host plant o Lighting can also fixate nitrogen – the high levels of energy combine nitrogen with oxygen and form usable nitrates rd 3 grade topic 5 What human activities affect the nitrogen cycle? o Fertilizers and burning fossil fuels – increases in amounts of nitrogen in the nitrogen cycle, which enhances productivity of certain plants and reduces biodiversity of plant species, o Increases in the amount of acid in the soil hurts plants also hurts aquatic animals by leading to anoxia or absence of oxygen in the water rd 3 grade topic 6 what are legumes – plants that convert atmospheric nitrogen into plant usable nitrogen o contain symbiotic bacteria called Rhizobia attached to their roots o these bacteria are nitrogen fixing bacteria that convert pure, inert nitrogen into nitrogen that is usable by other organisms – usually ammonium o this is why legumes are right in protein and nitrates, as nitrogen is essential in making amino acids and proteins 2nd grade topic 7 why do plants need nitrogen – grow, develop, produce seeds o used by the plant to produce enzymes and other proteins, as nitrogen is essential to amino acids o also used to make DNA, which has a nitrogen base o essential to the growth of leaves and stems, and plants that are nitrogen deficient will have yellow, sickly looking leaves cannot use pure nitrogen – have to use ammonia or other nitrates 2nd grade topic 8 why do organisms require nitrogen o same as plants – use to make amino acids and DNA o animals do not use nitrogen gas or nitrates – they get usable compounds from consuming other sources of nitrogen – animals break down protein into amino acids for cell function st 1 grade topic 9 How much of earth is composed of nitrogen o 80% of the Earth – nitrogen is not stable in a crystal lattice, so it is not found in the soil as much as its found in the atmosphere o it is very inert and nonreactive as a gas, so it exists as a gas in the atmosphere in much higher quantity than oxygen or any other element. Million dollar answer 1. Nitrogen fixation converts atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia, through bacteria or lightning. – brings nitrogen into the soil where it can be nitrified N2 NH3 2. Nitrification is the converts the ammonia to nitrate through bacteria – makes the nitrogen usable to plants and animals – most plants and animals cannot use ammonia NH3 NO2 NO3 3. Assimilation is when the inorganic nitrogen is taken up by the roots of the plants and becomes apart of the food chain – used to make amino acids and DNA NO3 organic nitrogen 4. Ammonification is the conversion of organic nitrogen into ammonia - decomposition of animals or animal waste converts the nitrogen into ammonia, which is available for other biological processes Organic nitrogen NH3 5. Dentrification is when nitrates are returned to the atmosphere by anaerobic bacteria – the nitrates are converted into gaseous nitrogen and released into the atmosphere NO3 N2