File - Ruawai College Science
advertisement

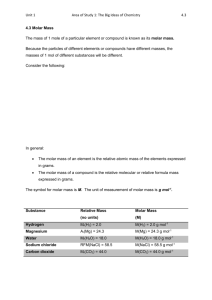
Name: Mole and Mole Calculations Year 12 Science Ruawai College 2013 The Periodic Table for Level 2 Chemistry The atomic number of an element indicates how many protons are in the nucleus of an atom of that element. 1. What is atomic number of hydrogen, H? 2. How many protons are in the nucleus of a hydrogen atom? 3. What is the atomic number of carbon, C? 4. How many protons are in the nucleus of a carbon atom? 5. Write a sentence to explain how to work out the number of protons in the nucleus of an element from the periodic table. The molar mass of an element indicates how much mass a mole of that atom has. A mole contains 6.02 x 1023 particles. Hydrogen has a molar mass of 1.0 g mol-1. 6. What is the unit of molar mass? 7. What is the molar mass of carbon? 8. What is the molar mass of iron? 9. What is the molar mass of sodium, Na? 10. What is the mass, in grams, of one mole of sodium? 11. How many sodium atoms are in one mole of sodium? 12. What is the mass, in grams, of 112 moles of sodium? 13. Write a sentence to explain how to calculate the mass of a certain number of moles of a substance. 14. Give your own example for #13. Remember the molar mass for all elements can be found on the periodic table. The molar mass of sodium chloride, NaCl, is found by adding the molar mass of Na and the molar mass of Cl. M(NaCl) = M(Na) + M(Cl) = 23.0 + 35.5 = 58.5 g mol-1 15. What does M stand for? 16. What does M(Na) mean? 17. What is the value of M(Na)? 18. What does M(Cl) mean? 19. What is the value of M(Cl)? 20. What does M(NaCl) mean? 21. What is the value of M(NaCl)? 22. Find the molar mass of the following: a. atomic iodine (I) M(I) = b. molecular iodine (I2) M(I2) = c. aluminium (Al) M(Al) = d. ethane (C2H6) M(C2H6) = e. copper oxide (Cu2O) M(Cu2O) = f. calcium sulfate (CaSO4) M(CaSO4)= The relationship between molar mass, mass and amount of substance is shown in the triangle below: M is molar mass measured in g mol-1 (read as grams per mole) m is mass measured in grams n is amount of substance measured in mol Rearranging the triangle allows you to perform calculations. M=m÷n Example: m n=m÷M m = n x M The mass of 3.00 mol of neon atoms is 60.6 g. = n x M = 3.00 mol x 20.2 g mol-1 = 60.6 g 23. What is the amount of substance in the example above (amount of neon)? 24. What is the molar mass of neon? 25. Where can you find the molar mass of neon? 26. What equation was used to find the mass of 3.00 mole of neon atoms? Example: n The amount of copper atoms in 5.00 kg of copper is 78.6 mol. =m÷M = ( 5 x 1000) g ÷ 63.6 g mol-1 = 78.6 mol 27. Why is the 5 multiplied by 1000? 28. Where did the 63.6 g mol-1 come from? 29. What is the unit for amount of cppper atoms? 30. What equation was used to find the amount of copper atoms in 5 kg of copper? 31. Complete the table using the equation m=nxM Name Formula Iodine atom I Amount of substance, n (mol) 2 Iodine molecule I2 0.5 Lead nitrate Pb(NO3)2 1.5 Magnesium iodide MgI2 0.4 Potassium oxide K2O 1.2 Aluminium sulfate Al2(SO4)3 0.3 32. Molar mass, M (g mol-1) Complete the table using the equation Name Formula Iodine molecule Mass of substance, m (g) n =m÷M Molar mass, M (g mol-1) Mass of substance, m (g) 38.1 Magnesium carbonate MgCO3 42.15 Calcium ethanoate Ca(CH3COO)2 63.24 Sucrose C12H22O11 17.1 Aluminium sulfate Copper (ll) sulfate 396.3 CuSO4 31.94 Amount of substance, n (mol) Practical Aim: To use the equation Equipment: safety glasses n = m ÷ M to calculate mass and amount of substance. balance samples empty container Method: Weigh empty container and record mass in the data table . (Assume constant mass for all containers) Go to any station and look for the label on plastic container. Record # and formula in data table. Weigh sample and record mass in data table. Calculate the amount of the substance in moles. Calculate the number of particles in the weighed sample. Results: Sample # Data Table Formula Molar mass Mass of sample + container (g) Mass of container (g) Mass of sample (g) Amount of substance (mol) Number of particles More Exercises: 33. Calculate the amount (mole) of atoms in 32 g of oxygen gas. 34. What is the molar mass of atomic chlorine if 20 moles has a mass of 710 g? 35. What is the mass of 3 moles of carbon atoms? 36. Calculate the amount of silicon in 0.14 g of silicon. 37. Calculate the amount of molecular nitrogen in 0.14 g of nitrogen gas. 38. Calculate the amount of lithium in 0.14 g of lithium. Extension Practical: Zinc Weigh 20 large zinc granules. m= M(Zn) = n(Zn) = n(Zn) in one granule = How many granules in one mole of zinc? Magnesium Measure the length of the magnesium ribbon and find its mass. length = mass = M(Mg) = n(Mg) = What length of ribbon would contain 1 mole of magnesium? What is the amount of magnesium in 1 metre of magnesium? Name: Answers Mole and Mole Calculations Year 12 Science Ruawai College 2013 The Periodic Table for Level 2 Chemistry The atomic number of an element indicates how many protons are in the nucleus of an atom of that element. 1. What is atomic number of hydrogen, H? 1 2. How many protons are in the nucleus of a hydrogen atom? 1 3. What is the atomic number of carbon, C? 6 4. How many protons are in the nucleus of a carbon atom? 6 5. Write a sentence to explain how to work out the number of protons in the nucleus of an element from the periodic table. The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of that element’s nucleus. The molar mass of an element indicates how much mass a mole of that atom has. A mole contains 6.02 x 1023 particles. Hydrogen has a molar mass of 1.0 g mol-1. 6. What is the unit of molar mass? g mol-1 7. What is the molar mass of carbon? 6 g mol-1 8. What is the molar mass of iron? 55.9 g mol-1 9. What is the molar mass of sodium, Na? 23.0 g mol-1 10. What is the mass, in grams, of one mole of sodium? 23 g 11. How many sodium atoms are in one mole of sodium? 6.02 x 1023 12. What is the mass, in grams, of 12 moles of sodium? 23 x 12 = 276 g 13. Write a sentence to explain how to calculate the mass of a certain number of moles of a substance. multiply the number of moles of a substance by the molar mass to get the total mass of the substance 14. Give your own example for #13. Remember the molar mass for all elements can be found on the periodic table. The molar mass of sodium chloride, NaCl, is found by adding the molar mass of Na and the molar mass of Cl. M(NaCl) = M(Na) + M(Cl) = 23.0 + 35.5 = 58.5 g mol-1 15. What does M stand for? molar mass 16. What does M(Na) mean? molar mass of sodium 17. What is the value of M(Na)? 23 g mol-1 18. What does M(Cl) mean? molar mass of chlorine 19. What is the value of M(Cl)? 35.5 g mol-1 20. What does M(NaCl) mean? molar mass of sodium chloride 21. What is the value of M(NaCl)? 23.0 + 35.5 = 58.5 g mol-1 22. Find the molar mass of the following: a. atomic iodine (I) M(I) = 127 g mol-1 b. molecular iodine (I2) M(I2) = 2 x 127 g mol-1 c. aluminium (Al) M(Al) = 27.0 g mol-1 d. ethane (C2H6) M(C2H6) = (2 x 12) + (6 x 1) = 30 g mol-1 e. copper oxide (Cu2O) M(Cu2O) = (2 x 63.6) + 16 = 143.2 g mol-1 f. calcium sulfate (CaSO4) M(CaSO4)= 40.1 + 32.1 + (4 x 16) = 136.2 g mol-1 The relationship between molar mass, mass and amount of substance is shown in the triangle below: M is molar mass measured in g mol-1 (read as grams per mole) m is mass measured in grams n is amount of substance measured in mol Rearranging the triangle allows you to perform calculations. M=m÷n Example: m n=m÷M m = n x M The mass of 3.00 mol of neon atoms is 60.6 g. = n x M = 3.00 mol x 20.2 g mol-1 = 60.6 g 23. What is the amount of substance in the example above (amount of neon)? 24. What is the molar mass of neon? 20.2 g mol-1 25. Where can you find the molar mass of neon? Periodic table 26. What equation was used to find the mass of 3.00 mole of neon atoms? Example: n 3.00 mol m = n xM The amount of copper atoms in 5.00 kg of copper is 78.6 mol. =m÷M = ( 5 x 1000) g ÷ 63.6 g mol-1 = 78.6 mol 27. Why is the 5 multiplied by 1000? There are 1000 grams in one kilogram 28. Where did the 63.6 g mol-1 come from? 29. What is the unit for amount of copper atoms? mol 30. What equation was used to find the amount of copper atoms in 5 kg of copper? n = m ÷ M molar mass of copper / periodic table 31. Complete the table using the equation Name Formula Iodine atom I Iodine molecule I2 Lead nitrate m=nxM Molar mass, M (g mol-1) 254 Mass of substance, m (g) 2 x 127 = 254 Amount of substance, n (mol) 2 254 0.5 x 254 = 127 0.5 Pb(NO3)2 331.0 1.5 x 331 = 496.5 1.5 Magnesium iodide MgI2 278.3 0.4 x 278.3 = 111.32 0.4 Potassium oxide K2O 94.2 1.2 x 94.2 = 113.04 1.2 Aluminium sulfate Al2(SO4)3 342.3 0.3 x 342.3 = 102.69 0.3 32. Complete the table using the equation Name Formula Iodine molecule I2 Magnesium carbonate MgCO3 Calcium ethanoate n =m÷M Molar mass, M (g mol-1) 254 Mass of substance, m (g) 38.1 Amount of substance, n (mol) 38.1 ÷ 254 = 0.15 84.3 42.15 42.15 ÷ 84.3 = 0.50 Ca(CH3COO)2 158.1 63.24 63.24 ÷158.1 = 0.40 Sucrose C12H22O11 342.0 17.1 17.1 ÷ 342.1 = 0.05 Ammonium sulfate (NH4)2SO4 132.1 396.3 396.3 ÷ 132.1 = 3.0 Copper (ll) sulfate CuSO4 159.7 31.94 31.94 ÷ 159.7 = 0.20 Practical Aim: To use the equation Equipment: safety glasses n = m ÷ M to calculate mass and amount of substance. balance samples empty container Method: Weigh empty container and record mass in the data table . (Assume constant mass for all containers) Go to any station and look for the label on plastic container. Record # and formula in data table. Weigh sample and record mass in data table. Calculate the amount of the substance in moles. Calculate the number of particles in the weighed sample. Results: Sample # Data Table Formula Molar mass Mass of sample + container (g) Mass of container (g) Mass of sample (g) Amount of substance (mol) Number of particles More Exercises: 33. Calculate the amount (mole) of atoms in 32 g of oxygen gas. 32 ÷ 16 2 mol 34. What is the molar mass of atomic chlorine if 20 moles has a mass of 710 g? 710 ÷ 20 35.5 g mol-1 35. What is the mass of 3 moles of carbon atoms? 3 x 12 36 g 36. Calculate the amount of silicon in 0.14 g of silicon. 0.14 ÷ 28 0.005 mol 37. Calculate the amount of molecular nitrogen in 0.14 g of nitrogen gas. 0.14 ÷ 28 0.005 mol 38. Calculate the amount of lithium in 0.14 g of lithium. 0.14 ÷ 7 0.02 mol Extension Practical: Zinc Weigh 20 large zinc granules. m= M(Zn) = n(Zn) = n(Zn) in one granule = How many granules in one mole of zinc? Magnesium Measure the length of the magnesium ribbon and find its mass. length = mass = M(Mg) = n(Mg) = What length of ribbon would contain 1 mole of magnesium? What is the amount of magnesium in 1 metre of magnesium?