Unit 1 - Curriculum Team News
advertisement

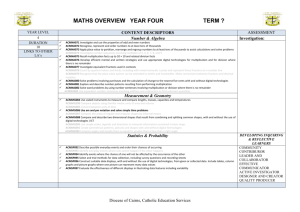
SCIENCE OVERVIEW, TERM ONE UNIT TITLE YEAR ONE: How would you design and create a home to withstand a storm? UNIT OUTLINE Students are asked to answer the unit question: How would you design and create a home to withstand a storm? CONTENT DESCRIPTORS Science Understanding Earth and Space: ASSESSMENT (A) Assessment For Learning Observational checklist (see assessment appendix). Observable changes occur in the sky and Assessment As Learning landscape. Anecdotal notes of discussions among students This unit relates to students’ throughout unit and in the planning stages of their everyday lives and applies their model house creations. new learnt knowledge in a Science as Human Endeavour creative, real life context. It Assessment of Learningprovides students with Nature and Development of Science: Fair Test Check List (see assessment appendix). opportunities to explore the way Science involves asking questions about, and that Science is used in the real describing changes in, objects and events. Criteria Sheet: Warning, Warning, Warning! world. This is achieved through an excursion to the Meteorological Science Inquiry Skills Office and a visit from a Questioning and Predicting: community member in the building industry. This is an Respond to and pose questions, and make important component in predictions about familiar objects and events. developing students’ scientific literacy as they come to understand and appreciate the way which Science influences society. Diocese of Cairns, Catholic Education Services LINKS TO OTHER LA’S Technology English- Literacy DEVELOPING INQUIRING AND REFLECTIVE LEARNERS Community Contributor Effective Communicator Designer and Creator Leader and Collaborator Active Investigator Quality Producer Diocese of Cairns, Catholic Education Services CROSS CURRICULA PRIORITIES Catholic Ethos The overarching purpose of Catholic schools of the past, as well as the future, is to bring the Good News of Jesus to all who hear it. In the midst of a world of educational, social and economic change the focus on the holistic growth of the individual remains the surest way catholic school can prepare students for the uncertainties of the future. Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Education Asian Education Active engagement of inclusive curriculum practices which reflect Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander perspectives, knowledge, histories, cultures and spirituality. A genuine commitment to Reconciliation, guided by principles of personal dignity, social justice and equity, which reflects the Gospel message and the mission of the Church. This perspective requires students to develop skills, knowledge and understandings related to Asia and Australia’s engagement with Asia. Social Emotional Learning Inclusive Education The curriculum provides opportunities to know, understand and be able to: 1. Understand ‘Asia’ 2. Develop informed attitudes and values Defining Features, Diocese of Cairns The curriculum provides opportunities to value and 3. Know about contemporary and traditional The curriculum provides opportunities for young respect: Asia people to connect their curriculum experiences to a 1. traditional knowledge and practices 4. Connect Australia and Asia living Christian faith. 2. culture and natural heritage 5. Communicate effectively with people of the 3. spirituality Asian region both within and outside and to critically examine and/or challenge: Australia confidently 1. social constructs 2. prejudice and racism Sustainability Education Access to current information about environmental Social and emotional competencies are integral to It is by the quality of interactions and relationships issues and promotion of a reflective and responsive academic and work success and are the basis of that all students learn to understand and appreciate attitude towards stewardship of the gifts of creation. resilience, relational quality and social capital. difference, to value diversity and learn to respond with dignity and respect to all through mutually The curriculum provides opportunities to reflect The curriculum provides opportunities to develop: enriching interactions. upon: 1. Self Awareness 1. the gift of creation 2. Social Awareness The curriculum provides equitable access for and/or 2. an attitude of responsible stewardship 3. Responsible Decision Making positive interactions with students from different and to critically examine and/or challenge: 4. Self-Management backgrounds and with diverse needs and abilities. 1. the impact of human interaction with the 5. Relationship Management natural, built and social environment 2. current environmental issues Diocese of Cairns, Catholic Education Services GENERAL CAPABILITIES Literacy Students become literate as they develop the skills to learn and communicate confidently at school and to become effective individuals, community members, workers and citizens. These skills include listening, reading, viewing, writing, speaking and creating print, visual and digital materials accurately and purposefully within and across all learning areas. Students become numerate as they develop the capacity to recognise and understand the role of mathematics in the world around them and the confidence, willingness and ability to apply mathematics to their lives in ways that are constructive and meaningful. Literacy involves students engaging with the language and literacy demands of each learning area. As they become literate students learn to: interpret, analyse, evaluate, respond to and construct increasingly complex texts (Comprehension and composition) understand, use, write and produce different types of text (Texts) manage and produce grammatical patterns and structures in texts (Grammar) make appropriate word selections and decode and comprehend new (basic, specialised and technical) vocabulary (Vocabulary) use and produce a range of visual materials to learn and demonstrate learning (Visual information) As they become numerate, students develop and use mathematical skills related to: Calculation and number Patterns and relationships Proportional reasoning Spatial reasoning Statistical literacy Measurement. Critical and Creative Thinking Information and Communication Technology Numeracy Students develop ICT competence when they learn to: Investigate with ICT: using ICT to plan and refine information searches; to locate and access different types of data and information and to verify the integrity of data when investigating questions, topics or problems Create with ICT: using ICT to generate ideas, plans, processes and products to create solutions to challenges or learning area tasks Communicate with ICT: using ICT to communicate ideas and information with others adhering to social protocols appropriate to the communicative context (purpose, audience and technology) Operate ICT: applying technical knowledge and skills to use ICT efficiently and to manage data and information when and as needed Apply appropriate social and ethical protocols and practices to operate and manage ICT. Students develop critical and creative thinking as they learn to generate and evaluate knowledge, ideas and possibilities, and use them when seeking new pathways or solutions. In learning to think broadly and deeply students learn to use reason and imagination to direct their thinking for different purposes. In the context of schooling, critical and creative thinking are integral to activities that require reason, logic, imagination and innovation. As they develop critical and creative thinking students learn to: Diocese of Cairns, Catholic Education Services pose insightful and purposeful questions apply logic and strategies to uncover meaning and make reasoned judgments think beyond the immediate situation to consider the ‘big picture’ before focussing on the detail suspend judgment about a situation to consider alternative pathways reflect on thinking, actions and processes generate and develop ideas and possibilities analyse information logically and make reasoned judgments evaluate ideas and create solutions and draw conclusions assess the feasibility, possible risks and benefits in the implementation of their ideas transfer their knowledge to new situations Ethical Behaviour Students develop ethical behaviour as they learn to understand and act in accordance with ethical principles. This includes understanding the role of ethical principles, values and virtues in human life; acting with moral integrity; acting with regard for others; and having a desire and capacity to work for the common good. As they develop ethical behaviour students learn to: recognise that everyday life involves consideration of competing values, rights, interests and social norms identify and investigate moral dimensions in issues develop an increasingly complex understanding of ethical concepts, the status of moral knowledge and accepted values and ethical principles explore questions such as: o What is the meaning of right and wrong and can I be sure that I am right? o Why should I act morally? o Is it ever morally justifiable to lie? o What role should intuition, reason, emotion, duty or self-interest have in ethical decision making? Personal and Social Competence Students develop personal and social competence as they learn to understand and manage themselves, their relationships, lives, work and learning more effectively. This involves recognising and regulating their emotions, developing concern for and understanding of others, establishing positive relationships, making responsible decisions, working effectively in teams and handling challenging situations constructively. As they develop personal and social competence students learn to: recognise and understand their own emotions, values and strengths, have a realistic assessment of their own abilities and a well-grounded sense of self-esteem and selfconfidence (Self-awareness) manage their emotions and behaviour, persevere in overcoming obstacles, set personal and academic goals, develop self-discipline , resilience, adaptability and initiative (Self-management) perceive and understand other people’s emotions and viewpoints, show understanding and empathy for others, identify the strengths of team members, define and accept individual and group roles and responsibilities, be of service to others (Social awareness) form positive relationships, manage and influence the emotions and moods of others, cooperate and communicate effectively with others, work in teams, build leadership skills, make decisions, resolve conflict and resist inappropriate social pressure (Social management). Diocese of Cairns, Catholic Education Services Intercultural Understanding Students develop intercultural understanding as they learn to understand themselves in relation to others. This involves students valuing their own cultures and beliefs and those of others, and engaging with people of diverse cultures in ways that recognise commonalities and differences, create connections and cultivate respect between people. As they develop intercultural understanding students learn to: identify increasingly sophisticated characteristics of their own cultures and the cultures of others recognise that their own and others’ behaviours, attitudes and values are influenced by their languages and cultures consider what it might be like to ‘walk in another’s shoes’ compare the experiences of others with their own, looking for commonalities and differences between their lives and seeking to understand these reflect on how intercultural encounters have affected their thoughts, feelings and actions accept that there are different ways of seeing the world and live with that diversity stand between cultures to facilitate understanding take responsibility for developing and improving relationships between people from different cultures in Australia and in the wider world contribute to and benefit from reconciliation between Indigenous and non-Indigenous Australians. WEEKLY PLANNER WEEK 1 2 3 4 5 6 GENERAL CAPABILITIES 7 8 9 10 CROSS CURRICULAR PRIORITIES CE SEL IE Engage Explore Explain ENGAGE Elaborate Evaluate RESOURCES Student Resources: Newspaper Articles Lesson 1: Photos Brainstorm what students know about the weather and seasons using a KWL chart or Y chart. Begin a pictures graffiti wall by recording the students’ responses. Teacher Resources: - Paper for KWL/Y Chart Lesson 2: - Pens Elicit questions about what we need to learn about weather e.g. What makes a storm? Why does it rain - Pictures/photos of weather so much? Why doesn’t it snow here? - Newspaper - Learning Space – Graffiti Wall Students are asked to bring in pictures, newspaper articles, photos etc of weather and seasons. These are to be added to the graffiti wall. Factual texts: Stormy weather Pike, Katy (Go facts readers level 3 series, Lesson 3: Blake Publishing, 2004, 12pp.) Draw/paint and label pictures of the sky at night and during the day. Use topic sight words e.g sky, moon, ISBN: 1865093017 available as a big book stars, rain, sun, cloud, day and night. Also add these words to the graffiti wall. – ISBN: 1865093033 Diocese of Cairns, Catholic Education Services DIFFERENTIATION ASSESSMENT OPPORTUNITIES Assessment For Learning Observational checklist SCIENTIFIC LANGUAGE sky, moon, stars, rain, sun, cloud, day and night, graffiti, weather, seasons, storm, snow, record. REFLECTION WEEK 1 2 3 4 5 6 GENERAL CAPABILITIES 7 8 9 10 CROSS CURRICULAR PRIORITIES CE SEL IE Engage Explore Explain EXPLORE Elaborate Evaluate RESOURCES This unit requires a student to be a ‘Weather Watcher.’ This requires the student or pairs to go and Student Resources: photograph the sky and landscape (ongoing/daily experience). Teacher Resources: Lesson 4: - Camera Begin a weather table as a whole class activity. Headings for table may include- What the sky looks like. - Weather table How is the land affected by the wind and rain? Weather forecast and Science Words (see unit resources). - Paper for concept map Diocese of Cairns, Catholic Education Services This weather table is added to the graffiti wall. - Pens Computer pictures) printer (to print Lesson 5: In pairs or as rotational activities, students play the interactive weather games on Scootle to consolidate Narrative texts: Seasons their learning e.g. Weather- Early Learning. Burningham, John (Red Fox, 1993, 40pp) ISBN: 0099899701 Lesson 6: Students take an excursion to the Meteorological Office (Cairns Airport- General Aviation). Meteorologist An account of the changes in landscape and weather that occur through the speaks to students specifically about wind and rain experienced in the local Cairns area. seasons. Each of the seasons is introduced with the same scene from a Lesson 7: different stage of the yearly cycle of Introduce unit question: How would you design and create a home to withstand a storm? Students create a concept map about their knowledge of storms. Students then brainstorm questions to nature. further their knowledge about storms. Questions may include: What can we build a house out of? What does a house look like? What materials are weather proof? How strong are winds during a storm? What DIFFERENTIATION does the sky look like when there is a storm? How much rain falls during a storm? Where does the water go after a storm? ASSESSMENT OPPORTUNITIES SCIENTIFIC LANGUAGE Weather, day, night, photograph, table, heading, watcher, ongoing, daily, experience, sky, land, observation, affected, wind, rain, forecast, interactive, meteorological, meteorologist, cairns, floods, cyclones, dry season, wet season, rainfall, withstand, home, storm, concept map, knowledge, brainstorm, materials, weather proof, strong winds, water cycle, moon, stars, rain, sun, cloud, graffiti, seasons, snow, record. REFLECTION Diocese of Cairns, Catholic Education Services WEEK 1 2 3 4 5 6 GENERAL CAPABILITIES 7 8 9 10 CROSS CURRICULAR PRIORITIES CE SEL IE Engage Explore Explain EXPLAIN Lesson 8: Fair Tests Discuss- What is a fair test? What are the variables of our test? All fair tests will require the following materials: - coat hangers - paddle pop sticks (wooden home) - small brick or stone - cardboard (fibro home) - aluminium foil (tin home) - cloth (tent) - Hairdryer - Leaf blower - String - Water - Watering can - Spray bottle - Bucket Diocese of Cairns, Catholic Education Services Elaborate Evaluate RESOURCES Student Resources: Teacher Resources: Fair Test - coat hangers - paddle pop sticks - small brick or stone - cardboard - aluminium foil - cloth - Hairdryer - Leaf blower - String - Water - Watering can - Spray bottle - Bucket - Observation table resources) (see unit DIFFERENTIATION Fair Test- Wind In groups attach materials to a coat hanger with string. Hang coat hanger outside. Record observationsWhich material moved in the wind? ASSESSMENT OPPORTUNITIES Repeat process with hair dryer and leaf blower. Record observations discussing which material would be best to build a house with withstand gale force winds (see unit resources). Fair Test- Rain In groups and using the same materials on the coat hanger, test the effect of rain (see unit resources). Assessment of Learning: Fair Test Check List Fair Test- Wind and Rain Using the same materials on the coat hanger, test wind and rain combining the wind (hair dryer and leaf blower) and rain (bucket, watering can and spray bottle) tools. Record observations and discuss findings (see unit resources). SCIENTIFIC LANGUAGE strong wind, heavy rain, fair test, variable, material, record, observations, movement, explain, weather, day, night, photograph, table, heading, watcher, ongoing, daily, experience, sky, land, affected, wind, rain, forecast, interactive, meteorological, meteorologist, cairns, floods, cyclones, dry season, wet season, rainfall, withstand, home, storm, concept map, knowledge, brainstorm, materials, weather proof, strong winds, watercycle, hair dryer, leaf blower, bucket, watering can, spray bottle. REFLECTION Diocese of Cairns, Catholic Education Services WEEK 1 2 3 4 5 6 GENERAL CAPABILITIES 7 8 9 10 CROSS CURRICULAR PRIORITIES CE SEL IE Engage Explore Explain ELABORATE Elaborate Evaluate RESOURCES Student Resources: Teacher Resources: - Glue - Sticky tape - Paint - Scissors - Shoe boxes Lesson 9: - Card A local builder visits the class to speak about building a house to withstand gale force wind and rain. - Card rolls - Paper Use the information gained from the fair tests to design and create a house that withstands strong gale - Tissue paper force wind and rain. - Foil - Paddle pop sticks - Fabric Diocese of Cairns, Catholic Education Services DIFFERENTIATION ASSESSMENT OPPORTUNITIES Assessment As Learning Anecdotal notes SCIENTIFIC LANGUAGE Builder, gale force winds, rain, information, fair tests, design, create, withstand, strong wind, heavy rain, , variable, material, record, observations, movement, weather, day, night, photograph, table, heading, watcher, ongoing, daily, experience, sky, land, affected, wind, rain, forecast, interactive, meteorological, meteorologist, cairns, floods, cyclones, dry season, wet season, rainfall, withstand, home, storm, concept map, knowledge, brainstorm, materials, weather proof, strong winds, watercycle, hair dryer, leaf blower, bucket, watering can, spray bottle. REFLECTION Diocese of Cairns, Catholic Education Services WEEK 1 2 3 4 5 6 GENERAL CAPABILITIES 7 8 9 10 CROSS CURRICULAR PRIORITIES CE SEL IE Engage Explore Explain EVALUATE Elaborate Evaluate RESOURCES Student Resources: Criteria Sheet Teacher Resources: - Design for model house. - Model house for oral presentation - Criteria Sheet - Observational Check List to be Lesson 10: used throughout the unit as Students orally present their design and model of house to a known audience. Students reflect on the ongoing assessment effectiveness of their design. DIFFERENTIATION ASSESSMENT OPPORTUNITIES Assessment of Learning Criteria Sheet: Warning, Warning, Warning! Diocese of Cairns, Catholic Education Services SCIENTIFIC LANGUAGE Orally, present, design, model, known, audience, reflect, effectiveness, Builder, gale force winds, rain, information, fair tests, create, withstand, strong wind, heavy rain, , variable, material, record, observations, movement, weather, day, night, photograph, table, heading, watcher, ongoing, daily, experience, sky, land, affected, wind, rain, forecast, interactive, meteorological, meteorologist, cairns, floods, cyclones, dry season, wet season, rainfall, withstand, home, storm, concept map, knowledge, brainstorm, materials, weather proof, strong winds, watercycle, hair dryer, leaf blower, bucket, watering can, spray bottle. REFLECTION Diocese of Cairns, Catholic Education Services Resources for Unit What I Know What I Want to Learn Diocese of Cairns, Catholic Education Services What I Have Learnt What does weather What does weather Look like Sound like What does weather Diocese of Cairns, Catholic Education Services Feel like Weekly Weather Watcher Table Date Range What the sky looks like? How is the land affected by the wind and rain? Weather forecast Diocese of Cairns, Catholic Education Services Science Words Wind Test Test Material paddle pop sticks small brick or stone Wind (Natural) Hair dryer Rain Test Leaf Blower Watering Can Bucket Spray Bottle cardboard aluminium foil cloth Test Material Element Wind and Rain Test Wind Rain Wind (Natural) Watering Can Bucket Hair dryer Spray Bottle Watering Can Bucket paddle pop sticks small brick or stone cardboard aluminium foil cloth Diocese of Cairns, Catholic Education Services Leaf Blower Spray Bottle Watering Can Bucket Spray Bottle Assessment Tools Observational Checklist Student Name: Student contributed to KWL Chart Student contributed to Concept Map Student can describe features of Student can explain how land is Student can generate questions the sky using correct terminology. affected by wind and rain. about weather and relate these questions to real life. Diocese of Cairns, Catholic Education Services General Notes Fair Testing Checklist Student understands that variables need to be constant in a fair test. Wind Test Least Effective Material Most Effective Material Rain Test Least Effective Material Most Effective Material Wind and Rain Test Least Effective Material Student name Student name Student name Student name Student name Student name Diocese of Cairns, Catholic Education Services Most Effective Material Student can identify appropriate materials to use when designing and creating their house. Glossary KWL Chart A table that shows what students already know; want to learn and have learnt about a specific topic. Y Chart A chart that shows what students think a specific topic looks like; sounds like and feels like. Graffiti Wall Strong Wind Heavy Rain Fair Test A wall dedicated to the developing knowledge of the students. Student knowledge, questions, sight words, etc are put on a wall which displays their knowledge as the unit develops. Large branches in motion; whistling heard in telephone wires; umbrellas hard to use. (The leaf blower test should be used to demonstrate this) Lots of rain that may eventuate into minor or major flooding. (The bucket should be used to demonstrate this) A test carried out under fair conditions. Variables must be limited and constants must remain the same (as much as possible). Diocese of Cairns, Catholic Education Services