Supplementary Information (docx 246K)

SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
Changes in Intensive Care for Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplant
Recipients
Etienne Lengliné, Sylvie Chevret,
Anne-Sophie Moreau, Frédéric Pène, François Blot, Jean-
Henri Bourhis, Agnès Buzyn, Benoît Schlemmer, Gérard Socié, and Elie Azoulay
Supplemental Methods
3 Tables
1 Figure
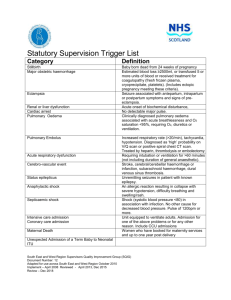
Supplemental Table 1: Cox univariate regression analyses of the risk of day-90 mortality in the 2004-2011 cohort.
Supplemental Table 2 : Identified causes and circumstances of deaths in the recent cohort.
Supplemental Table 3 : Interaction between period and effect of covariates on 90-day mortality
Supplemental Figure 1 : Changes in HSCT procedures in patients admitted to the ICU
8 pages
1
SUPPLEMENTALS METHODS
HSCT procedures
The stem cells were mobilized peripheral-blood cells, bone-marrow cells, or cordblood cells. Various conditioning regimens were used. Myeloablative conditioning (MAC) regimens included either high dose busulvan (>8 mg/Kg orally or intravenous equivalent) or high-dose total-body irradiation (≥8 Gy fractionated dose), both combined with cyclophosphamide. Regimens not meeting these criteria were classified as reduced-intensity conditioning (RIC).
1
All patients received GVHD prophylaxis with cyclosporine A (CsA) plus methotrexate or CsA plus mycophenolate mofetil or CsA alone. Methylprednisolone
(>1 mg/Kg/d) was introduced promptly as first-line treatment in case of acute GVHD symptoms. Second-line treatments varied across centers and study periods.
ICU admission policy
In all three centers, the transplant team determined HSCT indications and chose conditioning regimens and GVHD prophylaxis according to guidelines. In patients with lifethreatening complications, the hematologists and intensivists in charge of the patient decided together whether to admit the patient to the ICU, at the time of clinical deterioration or prophylactically. In all three centers, hematologists and intensivists were on site 24/7.
Reasons for ICU admission were recorded based on the main symptoms at ICU admission. Acute respiratory failure was defined as oxygen saturation <90% or PaO
2
<60 mmHg on room air combined with severe dyspnea at rest with an inability to speak in sentences or a respiratory rate >30 breaths/minute or clinical signs of respiratory distress.
2
Shock was defined as previously reported.
3
Life-supporting interventions, antimicrobial agents, prophylactic treatments, and diagnostic procedures were administered at the
2
discretion of the attending intensivists, who followed best clinical practice and guidelines.
Successful noninvasive ventilation (NIV) was defined as NIV not followed by MV.
Corticosteroids, hematopoietic growth factors, immunosuppressive drugs, and other cancerrelated treatments were prescribed by the hematologist in charge of each patient in accordance with institutional guidelines. Neutropenia was defined as a neutrophil count <0.5
Giga/L. Invasive aspergillosis was defined according to EORTC/MSG guidelines.
4
REFERENCES
1. Bacigalupo A, Ballen K, Rizzo D, Giralt S, Lazarus H, Ho V, et al. Defining the intensity of conditioning regimens: working definitions. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. déc 2009;15(12):1628 ‑ 1633.
2. Azoulay E, Mokart D, Lambert J, Lemiale V, Rabbat A, Kouatchet A, et al. Diagnostic strategy for hematology and oncology patients with acute respiratory failure: randomized controlled trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 15 oct 2010;182(8):1038 ‑ 1046.
3. Legrand M, Max A, Peigne V, Mariotte E, Canet E, Debrumetz A, et al. Survival in neutropenic patients with severe sepsis or septic shock. Crit Care Med. janv
2012;40(1):43 ‑ 49.
4. De Pauw B, Walsh TJ, Donnelly JP, Stevens DA, Edwards JE, Calandra T, et al. Revised definitions of invasive fungal disease from the European Organization for Research and
Treatment of Cancer/Invasive Fungal Infections Cooperative Group and the National
Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Mycoses Study Group (EORTC/MSG)
Consensus Group. Clin Infect Dis. 15 juin 2008;46(12):1813 ‑ 1821.
3
Supplemental Table 1: Cox univariate regression analyses of the risk of day-90 mortality in the 2004-2011 cohort. n HR 95%CI P value
Demographics
Age
Sex
Complete remission at admission
WBC <1000 /mm
HSCT characteristics
3 at admission
EBMT score
Diagnosis to HSCT (days)
Conditioning regimen
Stem cell source
HLA-identical sibling donor
Total body irradiation
ATG as part of conditioning
GVHD at admission (acute or chronic)
Steroids >0.5 mg/Kg/d
Acute GVHD grade >2
Chronic GVHD limited
Chronic GVHD extensive
HSCT to ICU (months)
HSCT to ICU (days)
Organ dysfunctions at ICU admission
Acute respiratory failure
Shock
Acute kidney injury
Serum creatinine at admission
Coma
Hepatic failure
SAPSII
LOD
SOFA
Infections
CMV reactivation at admission
Emerging invasive fungal infection
Invasive aspergillosis (>probable)
Gram negative bacteremia
Duration of neutropenia before admission
Life-sustaining interventions
Noninvasive ventilation
Invasive mechanical ventilation
Renal replacement therapy
F vs. M
RIC vs. MAC
PBSC vs. BM
1.01 (1 ; 1.02 ) 0.063
0.77 (0.55 ; 1.08 ) 0.13
0.97 (0.68 ; 1.38 ) 0.85
173 0.98 (0.7 ; 1.37 ) 0.91
1.06 (0.95 ; 1.18 )
1.00 (0.99 ; 1.00 )
0.86 (0.62 ; 1.19 )
1.07 (0.69 ; 1.65 )
0.79 (0.57 ; 1.1 )
1.17 (0.82 ; 1.67 )
1.53 (1.03 ; 2.27 )
0.31
0.51
0.37
0.76
0.16
0.39
0.036
136 1.71 (1.24 ; 2.37 ) 0.001
106 1.5 (1.08 ; 2.07 ) 0.015
77 1.38 ( 0.98 ; 1.95 ) 0.064
47 1.69 ( 1.13 ; 2.54 ) 0.011
19 1.51 ( 0.81 ; 2.81 ) 0.190
0.99 (0.99 ; 1.01) 0.27
1.00 (1.00 ; 1.00 ) 0.27
180 1.64 (1.16 ; 2.33 ) 0.006
98 1.13 (0.81 ; 1.59 ) 0.47
123 2.05 (1.48 ; 2.83 ) <0.0001
285 1 (1 ; 1 ) <0.0001
58 1.63 (1.12 ; 2.37 ) 0.011
43 1.99 (1.34 ; 2.96 ) 0.0007
110 1.00
276 1.04 (1.03 ; 1.05 ) <0.0001
258 1.2 (1.15 ; 1.26 ) <0.0001
286 1.16 (1.12 ; 1.21 ) <0.0001
43 2.18 (1.48 ; 3.21 ) <0.0001
10 2.25 (1.1 ; 4.59 ) 0.027
31 1.35 (0.84 ; 2.19 ) 0.22
52 1.2 (0.8 ; 1.8 )
62 1 (1 ; 1.01 )
0.39
0.015
82 1.33 ( 0.94 ; 1.87 ) 0.1
126 2.73 ( 1.96 ; 3.81 ) <0.0001
57 2.8 ( 1.97 ; 3.98 ) <0.0001
4
WBC, white blood cells; HSCT, hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation; EBMT, European
Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation risk score; ATG, antithymocyte globulin; RIC, reduced-intensity conditioning; MAC, myeloablative conditioning; PBSCs, peripheral-blood stem cells; BM, bone marrow; ICU, intensive care unit; GVHD, graft-versus-host disease;
CMV, cytomegalovirus; SAPSII, Simplified Acute Physiology Score version II; LOD,
Logistic Organ Dysfunction; SOFA, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; NIV, noninvasive ventilation; MV, invasive mechanical ventilation
5
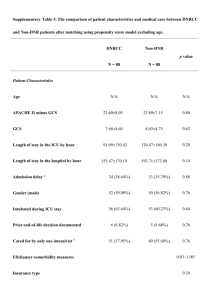
Supplemental Table 2 : Identified causes and circumstances of deaths in the recent cohort.
Causes
Relapse
HSCT-related, non-infectious
Rejection
Graft-versus-host disease n %
25 12.6%
5 2.5%
43 21.6%
Veno-occlusive disease 10 5%
Thrombotic microangiopathy 7 3.5%
Secondary malignancy
Infections
Bacterial
Fungal
Virus
6 3.0%
29 14.6%
18 9.0%
8 4.0%
Parasite
Organ failure of unknown cause
Cardiac arrest
Fulminant hepatitis
Multiple organ failure
No data
Circumstances
6 3.0%
5 2.5%
4 2.0%
17 8,5%
16 8.0%
No limitation
Active-treatment limitation
67 33.7%
78 39.2%
Active-treatment withdrawal 16 8.0%
No data 38 19.1%
6
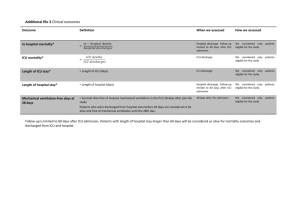
Supplemental Table 3 : Interaction between period and effect of covariates on 90-day mortality
Age
Sex
Center
HSCT characteristics
AML
Conditioning regimen (MAC vs. RIC)
Bone marrow graft
PBSC graft
Sibling donor
TBI
HR
(recent)
95CI low
1.01
0.77
1.00
0.55
95CI upper
1.02
1.08
HR
(historical)
1.01
0.99
1.04
0.93
0.79
0.65
0.86
0.89
1.17
0.18 2.35 0.7
0.73
0.62 1.19 1.22
0.58 1.36 0.78
0.66
0.57
1.47
1.29
1.1
0.91
1.23
0.85
0.82 1.67 1.03
95CI low
95CI P value upper (interaction)
0.99 1.02 0.64
0.71 1.37 0.31
0.06 8.11 0.88
0.64 1.3 0.61
0.71 2.13 0.28
0.55 1.09 0.63
0.87 1.75 0.25
0.6 1.2 0.77
0.73 1.45 0.60
Organ dysfunctions at ICU admission
Respiratory failure
Hemodynamic failure
1.64
1.13
Kidney failure
Neurologic failure
Hepatic failure
2.05
1.63
1.99
Admission SOFA
Admission LOD
Admission SAPSII
Infections
CMV reactivation
1.16
1.2
1.04
2.18
Invasive aspergillosis
Invasive fungal infection (others)
1.35
2.25
1.16 2,33 0.89
0.81 1.59 1.48
1.48 2.83 1.1
1.12 2.37 1.41
1.34 2.96 2,19
1.12 1.21 1.23
1.15 1.26 1.21
1.03 1.05 1.05
1.48 3.21 1.15
0.84 2.19 1.44
1.1 4.59 1.63
0.63 1.25 0.01
1.01 2.17 0.30
0.76 1.58 0.01
0.81 2.44 0.67
1.02 4.68 0.83
1.18 1.29 0.06
1.16 1.27 0.81
1.04 1.06 0.14
0.73 1.79 0.03
0.93 2.24 0.85
1.05 2.53 0.46
HR, hazard ratio; 95CI, 95% confidence interval; HSCT, hematopoietic stem cell transplant;
AML, acute myeloid leukemia; MAC, myeloablative conditioning; RIC, reduced-intensity conditioning; PBSC, peripheral blood stem cells; TBI, total body irradiation; ICU, intensive care unit; SOFA, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; LOD, Logistic Organ Dysfunction;
SAPSII, Simplified Acute Physiology Score version II; CMV, cytomegalovirus
7
Supplemental Figure 1 : Changes in HSCT procedures in patients admitted to the ICU
HSCT, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
8