12. Bioaccumulation
advertisement

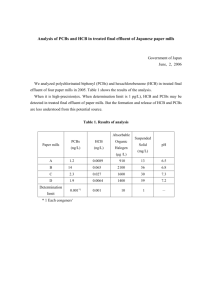
Before You Read Everyday activities, such as driving or heating your home, often pollute ecosystems. In your opinion, which human activity is the most harmful to the environment? Explain. I believe that the most harmful human activity is burning fossil fuels because they release a lot of carbons in to the air. 1. Bioaccumulation is the gradual build-up of synthetic and organic chemicals in living organisms. 2. Keystone species are species that can greatly affect population numbers and the health of an ecosystem. 3. Bio magnification is the process in which chemicals not only accumulate but become more concentrated at each tropic level in a food pyramid. 4. Even small concentrations of chemicals in producers and primary and secondary consumers can build up to cause problems in higher trophic levels. 5. PCBs are synthetic chemicals that were widely used from the 1930s to the 1970s in industrial products. 6. Half-life is the time it takes for the amount of a chemical to decrease by half. 7. Persistent organic pollutants are carbon-containing compounds that remain in water and soil for many years. 8. Chemical accumulation is measured in parts per million. 9. Heavy metals are metallic elements with a high density that are toxic to organisms at low concentrations. 10. Three polluting heavy metals are lead, mercury, and cadmium. . 11. Bioremediation is the use of living organisms to clean up chemical pollution naturally, only faster, through biodegradation. Chemical Toxic organic chemicals from red tide. Effects on producers, primary consumers, and secondary consumers Effects calms, muscles and oysters, bio accumulates to levels harmful to other organisms Effects on humans If shellfish are eaten, it can cause paralysis. This can result in a serious illness or even death DDT Lead bio accumulates in fat tissue and can cause nervous system, immune system, and reproductive disorders There are similar effects of the human effects are seen on fish and birds. Cadmium In fish, it is associated with higher death rates and lower reproduction and growth rates. Highly toxic to earthworms Mercury Organisms also circulate mercury through the food chain. Some bacteria in soils change compounds such as mercury sulfide into methylmercury, a highly toxic compound that bioaccumulates in the brain, heart, and kidneys of vertebrates bio accumulates in fat tissue and can cause nervous system, immune system, and reproductive disorders anemia (a blood condition), nervous system damage, sterility in men, low fertility rates in women, impaired mental development, and kidney failure smoking, as tobacco plants easily absorb the metal (Figure 2.58). Cadmium can accumulate in lung tissue, causing lung diseases such as cancer. Non-smokers ingest cadmium mainly through foods such as mushrooms, shellfish, fish, and seaweed. Cadmium moves from the digestive system to the liver and then to the kidneys. methylmercury is absorbed during digestion, then enters the blood and is stored in the brain. It affects nerve cells, the heart, kidneys, and lungs and suppresses the immune system PCBs and the orca 1. What are PCBs? What is their full chemical name? PCBs were one of the most widely used industrial products, but they are now banned. They interfere with the normal functioning of the body’s immune system and cause problems with reproduction. Their full chemical name is Polychlorinated Byphenyls. 2. What were PCBs used for in the 1970s? They were used as industrial products. 3. In North America, PCBs were banned in 1977. Explain why they are still having an effect on organisms today. Because they stay in the environment for a long time, and aquatic ecosystems especially are affected by them 4. Explain what happens to PCBs when they enter an orca’s body. They go into the blubber. 5. How do orcas survive when salmon stocks are low? What effect does this have on their survival? Orcas use their blubber for energy. 6. Draw a diagram to illustrate how biomagnification occurs in orcas. Effects of bioaccumulation on ecosystems 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. F D E B C A 7. C 8. C 9. B 10. C 11. D 12. D