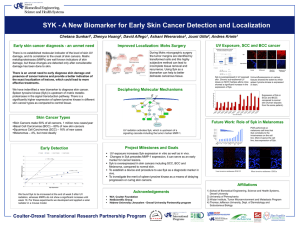
O25 Treatment of Experimental Autoimmune Vasculitis with a SYK
advertisement
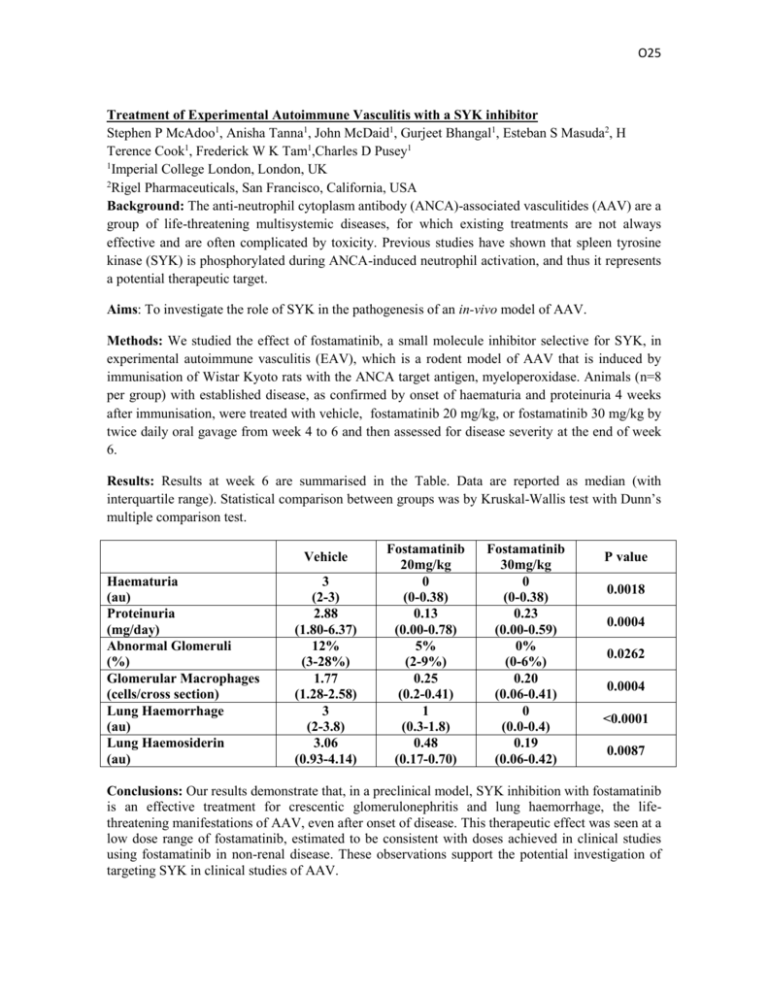
O25 Treatment of Experimental Autoimmune Vasculitis with a SYK inhibitor Stephen P McAdoo1, Anisha Tanna1, John McDaid1, Gurjeet Bhangal1, Esteban S Masuda2, H Terence Cook1, Frederick W K Tam1,Charles D Pusey1 1 Imperial College London, London, UK 2 Rigel Pharmaceuticals, San Francisco, California, USA Background: The anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitides (AAV) are a group of life-threatening multisystemic diseases, for which existing treatments are not always effective and are often complicated by toxicity. Previous studies have shown that spleen tyrosine kinase (SYK) is phosphorylated during ANCA-induced neutrophil activation, and thus it represents a potential therapeutic target. Aims: To investigate the role of SYK in the pathogenesis of an in-vivo model of AAV. Methods: We studied the effect of fostamatinib, a small molecule inhibitor selective for SYK, in experimental autoimmune vasculitis (EAV), which is a rodent model of AAV that is induced by immunisation of Wistar Kyoto rats with the ANCA target antigen, myeloperoxidase. Animals (n=8 per group) with established disease, as confirmed by onset of haematuria and proteinuria 4 weeks after immunisation, were treated with vehicle, fostamatinib 20 mg/kg, or fostamatinib 30 mg/kg by twice daily oral gavage from week 4 to 6 and then assessed for disease severity at the end of week 6. Results: Results at week 6 are summarised in the Table. Data are reported as median (with interquartile range). Statistical comparison between groups was by Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparison test. Vehicle Haematuria (au) Proteinuria (mg/day) Abnormal Glomeruli (%) Glomerular Macrophages (cells/cross section) Lung Haemorrhage (au) Lung Haemosiderin (au) 3 (2-3) 2.88 (1.80-6.37) 12% (3-28%) 1.77 (1.28-2.58) 3 (2-3.8) 3.06 (0.93-4.14) Fostamatinib 20mg/kg 0 (0-0.38) 0.13 (0.00-0.78) 5% (2-9%) 0.25 (0.2-0.41) 1 (0.3-1.8) 0.48 (0.17-0.70) Fostamatinib 30mg/kg 0 (0-0.38) 0.23 (0.00-0.59) 0% (0-6%) 0.20 (0.06-0.41) 0 (0.0-0.4) 0.19 (0.06-0.42) P value 0.0018 0.0004 0.0262 0.0004 <0.0001 0.0087 Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that, in a preclinical model, SYK inhibition with fostamatinib is an effective treatment for crescentic glomerulonephritis and lung haemorrhage, the lifethreatening manifestations of AAV, even after onset of disease. This therapeutic effect was seen at a low dose range of fostamatinib, estimated to be consistent with doses achieved in clinical studies using fostamatinib in non-renal disease. These observations support the potential investigation of targeting SYK in clinical studies of AAV.