OCR A GCSE Geography Hot Deserts Revision assessment 1The
advertisement

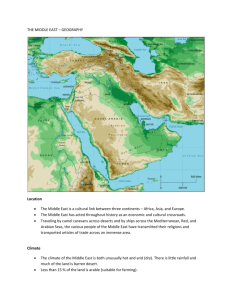
OCR A GCSE Geography Hot Deserts Revision assessment 1The correct definition of an extreme environment is... A An environment in which it is difficult for humans to survive. 2. Which of these is not a typical characteristic of hot deserts 3. Which of these is not true regarding the global distribution of hot desert environments 4. Hot deserts have a large diurnal range because A High daytime temperatures 5. Hot desert ecosystems 6. Camels store fat in their humps to... 7. Which of these is not a characteristic of xerophytic vegetation 8. Which of the following is not a process of weathering in a hot desert 9. Which of the following desert landforms has been created by wind erosion 10. Which of the following desert landforms has been created by deposition. B An environment in which it is impossible for humans and other forms of life to survive B No vegetation cover C An environment in which it is impossible for humans to survive. A They are usually found near the tropic of cancer and Capricorn B They are found in most continents C They are usually found on the western side of most continents D They are usually found on the Equator A The lack of cloud cover allows heat energy to escape at night. A Producers / carnivores / herbivores A Provide a store of water as it is rare in a hot desert. A Short growing seasons B They are hot in the day but cold at night. C Low air pressure means few clouds are formed. D Deserts are found on the equator B Herbivores / carnivores / producers B Make it easy for humans to be transported over long distances B Stores water C Carnivores / produces / herbivores C Help to reduce their body temperature. D Producers / herbivores / carnivores D Provide energy when they need it. C White upper surface D Extensive root system A Exfoliation B Abrasion C Block disintegration D Freeze thaw weathering A Canyon B Wadi C Yardang D Sand Dunes A Mesa and Butte B Salt pans C Dunes D Rock pedestal C rainfall under 250mm per year D An environment in which it is difficult for humans and other forms of life to survive. D Low population densities 11. Which of these are not typical Sinai Bedouin uses of a hot desert environment. 12. Energy companies use of hot deserts conflicts with the Bedouin lifestyle in Algeria primarily because... 13. Desertification isn’t directly caused by... 14. Tree planting, storing water, reducing overgrazing and mixed agriculture are all solutions to desertification which primarily... 15. The Great Green wall is an ambitious afforestation project started in Sengal which will... 16. The Desert Tech project aims to create a more sustainable future by making use of hot desert environments to generating energy primarily through which renewable energy source... A Keep camels/goats, trade supplies, collect water, provide cultural exchange for tourists. A Large drilling sites require the development of permanent settlements and the Bedouin are nomadic. B Send increasing numbers of children to schools. Bedouin numbers are decreasing. C Migrate from one place to another, using some camels for meat and source of protein. D. Use animal skin for shelter and clothing, trade in commodities such as salt. B Large drilling sites disrupt the natural migration of camels which the Bedouin track across the desert. C Large drilling sites contribute to atmospheric pollution and increase levels of CO2 D Large drilling sites use huge quantities of water to cool drills. A Variation in rainfall over time B Overgrazing C Over-cultivation D Poor nutrition. A Increases the risk of soil erosion B. Encourages people to migrate away from the area. C Increases vegetation cover to hold nutrients in the soil. D Improves the diet of local people. A Reduce the risk of desertification, improve diet, increase biodiversity and stimulate a range of economic activities. A Oil and gas drilling B Reduce the risk of desertification, improve diet, reduce biodiversity and stimulate a range of economic activities. B Solar Panels C Increase the risk of desertification, improve diet, Increase biodiversity and stimulate a range of economic activities. C Biomass D Reduce the risk of desertification, improve diet, Increase biodiversity and reduce the range of economic activities. D Coal mining