6.EE_.2 c Expressions and Equations
advertisement

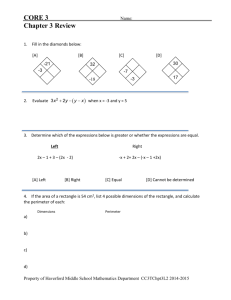
Expressions and Equations – Apply and extend previous understandings of arithmetic to algebraic expressions. TEACHERS: Terri Pemberton SUBJECT: 6th Grade Math STANDARD: 6.EE.2.c – Evaluate expressions at specific values for their variables. OBJECTIVE (EXPLICIT): Solve expressions for a given value of a variable including those used in formulas. EVIDENCE OF MASTERY (MEASURABLE): SUB-OBJECTIVES, SWBAT (SEQUENCED FROM BASIC TO COMPLEX): Evaluate an algebraic expression for a given value. Substitute values in formulas (perimeter and area) to solve real-world problems. KEY VOCABULARY: Substitute Evaluate Order of operations MATERIALS: 20 - Color tiles (represent variable terms) 30 - Color chips (units) White boards & markers BEFORE ENGAGE (MAKE CONTENT AND LEARNING RELEVANT TO REAL LIFE AND CONNECT TO STUDENT INTEREST) It takes 4 minutes for the cook to create a burger at Bob’s Burger Barn once it is ordered. If 5 people have placed their order before Tommy, how long will it take Tommy to get his burger? TEACHER WILL: STUDENT WILL: 1. Ask students to create an 1. Create an expression for the cost of x expression that would find the cost number of sundaes at $3 each with of sundaes for x number of people shoulder partner. if the sundaes cost $3. 2. Share their expression with the class. 2. Ask students to share their 3. Using a white board, substitute the expressions and write them on the given values for the variable to board. determine the cost depending on the 3. Ask students to “substitute” number of people ordering sundaes. different values for the variable to 4. Brainstorm other uses for expressions determine the total cost of sundaes where simply substituting a value can depending on the number of people change the answer. ordering them. 4. Ask students to brainstorm other uses for expressions where simply substituting a value can change the answer (guide them towards finding perimeter and area). DURING TEACHER WILL: STUDENT WILL: 1. Distribute bags of color tiles and 1. Separate tiles and chips. chips and remind students that the 2. Follow along with teacher to create a tiles represent terms with a variable visual representation of “3x” using and the chips represent units. chips and tiles. 2. Model how “3 times a number x” 3. Use tiles and chips to create a model. would look using tiles and chips. 4. Count the chips to find the solution. (Place 3 tiles under document 5. Use chips and tiles to solve additional camera) examples then write the expression 3. Tell students that we are going to and its solution on a sheet of paper. substitute 4 for x so that we can 6. With shoulder partner, identify what evaluate the expression. (Replace the variables represent in the each of the 3 tiles with 4 chips perimeter and area. each.) 7. With shoulder partner, find the 4. Count the tiles. perimeter and area of the square 5. Guide additional examples for drawn on the board. Be able to evaluating each expression using explain how substitution was used in order of operations (see attached each expression to evaluate each for sample): formula. Discuss a real world o 15 + x for x = 6. example for how finding the perimeter o 2f – 3 for f = 5. and area of a shape could be useful. o 24 ÷ b for b = 3 (guide 8. Use pictures and numbers to students to separate 24 into complete additional practice groups of 3) worksheet. o 7x for x = 3 9. Discuss the importance of the 6. Review the perimeter and area expression or formula in regards to formulas for rectangles and the value being substituted for the squares and ask students what the variable. variables represent. (P = s+s+s+s or 4s; A = lw or 𝑠 2 ) 7. Draw a square. Tell them that one side is 5 feet long and ask them to use the formulas to find perimeter and area. Ask students to come up with a real world example for how finding the perimeter and area of a shape could be useful. 8. Hand out worksheets with additional practice (attached) 9. Bring students back together and guide them to discover that as the number being substituted into an expression or a formula changes so does the answer, but the expression or formula does not. AFTER TEACHER WILL: STUDENT WILL: Ask students the engage question With your shoulder partner, discuss from above. With shoulder partner the answer to the engage question. discuss an answer. How would your time differ if there were 3 Discuss how the time will differ people ahead of you? 6? 7? depending on the number of people Ask students to write a real-word ahead of you. problem using a coefficient, operation and variable. Then, pick Create an expression for a real world a value for the variable to prove situation. Write a journal entry their algebraic expression works. explaining how you use substitution to Additional practice problems: evaluate your expression for a variety https://www.georgiastandards.org/C of values of your variable. ommonCore/Common%20Core%20Frame works/CCGPS_Math_6_6thGrade_ Unit3SE.pdf pgs. 14-17 Examples for student work that can be put in notebook or on a blank piece of paper: Expression: 15 + x for x = 6 Expression: 2f – 3 for f = 5 Picture: Picture: OOOOOOOOOOOOOOO - OOO + OOOOOO = 21 OOOOO OOOOO – OOO = 7 Solution: 15 + 6 = 21 Solution: 2(5) – 3 = 7 Name ______________________________________ Block_____ Date_________ ____ (Practice Worksheet 6.EE.2.c) Directions: Solve each expression for the given variable. Use pictures and numbers for each problem. 1. 8x – 4; when x = 4 Picture: Numbers: 2. (7 + c) ÷ 4; when c = 5 Picture: Numbers: 3. 8b – (b + 4); when b = 4 Picture: Numbers: 4. 𝑥 2 + 3y - (z + 4); when x = 2, y = 4, and z = 6. Pictures: Numbers: Answer the following questions keeping in mind the perimeter and area formulas. 5. The length of a rectangle is 5 feet and the width is 3 feet. Draw and label the rectangle, then find the perimeter and area. Make sure you label your answers. Picture: Perimeter: Area: 6. The area of square is 3 square inches. Draw and label a picture of the square. Then, find the perimeter of the square. Picture: Perimeter: 7. Find the area and perimeter for the given rectangle. 5 in. 5 in. Perimeter: 8 in. 8. Explain how you were able to find the perimeter and area for #7. Area: