Name Period ______ U8 L2 Reading Notes: Roles in Energy
advertisement

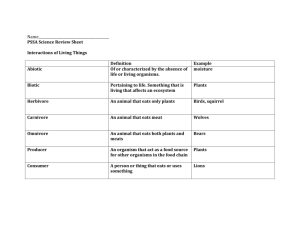
Name _______________________________ Period ______ U8 L2 Reading Notes: Roles in Energy Transfer, pp 424-433 Benchmark (for both Lesson 1 and Lesson 2): Explain and illustrate the roles of and relationships among producers, consumers, and decomposers in the process of energy transfer in a food web. Essential Question: How does energy move through an ecosystem? Learning Goal: By the end of this lesson, you should be able to relate the roles of organisms to the transfer of energy in food chains and food webs. How do organisms get energy? 1. Energy is transferred from the ________________ to producers. 2. Producers convert this ____________________ into food (carbohydrates). 3. A producer is also called an ___________________________ (meaning an organism that feeds itself). 4. In the process of_________________________________ producers use light energy from the Sun to make _____________ (carbs) from water, carbon dioxide, and nutrients found in water and soil. 5. *The waste product of photosynthesis is ____________________, which we all need to survive. 6. *In the process of cellular ___________________________, the exact opposite occurs; we take in oxygen and our waste product is _______________ ________________ (CO2), which the autotroph producers must have for photosynthesis. 7. All _______________ plants are _______________________. 8. ____________________________ break down matter. 9. Decomposers are nature’s ________________________. 10. By converting dead organisms into materials such as water and nutrients, decomposers help move matter through __________________________. 11. A _____________________ is an organism that eats other organisms. 12. Consumers use the energy and ______________________ stored in other living organisms because they _____________________ make their own food (as producers do). 13. A consumer that eats only plants is called an __________________________. 14. A __________________________ eats other animals. 15. An _________________________ eats both plants and animals. 16. A _________________________ is a specialized consumer that feeds on dead organisms. How is energy transferred among organisms? 17. Organisms change energy from the environment into other types of __________________. 18. Some of this energy is used for the organism’s activities and some of the energy is __________ within the organism to use later. 19. If an organism is eaten or decomposes, the consumer or ____________________ takes in the energy _______________ in the original organism. 20. In this way, energy is _______________________ from organism to organism. 21. By what process does a tree get its energy? _________________________________. CONTINUED ON THE OTHER SIDE -> 22. What type of energy does an ant consume when it eats other insects? _________________________ 23. Energy flows through a ________________ __________________from producers to __________________________. 24. The arrows in a food chain represent the _______________________ of ______________ as one organism eats another, 25. _____________________ form the base of the food chains, transferring ____________________ to the first, or primary, _______________________ in the food chain. 26. The secondary consumer in the food chain only consumes the _________________ consumer and the ________________ (third) consumer consumes only the _____________________ consumer, & so on. 27. Finally, ______________________ recycle matter back to the soil. How do food webs show energy connections? 28. A ________________ ____________ is the feeding relationships among organisms in ecosystem and are made up of many _____________ __________________. 29. The food web on p 431 is a _________________________ food web. 30. What forms the base of this food web? _____________________________, which are tiny _______ that are _______________________________ just like plants are on land. 31. Consumers can eat _________________________ and other ______________________________. 32. Energy flows up the food web when __________________________ eat puffins. 33. Puffins get energy by eating ___________________________ and __________________________. 34. What is the top predator shown in this coastal food web? __________________________________. 35. What does a seal consume? __________________________ and __________________________ 36. What organisms does a Cod get its chemical energy from? ____________, ___________ and ______ How are organisms connected by food webs? 37. Energy flows from ______________________________ to _______________________________. 38. All living organisms are connected by ____________________ _________________ ___________. 39. Many organisms have feeding relationships that connect __________ & _____________ use food webs. 40. Because the global food webs are _________________________, removing even ______ organism can affect ____________ organisms in other _______________________________. 41. When an organism is removed from a _________ ______, the population size of the organisms that it eats may __________________, and the population size of organisms that eat it may _____________ 42. Sometimes, species are introduced into new areas. These ___________________ species often compete with __________________ species for ______________________ such as sunlight & food. 43. What is an invasive species (define)? __________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 44. What are native species (define)? ____________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________