Support information - Springer Static Content Server
advertisement

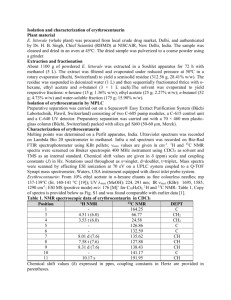
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Stereoselective Bioreduction of α-Azido Ketones by Whole Cells of Marinederived Fungi Lenilson C. Rocha Mirna H. R. Seleghim João V. Comasseto Lara D. Sette André L. M. Porto Preparation of α-azido ketones 5-8 A mixture of the appropriate α-haloacetophenones 1-4 (14.0 mmol) and sodium azide (1.82 g, 28.0 mmol) in acetone (250 mL) was stirred at room temperature until completion of the reaction and monitored by TLC. After that the mixture was poured into water and extracted with EtOAc (3 x 30 mL), and the organic layer was dried with MgSO4, concentrated under reduced pressure, and the residue was purified by column chromatography. 2-azido-1-phenylethanone (5): 1H NMR (200 MHz, CDCl3): δ 4.57 (s, 2H); 7.48-7.68 (m, 3H); 7.90-7.95 (m, 2H). IR (KBr, = cm−1): 2103 (N3), 1695 (C=O). 7.68 7.66 7.64 7.63 7.61 7.61 7.60 7.55 7.55 7.52 7.51 7.48 7.95 7.94 7.91 7.90 002001.FID 2.15 3.39 7.75 Chemical Shift (ppm) 7.50 2.15 8.5 8.0 7.48 7.47 7.69 7.68 7.95 7.94 7.91 7.90 7.64 7.55 7.55 7.51 7.27 4.57 8.00 3.39 7.5 2.00 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 Chemical Shift (ppm) 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0 Figure S1. 1H NMR spectrum (200 MHz, CDCl3) of 2-azido-1-phenyletanone (5) Wavenumber (cm-1) Figure S2. IR spectrum (KBr) of 2-azido-1-phenylethanone (5) -0.5 2-azido-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethanone (6): 1H NMR (200 MHz, CDCl3): δ 3.89 (s, 3H); 4.51 (s, 2H); 6.97 (d, 2H, J 8.0 Hz); 7.90 (d, 2H, J 8.0 Hz). IR (KBr, = cm−1): 2120 0.01 (N3), 1684 (C=O). 3.89 7.27 6.94 7.92 7.87 6.99 002001.FID 2.01 1.91 7.5 Chemical Shift (ppm) 7.0 2.01 8.5 8.0 6.99 6.94 7.27 7.92 7.87 4.51 8.0 1.91 7.5 7.0 2.08 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 2.86 4.5 4.0 Chemical Shift (ppm) 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0 -0.5 Figure S3. 1H NMR spectrum (200 MHz, CDCl3) of 2-azido-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethanone (6) Wavenumber (cm-1) Figure S4. IR spectrum (KBr) of 2-azido-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethanone (6) 2-azido-1-(4-bromophenyl)ethanone (7): 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 4.53 (s, 2H); 7.66 7.27 (d, 2H, J 8.0 Hz); 7.79 (d, 2H, J 8.0 Hz). IR (KBr, = cm−1): 2102 (N3), 1690 (C=O). 7.65 1.99 7.5 7.65 7.80 7.78 7.67 7.8 7.7 7.6 Chemical Shift (ppm) 4.53 7.78 7.80 2.02 7.9 7.67 9D929_BROMOCITOAZIDA.001.esp 2.02 1.99 9.0 8.5 8.0 7.5 2.00 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 Chemical Shift (ppm) 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0 -0.5 Figure S5. 1H NMR spectrum (400 MHz, CDCl3) of 2-azido-1-(4-bromophenyl)ethanone (7) Wavenumber (cm-1) Figure S6. IR spectrum (KBr) of 2-azido-1-(4-bromophenyl)ethanone (7) 2-azido-1-(4-nitrophenyl)ethanone (8): 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 4.64 (s, 2H); 8.08 (d, 2H, J 8.0 Hz); 8.31 (d, 2H, J 8.0 Hz). IR (KBr, = cm−1): 2105 (N3), 1706 (C=O), 1554, 1349. Figure S7. 1H NMR spectrum (400 MHz, CDCl3) of 2-azido-1-(4-nitrophenyl)ethanone (8) Wavenumber (cm-1) Figure S8. IR spectrum (KBr) of 2-azido-1-(4-nitrophenyl)ethanone (8) Preparation of ()-β-azidophenylethanols 9-12 The ketones 5-8 (5.0 mmol), NaBH4 (5.5 mmol) and methanol (10 mL) were added to a 25 mL flask equipped with a magnetic stirrer. The mixtures were stirred for 1 h at 0 oC. After that, the reaction mixtures were quenched by the addition of water (5 mL), the methanol was removed under vacuum and the residue was extracted with EtOAc (3 x 20 mL). The combined organic phases were dried over MgSO4 and then filtered. The organic solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure and the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography using hexane and ethyl acetate as eluent to produce racemic βazidophenylethanols 9-12. 2-azido-1-phenylethanol (9): 1H NMR (200 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 2.49 (s, 1H); 3.35-3.52 (m, 2H); 4.84 (dd, 1H, J 8.0, 4.0 Hz); 7.35 (m, 5H). 13C RMN (50 MHz, CDCl3): 58.0, 73.3, 7.35 125.9, 128.6, 140.5. IR (KBr, = cm−1): 3400 (OH), 2103 (N3). 001001.FID 3.35 3.38 1.00 2.29 4.85 4.80 Chemical Shift (ppm) 3.50 3.45 3.40 Chemical Shift (ppm) 3.35 5.02 8.5 8.0 1.00 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 0.00 3.38 3.35 3.52 3.48 2.49 4.87 4.85 4.84 4.81 3.46 3.44 3.42 3.42 4.90 3.42 3.42 3.44 3.46 3.52 3.48 4.81 4.87 4.85 001001.FID 4.84 001001.FID 2.29 4.5 4.0 Chemical Shift (ppm) 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0 -0.5 128.64 125.87 Figure S9. 1H NMR spectrum (200 MHz, CDCl3) of 2-azido-1-phenylethanol (9) 125.87 128.29 001001.FID 128.29 128.64 001001.FID 126 125 57.98 128 127 Chemical Shift (ppm) 140.51 77.00 73.34 129 192 184 176 168 160 152 144 136 128 120 112 104 96 88 Chemical Shift (ppm) 80 72 64 56 48 40 32 24 16 8 Figure S10. 13C NMR spectrum (50 MHz, CDCl3) of 2-azido-1-phenylethanol (9) 0 -8 Wavenumber (cm-1) Figure S11. IR spectrum (KBr) of 2-azido-1-phenylethanol (9) 2-azido-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethanol (10): 1H NMR (200 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 2.19 (s, 1H); 3.36-3.54 (m, 3H); 3.82 (s, 3H); 4.84 (dd, 1H, J 8.0, 4.0 Hz); 6.90 (d, 2H, J 8.0 Hz); 7.30 (d, 2H, J 8.0 Hz). 13 C RMN (50 MHz, CDCl3): 55.0, 57.6, 72.6, 113.8, 127.0, 132.7, 3.82 159.2. IR (KBr, = cm−1): 3418 (OH), 2103 (N3). ALCOOL METOXI AZIDA 2.ESP 3.38 3.36 3.51 3.54 3.48 3.42 3.45 ALCOOL METOXI AZIDA 2.ESP 2.90 7.5 3.55 3.50 3.45 3.40 3.35 Chemical Shift (ppm) 3.30 3.25 3.20 3.15 1.15 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 3.24 3.38 3.36 2.19 3.48 3.45 3.42 2.35 7.0 3.54 4.87 4.85 4.83 4.81 2.26 8.0 3.60 6.94 6.89 7.33 7.28 3.65 2.90 4.5 4.0 3.5 Chemical Shift (ppm) 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0 Figure S12. 1H NMR spectrum (200 MHz, CDCl3) of 2-azido-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethanol (10) 113.78 159.22 132.72 55.02 72.61 57.59 127.02 9D930_AZIDO ALCOOL.002.esp 192 184 Figure S13. 13 176 168 160 152 144 136 128 120 112 104 96 88 Chemical Shift (ppm) 80 72 64 56 48 40 32 24 16 8 0 C NMR spectrum (50 MHz, CDCl3) of 2-azido-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethanol (10) Wavenumber (cm-1) Figure S14. IR spectrum (KBr) of 2-azido-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethanol (10) 2-azido-1-(4-bromophenyl)ethanol (11): 1H NMR (200 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 3.45 (d, 2H, J 6,0 Hz); 4.85 (dd, 1H, J 12.0, 6.0 Hz); 7.26 (d, 2H, J 8.0 Hz); 7.50 (d, 2H, J 8.0 Hz). 13C RMN (50 MHz, CDCl3): 57.9, 72.7, 122.2, 127.6, 131.8, 139.4, 159.4. IR (KBr, = cm−1) 7.28 3406 (OH), 2103 (N3). 4.88 4.82 4.85 7.24 7.27 7.53 3.46 3.43 7.49 001001.FID 2.13 2.34 9.0 8.5 8.0 7.5 1.00 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 2.24 5.0 4.5 4.0 Chemical Shift (ppm) 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0 Figure S15. 1H NMR spectrum (200 MHz, CDCl3) of 2-azido-1-(4-bromophenyl)ethanol 139.45 122.23 72.75 57.91 131.79 001001.FID 127.61 (11) 208 200 192 184 176 168 160 152 144 136 128 120 112 104 96 Chemical Shift (ppm) 88 80 72 64 56 48 40 32 24 16 8 0 Figure S16. 13C NMR spectrum (50 MHz, CDCl3) 2-azido-1-(4-bromophenyl)ethanol (11) Wavenumber (cm-1) Figure S17. IR spectrum (KBr) of 2-azido-1-(4-bromophenyl)ethanol (11) 2-azido-1-(4-nitrophenyl)ethanol (12): 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 1.95 (s, 1H); 3.39-3.47 (m, 2H); 4.97 (dd, 1H, J 8.0, 4.0 Hz); 7.51 (d, 2H, J 8.0 Hz); 8.08 (d, 2H, J 8.0 Hz). C RMN (100 MHz, CDCl3): 57.1, 72.0, 123.3, 126.6, 147.0, 148.0 IR (KBr, = 13 7.52 cm−1): 3401 (OH), 2108 (N3). 9D930_NITRO AZIDO ALCOOL.001.esp 3.44 4.975 4.950 Chemical Shift (ppm) 3.39 3.39 3.41 3.40 3.46 3.47 3.42 3.43 1.00 5.000 1.95 3.44 8.09 8.07 3.43 3.42 3.44 3.44 4.96 4.95 4.98 4.97 9D930_NITRO AZIDO ALCOOL.001.esp 7.50 9D930_NITRO AZIDO ALCOOL.001.esp 2.08 3.39 3.39 3.450 3.425 3.400 Chemical Shift (ppm) 7.27 3.47 3.46 4.98 4.97 4.96 4.95 3.475 1.83 9.5 9.0 8.5 8.0 2.00 1.00 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 Chemical Shift (ppm) 2.08 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0 -0.5 126.60 Figure S18. 1H NMR spectrum (400 MHz, CDCl3) of 2-azido-1-(4-nitrophenyl)ethanol (15) 148.06 147.08 57.14 72.01 123.33 9D930_NITRO AZIDO ALCOOL.002.esp 192 184 176 168 160 152 144 136 128 120 112 104 96 88 Chemical Shift (ppm) 80 72 64 56 48 40 32 24 16 8 0 -8 Figure S19. 13C NMR spectrum (100 MHz, CDCl3) 2-azido-1-(4-nitrophenyl)ethanol (12) Wavenumber (cm-1) Figure S20. IR spectrum (KBr) of 2-azido-1-(4-nitrophenyl)ethanol (12) Chromatograms of the reduction of α-azido ketones 5-8 using whole cells of fungi. Bioreduction (±)-2-azido-1-phenyltanone (5) by whole cells of fungi M. racemosus CBMAI 847 c = 10% t = 12 min A. sclerotiorum CBMAI 849 A c = 90% 72% ee t = 26 min 27 min c = 2% t = 12 min C B. felina CBMAI 738 B c = 98% 85% ee t = 26 min 27 min P. raistrickii CBMAI 931 c = 100% 80% ee c = 10% t = 12 min t = 26 min 27 min D c = 90% 90% ee t = 26 min 27 min Figure S21. Chiral analyses obtained by HPLC chromatograms. Conditions for HPLC analysis in 10% isopropanol, 90% hexane, flow 0.5 mL/min, 190 nm. (A) M. racemosus CBMAI 847 (B) A. sclerotiorum CBMAI 849 (C) B. felina CBMAI 738 (D) P. raistrickii CBMAI 931 Bioreduction (±)-2-azido-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)etanone (6) by whole cells of fungi A t = 33 min C. cladosporiodes CBMAI 857 B A. sclerotiorum CBMAI 849 c = 100% >99% ee c = 100% >99% ee t = 33 min C P. raistrickii CBMAI 931 c = 32% t = 23 min t = 33 min c = 68% >99% ee P. citrinum CBMAI 1186 t = 33 min D c = 99% >99% ee Figure S22. Chiral analyses obtained by HPLC chromatograms. Conditions for HPLC analysis in 10% isopropanol, 90% hexane, flow 0.5 mL/min, 190 nm. (A) C. cladosporioides CBMAI 857 (B) A. sclerotiorum CBMAI 931 (C) P. raistrickii CBMAI 849 (D) P. citrinum CBMAI 1186 Bioreduction (±)-2-azido-1-(4-bromophenyl)etanone (7) by whole cells of fungi M. racemosus CBMAI 847 c = 21% t = 24 min 28 min A c = 79% 29% ee t = 15 min C. cladosporiodes CBMAI 857 A. sclerotiorum CBMAI 849 c = 25% C t = 24 min 28 min t = 24 min 28 min B t = 15 min c = 75% 39% ee D P. raistrickii CBMAI 931 t = 15 min c = 98% 44% ee c = 2% c = 68% t = 15 min c = 32% 70% ee t = 24 min 28 min Figure S23. Chiral analyses obtained by HPLC chromatograms. Conditions for HPLC analysis in 10% isopropanol, 90% hexane, flow 0.5 mL/min, 190 nm. (A) M. racemosus CBMAI 847 (B) A. sclerotiorum CBMAI 849 (C) C. cladosporioides CBMAI 857 (D) P. raistrickii CBMAI 931 Bioreduction (±)-2-azido-1-(4-nitrophenyl)etanone (8) by whole cells of fungi t = 21 min 23 min P. citrinum CBMAI 1186 A t = 21 min 23 min P. oxalicum CBMAI 1185 c = 95% 28% ee B c = 96% 51% ee c = 5% c = 4% C P. chrysogenum CBMAI 1199 t = 21 min 23 min c = 98% 41% ee Figure S24. Chiral analyses obtained by HPLC chromatograms. Conditions for HPLC analysis in 10% isopropanol, 90% hexane, flow 0.5 mL/min, 254 nm. (A) P. citrinum CBMAI 1186 (B) P. oxalicum CBMAI 1185 (C) P. chrysogenum 1199