Solid State Physics (MS613) Homework #4
advertisement

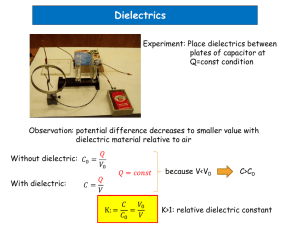
2014-11-21 due date: 2014-12-02 Solid State Physics (MS613) Homework #4 Research Paper Please submit a research paper prepared as follows. Title: Current status and future of multi-ferroic materials length: 10 pages of A4 (minimum) font size ; 10 word-processor s/w : Word due: Dec 11 1. (a) Given that the atomic polarizabilities of K+ and Cl- ions measured at optical frequencies are 1.48×10-40 Fm2 and 3.29×10-40 Fm2, respectively, and that the molar volume of KCl is 3.71×10-5m3, use the Clausius-Mossotti formula to determine the optical dielectric constant εopt for KCl. (b) Assuming that the atomic polarizabilities are the same in the static case as at optical frequencies, use the data given in part (a) to determine the amplitude of the displacements of the ions in KCl when placed in a static electric field of 105Vm-1. (The static dielectric constant of KCl is 4.84) 2. (a) Estimate the dipole moment of a hydrogen chloride molecule assuming that there is a complete transfer of the electron from the hydrogen atom to the chlorine atom. (The separation of the hydrogen and chlorine nuclei is 0.128 nm.) (b) Given that the measured dipole moment of a hydrogen chloride molecule is 3.3 10-30 Cm, determine the actual amount of charge transferred from the hydrogen to the chlorine atom. 3. KH2PO4 is a colorless crystalline material which has a relative dielectric constant at low frequencies of 100. On the assumption that the low-frequency dielectric constant is due predominantly to the vibration of the H+ ions (of which there are 2×1028 per cubic meter) about their equilibrium positions, estimate the frequency at which the peak of the dielectric absorption will occur. 4. The dielectric constant of NaCl is 5.9 at low frequencies, but the effective dielectric constant at the frequencies of visible light is only 2.25. What are the relative contributions of electronic and ionic polarization to dc polarization?