HISD TEKS/SEs Road Map ELAR 3rd Six Weeks Bundle 1 (2 Weeks
advertisement

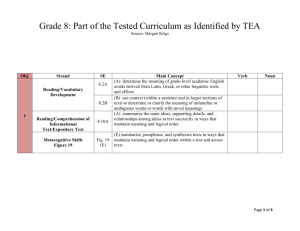
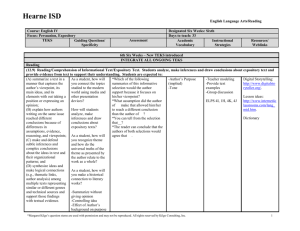
HISD TEKS/SEs Road Map ELAR 3rd Six Weeks Bundle 1 (2 Weeks)- November 18-December 6 Reading Genre Focus: Informational and Persuasive Informational and Persuasive Text ~ Writing Genre Focus: Persuasive Essay (Letter format) Big Idea/Enduring Understanding: Writers use techniques to elicit an intended response from the reader. Guiding Questions: Knowledge and Skills Why is it important to consider the way information is presented? What is the relationship between organization and meaning? How can context help me identify the meaning of an unknown word? What techniques do writers and speakers us to persuade others? TEKS Integrations 7.2-Reading/Vocabulary Development. Students understand new vocabulary and use it when reading and writing. 7.2.B-use context (within a sentence and in larger sections of text) to determine or clarify the meaning of unfamiliar or ambiguous words; Specificities & Examples Prefixes: ambiRoots: macro, tent Suffixes: -rupt Commonly confused words: weather/whether/rather Question Stems 7.2(B) In paragraph __, what does the word __ mean? What (or which) words in paragraph __ help the reader understand what __ means? 7.9-Reading/Comprehension of Question Stems 7.9(A) Informational Text/Culture and History. What is the difference between the theme in Students analyze, make inferences and the story _____ and the author's purpose in draw conclusions about the author's the article _____? purpose in cultural, historical, and contemporary contexts and provide Compare the author's purpose in _____ with evidence from the text to support their the overall theme in _____. understanding. 7.9.A-explain the difference between the theme of a literary work and the author's purpose in an expository text. 7.10-Reading/Comprehension of Question Stems 7.10(A) 7.Fig.19.E - summarize, paraphrase, Informational Text/Expository Text. and synthesize texts in ways that maintain What important information is missing in the Students analyze, make inferences and meaning and logical order within a text and summary of the article? draw conclusions about expository text and across texts provide evidence from text to support their What misleading information is in the ELPS.4.B - recognize directionality of understanding. summary of _____? 7.10.A-evaluate a summary of the original English reading such as left to right and top to bottom; text for accuracy of the main ideas, In comparing the summary and the original supporting details, and overall meaning; article, how does the meaning change in the 7.10.B-distinguish factual claims from summary? commonplace assertions and opinions; Question Stems 7.10(B) 7.10.C-use different organizational patterns What of the following lines from the article is as guides for summarizing and forming an an opinion? overview of different kinds of expository HISD (2013-2014) HISD TEKS/SEs Road Map ELAR 3rd Six Weeks text; and 7.Fig.19-Reading/Comprehension Skills. Students use a flexible range of metacognitive reading skills in both assigned and independent reading to understand an author's message. Students will continue to apply earlier standards with greater depth in increasingly more complex texts as they become self-directed, critical readers. The student is expected to: Which of the following lines from the article is a fact? An opinion expressed in this information is... An assertion not based on facts in this information is... Question Stems 7.10(C) How does the author's organization of ideas help the reader to summarize this article? What is a summary of this article? Which of the following is the best summary of this information? Why? An accurate overview of this information would be -A guide to developing a summary of this information would be the author's organization of -- 7.11-Reading/Comprehension of Informational Text/Persuasive Text. Students analyze, make inferences and draw conclusions about persuasive text and provide evidence from text to support their analysis. 7.11.A-analyze the structure of the central argument in contemporary policy speeches (e.g., argument by cause and effect, analogy, authority) and identify the different types of evidence used to support the argument; and 7.11.B-identify such rhetorical fallacies as ad hominem, exaggeration, stereotyping, or categorical claims in persuasive texts. Question Stems 7.11(A) How does the author/speaker structure the central argument in this speech? How does the author/speaker present the central argument in this speech? What evidence does the author/speaker of this speech use to support his/her argument? Question Stems 7.11(B) What is a fallacy in the argument presented in this article? What is an exaggeration in this advertisement? How does the author of this advertisement try to appeal to a reader personally without logic? 7.13-Reading/Media Literacy. Students use Question Stems 7.13(A) 7.Fig.19.F - make connections between comprehension skills to analyze how and across texts, including other media How does the narrator of _____ feel about words, images, graphics, and sounds work (e.g., film, play), and provide textual _____? together in various forms to impact evidence. meaning. Students will continue to apply What can the reader tell about the person in Note: earlier standards with greater depth in this story in the newspaper? Use examples of speeches to show increasingly more complex texts. persuasive techniques (i.e. gesture, 7.13.A-interpret both explicit and implicit inflection, etc.) messages in various forms of media; Question Stems 7.13(C) 7.13.C-evaluate various ways media Was the news reporter's strategy for using a influences and informs audiences; and story line from a famous novel successful in 7.13.D-assess the correct level of formality positively influencing the audience? and tone for successful participation in various digital media. What technique did the television announcer use to impact the audience with his/her point of view? 7.17-Writing/Expository and Procedural Persuasive Essay in letter format, 7.14 - Writing/Writing Process. Students Texts. Students write expository and including counter-argument use elements of the writing process procedural or work-related texts to (planning, drafting, revising, editing, and communicate ideas and information to NOTE: Encourage students to find an publishing) to compose text. specific audiences for specific purposes. authentic persuasive topic and audience for 7.14.A - plan a first draft by selecting a Students are expected to: the letter. HISD (2013-2014) HISD TEKS/SEs Road Map ELAR 3rd Six Weeks 7.17.B-write a letter that reflects an genre appropriate for conveying the opinion, registers a complaint, or requests intended meaning to an audience, information in a business or friendly determining appropriate topics through a context; range of strategies (e.g., discussion, 7.18-Writing/Persuasive Texts. Students background reading, personal interests, write persuasive texts to influence the interviews), and developing a thesis or attitudes or actions of a specific audience controlling idea; on specific issues. Students are expected 7.14.B - develop drafts by choosing an to write a persuasive essay to the appropriate organizational strategy (e.g., appropriate audience that: sequence of events, cause-effect, 7.18.A-establishes a clear thesis or compare-contrast) and building on ideas to position; create a focused, organized, and coherent 7.18.B-considers and responds to the piece of writing; views of others and anticipates and 7.14.C - revise drafts to ensure precise answers reader concerns and counterword choice and vivid images; consistent arguments; and 7.18.C-includes evidence that is logically point of view; use of simple, compound, organized to support the author's viewpoint and complex sentences; internal and external coherence; and the use of and that differentiates between fact and effective transitions after rethinking how opinion. well questions of purpose, audience, and genre have been addressed; 7.19-Oral and Written Conventions/Conventions. Students understand the function of and use the conventions of academic language when speaking and writing. Students will continue to apply earlier standards with greater complexity. Students are expected to: 7.19.A-identify, use, and understand the function of the following parts of speech in the context of reading, writing, and speaking: 7.19.A.vii-subordinating conjunctions (e.g., because, since); 7.19.B-write complex sentences and differentiate between main versus subordinate clauses; and HISD (2013-2014) HISD TEKS/SEs Road Map ELAR 3rd Six Weeks 7.26-Listening and Speaking/Listening. ELPS.1.B - monitor oral and written Students will use comprehension skills to language production and employ selflisten attentively to others in formal and corrective techniques or other resources informal settings. Students will continue to apply earlier standards with greater complexity. Students are expected to: 7.26.A-listen to and interpret a speaker's purpose by explaining the content, evaluating the delivery of the presentation, and asking questions or making comments about the evidence that supports a speaker's claims; HISD (2013-2014) Teacher Note: focus on "asking questions or making comments about the evidence that supports a speaker's claims" HISD TEKS/SEs Road Map ELAR 3rd Six Weeks Bundle 2 (2 weeks)- December 9-December 20 Literary Text - Fiction ~ Reading Genre Focus: Fiction, Poetry, and Drama Writing Genre Focus: Literary Response Big Idea/Enduring Understanding: Strong readers use textual evidence to support inferences and interpretations about a text. Guiding Questions: How do your personal and cultural experiences affect your interpretation of literary works? How do an author’s use of style, tone and mood affect the reader’s experience? What are the elements of style? What textual evidence supports my interpretation of a text? Knowledge and Skills TEKS Integrations 7.2.A-determine the meaning of gradelevel academic English words derived from Latin, Greek, or other linguistic roots and affixes; 7.2-Reading/Vocabulary Development. Students understand new vocabulary and use it when reading and writing. 7.4-Reading/Comprehension of Literary Text/Poetry. Students understand, make inferences and draw conclusions about the structure and elements of poetry and provide evidence from text to support their understanding. 7.4.A-analyze the importance of graphical elements (e.g., capital letters, line length, word position) on the meaning of a poem. 7.5-Reading/Comprehension of Literary Text/Drama. Students understand, make inferences and draw conclusions about the structure and elements of drama and provide evidence from text to support their understanding. 7.5.A-explain a playwright's use of dialogue and stage directions. Specificities & Examples Question Stems 7.2(A) What is the root word for the word in paragraph __ help the reader understand what __ means? Question Stems 7.4(A) Why is line __ presented differently by the author of this poem? How does the poet demonstrate to the reader that lines __ through __ are important? Question Stems 7.5(A) In paragraph _____ of this play, how does the playwright use the dialogue of _____ to enhance the reader's understanding? How will the overall message of the play change if the playwright's specific stage directions are not followed? 7.8-Reading/Comprehension of Literary Question Stems 7.8(A) ELPS.4.C - develop basic sight Text/Sensory Language. Students vocabulary, derive meaning of When the author used the words "_____", understand, make inferences and draw environmental print, and comprehend what was the intended impact on the conclusions about how an author's English vocabulary and language reader? sensory language creates imagery in structures used routinely in written literary text and provide evidence from text classroom materials; What did the author mean by the phrase, to support their understanding. "_____" in paragraph _____? 7.Fig.19.C - reflect on understanding to 7.8.A-determine the figurative meaning of phrases and analyze how an author's use monitor comprehension (e.g., summarizing What does the phrase _____ mean in this of language creates imagery, appeals to and synthesizing; making textual, personal, passage? and world connections; creating sensory the senses, and suggests mood. Question Stems 7.Fig 19(C) 7.Fig.19-Reading/Comprehension Skills. images) What part of this story should I reread to Students use a flexible range of 7.Fig.19.D - make complex inferences HISD (2013-2014) HISD TEKS/SEs Road Map ELAR 3rd Six Weeks metacognitive reading skills in both about text and use textual evidence to assigned and independent reading to support understanding understand an author's message. Students will continue to apply earlier standards with greater depth in increasingly more complex texts as they become selfdirected, critical readers. The student is expected to: gain a deeper understanding in this informative article? What images are created in my mind when I read paragraph _____? Question Stems 7.Fig 19(D) What can you conclude about _____? (Fiction & literary NF) What did ____ (character) mean when he/she said, "_____"? (Drama) An important inference that the reader can make about _____ is... (Fiction & literary NF) What inference can be made from this information? 7.17-Writing/Expository and Procedural Texts. Students write expository and procedural or work-related texts to communicate ideas and information to specific audiences for specific purposes. Students are expected to: 7.17.C-write responses to literary or expository texts that demonstrate the writing skills for multi-paragraph essays and provide sustained evidence from the text using quotations when appropriate; and 7.19-Oral and Written Conventions/Conventions. Students understand the function of and use the conventions of academic language when speaking and writing. Students will continue to apply earlier standards with greater complexity. Students are expected to: 7.19.C-use a variety of complete sentences (e.g., simple, compound, complex) that include properly placed modifiers, correctly identified antecedents, parallel structures, and consistent tenses. 7.20-Oral and Written Conventions/Handwriting, Capitalization, and Punctuation. Students write legibly and use appropriate capitalization and punctuation conventions in their compositions. Students are expected to: 7.20.B-recognize and use punctuation marks including: 7.20.B.ii-semicolons, colons, and hyphens. 7.26-Listening and Speaking/Listening. Students will use comprehension skills to listen attentively to others in formal and informal settings. Students will continue to apply earlier standards with greater complexity. Students are expected to: 7.26.B-follow and give complex oral instructions to perform specific tasks, answer questions, or solve problems; and HISD (2013-2014) HISD TEKS/SEs Road Map ELAR 3rd Six Weeks Bundle 3 (2 weeks) - January 7- January 17 Exploring Ideas Across Genres ~ Reading Genre Focus: Emphasize Genres indicated by assessment data Writing Genre Focus: Multi-Paragraph Essay (Revisit expository essay and personal narrative as needed for STAAR) Big Idea/Enduring Understanding Writers share what they know from experiences in narrative and expository forms. Guiding Questions : Knowledge and Skills 7.2-Reading/Vocabulary Development. Students understand new vocabulary and use it when reading and writing. 7.2.A-determine the meaning of gradelevel academic English words derived from Latin, Greek, or other linguistic roots and affixes; 7.2.B-use context (within a sentence and in larger sections of text) to determine or clarify the meaning of unfamiliar or ambiguous words; 7.2.E-use a dictionary, a glossary, or a thesaurus (printed or electronic) to determine the meanings, syllabication, pronunciations, alternate word choices, and parts of speech of words. What kinds of information are better suited for narrative vs. expository? How does the form of the writing shape the effect it has on the reader? How can a writer’s use of conventions influence the effectiveness of the writing? TEKS Integrations ELPS.4.A - learn relationships between sounds and letters of the English language and decode (sound out) words using a combination of skills such as recognizing sound-letter relationships and identifying cognates, affixes, roots, and base words; Specificities & Examples Question Stems 7.2(A) What is the root word for the word in paragraph __ help the reader understand what __ means? Question Stems 7.2(B) What (or which) words in paragraph __ help the reader understand what __ means? Question Stems 7.2(E) Read the dictionary entry for the word __. Which definition represents the meaning of the word __ as used on paragrpah __? (Dictionary entry with four definitions is shown and students must use context clues to determine the meaning of the word as it is used in the passage.) 7.3-Reading/Comprehension of Literary Text/Theme and Genre. Students analyze, make inferences and draw conclusions about theme and genre in different cultural, historical, and contemporary contexts and provide evidence from the text to support their understanding. 7.3.A-describe multiple themes in a work of fiction; 7.3.B-describe conventions in myths and epic tales (e.g., extended simile, the quest, the hero's tasks, circle stories); and 7.3.C-analyze how place and time influence the theme or message of a literary work. Question Stems 7.3(A) A description of a theme in this story is__? Descriptions of two themes in this story are __amd __. The two themes in the story are __ and __. This story has mulitple themes including __ and__. HISD (2013-2014) HISD TEKS/SEs Road Map ELAR 3rd Six Weeks 7.6-Reading/Comprehension of Literary Text/Fiction. Students understand, make inferences and draw conclusions about the structure and elements of fiction and provide evidence from text to support their understanding. Students are expected to: 7.6.B-analyze the development of the plot through the internal and external responses of the characters, including their motivations and conflicts; and Question Stems 7.6(B) Why did _____ respond to _____ the way he/she did in paragraph _____? What does paragraph _____ demonstrate about the internal conflict in _____? What is paragraph _____ important in understanding the motives of _____? What is inferred about _____'s thinking in this selection? 7.8-Reading/Comprehension of Literary Text/Sensory Language. Students understand, make inferences and draw conclusions about how an author's sensory language creates imagery in literary text and provide evidence from text to support their understanding. 7.8.A-determine the figurative meaning of phrases and analyze how an author's use of language creates imagery, appeals to the senses, and suggests mood. Question Stems 7.8(A) When the author used the words "_____", what was the intended impact on the reader? What did the author mean by the phrase, "_____" in paragraph _____? What mood was the author trying to create by the wording of the phrase, "_____"? What does the phrase "_____" mean in this passage? 7.9-Reading/Comprehension of Informational Text/Culture and History. Students analyze, make inferences and draw conclusions about the author's purpose in cultural, historical, and contemporary contexts and provide evidence from the text to support their understanding. 7.9.A-explain the difference between the theme of a literary work and the author's purpose in an expository text. 7.10-Reading/Comprehension of Informational Text/Expository Text. Students analyze, make inferences and draw conclusions about expository text and provide evidence from text to support their understanding. 7.10.C-use different organizational patterns as guides for summarizing and forming an overview of different kinds of expository text; and 7.10.D-synthesize and make logical connections between ideas within a text and across two or three texts representing similar or different genres, and support those findings with textual evidence. 7.Fig.19-Reading/Comprehension Skills. Students use a flexible range of metacognitive reading skills in both assigned and independent reading to understand an author's message. Students will continue to apply earlier standards with greater depth in increasingly more complex texts as they become self-directed, critical readers. The student is expected to: Question Stems 7.9(A) What is the difference between the theme in the story _____ and the author's purpose in the article _____? Compare the author's purpose in _____ with the overall theme in _____. 7.Fig.19 - Reading/Comprehension Skills. Students use a flexible range of metacognitive reading skills in both assigned and independent reading to understand an author's message. Students will continue to apply earlier standards with greater depth in increasingly more complex texts as they become self-directed, critical readers. The student is expected to: 7.Fig.19.D - make complex inferences about text and use textual evidence to support understanding 7.Fig.19.E - summarize, paraphrase, and synthesize texts in ways that maintain meaning and logical order within a text and across texts Question Stems 7.10(C) How does the author's organization of ideas help the reader to summarize this article? What is a summary of this article? Which of the following is the best summary of this information? Why? An accurate overview of this information would be -A guide to developing a summary of this information would be the author's organization of -Question Stems 7.Fig 19(D) What inference can be made from this information? What is a conclusion the reader can draw about _____? Which sentence in this informative article (textual evidence) provides the proof for the inference _____? HISD (2013-2014)