Indian Journal of Basic and Applied Medical Research, March 2015
advertisement

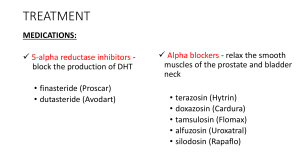
Indian Journal of Basic and Applied Medical Research, March 2015: Vol.-4, Issue- 2, P. 546-551 Original article A comparative study of two surgical approaches of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in a tertiary care teaching hospital. 1Janmejai 1Associate Prasad Sharma,2Subhash Chandra Sharma Professor, Department of General Surgery, SGRRIMHS & Associated SMIH, Patel Nager, Dehradun, Uttrakhand, India 2Assistant Professor, Department of General Surgery, SGRRIMHS & Associated SMIH, Patel Nager, Dehradun, Uttrakhand, India Corresponding author: Dr Janmejai Prasad Sharma, Associate Professor, Department of General Surgery, SGRRIMHS & Associated SMIH, Patel Nager , Dehradun, Uttrakhand, India Abstract: Background: Benign prostatic hyperplasia is an age related common urinary complaint. The treatment of such disease can be accomplished by conservative and operative means. Many surgical options are available for the resection of hypertrophic tissue of prostate. We organised a prospective study to compare the two surgical techniques (Transvesical and Transurethral) in terms of complications, morbidity/mortality. Materials and Methods: 60 patients were divided into two groups; Group I (30 patients) were planned for Transvesical prostatectomy while Group II (30 patients) were posted for Transurethral resection of prostate. The two groups were compared in terms of immediate complication, duration of hospital stay, duration of immobilisation and overall morbidity and mortality of the patients. Results: Most of the patients were of 51-70 years in both the study groups. The most common complaint of the patients visiting to our out-patient clinic was increased frequency of urination in both the groups. On comparing the delayed post-operative complications, urinary tract infection (UTI) was observed in 5 patients in Group I while only one patient had symptoms of UTI in Group II (p=0.01).Statistical significant difference was observed in duration of hospital stay in between the groups with TURP operated patients had better recovery (p=0.001). Conclusion: TURP is more advantageous than Transvesical prostatectomy in terms of shorter duration of hospital stay, lesser immediate and delayed post-operative complications and hence better patient outcome. Keywords: Benign Hypertrophy of Prostate, Transurethral resection of Prostate, Transvesical Prostatectomy