Pacing guide - 4th Grade Math 2nd 9
advertisement

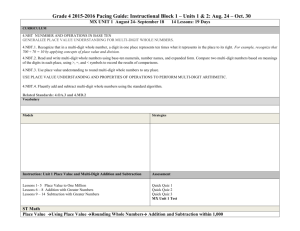
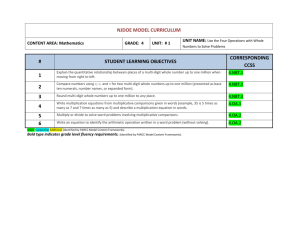
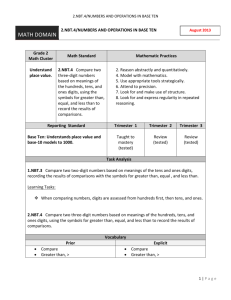
Ocean Springs School District - 4th Grade – 2nd 9 Weeks Instructional Map Common Core Standard Topic 5 Standard Expectations(s) Students will be able to …. Clarity of the Standard Vocabulary Resources Mathematical Practices Number Sense: Multiplying 1Digit Numbers 4.NBT.5 Multiply a whole number of up to four digits by a one-digit whole number, and multiply two two-digit numbers, using strategies based on place value and the properties of operations. Illustrate and explain the calculation by using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models. I Can: 4.NBT.5 Apply the properties of operations to multiply numbers 4.NBT.5 Multiply a 4 digit number by a 1 digit number 4.NBT.5 Multiply numbers using written equations 4.NBT.5 Illustrate and explain multiplication using rectangular arrays 4.NBT.5 Illustrate and explain multiplication using area modules Use place value understanding to round multi-digit whole numbers to any place. Major cluster 4.NBT.5 calls for students to multiply numbers using a variety enVision 4.MP.1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving Suggested number of days of strategies. properties- rules about how numbers work Example: There are 25 dozen cookies in the bakery. What is the total number of cookies at the bakery? Student 3 Student 1 25 x 12 25 x12 I broke 12 up I doubled 25 into 10 and 2 25 x 10 and cut 12 in = 250 25 x 2 = 50 Student 2 half to get 50 x 250 +50 = 300 25 x 12 I broke 25 up 6 into 5 groups of 5 5 x 50 x 6 = 300 12 = 60 I have 5 groups of 5 in 25 60 x 5 = 300 Multiples (Topic- Section) them 4.MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively. Arrays 5-1 Factor 5-2 4.MP. 3 Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. 4.MP.4. Model with mathematics Product 5-3 Partial Products 4.MP.5 Use appropriate tools strategically 4.MP.6 Attend to precision. 5-4 Compensation 5-5 4.MP.7. Look for and make use of structure. 4.MP.8. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. Students who develop flexibility in breaking numbers apart have a better understanding of the importance of place value and the distributive property in multi-digit multiplication. Students use base ten blocks, area models, partitioning, compensation strategies, etc. when multiplying whole numbers and use words and diagrams to explain their thinking. They use the terms factor and product when communicating their reasoning. Multiple strategies enable students to develop fluency with multiplication and transfer that understanding to division. I Can: 4.NBT.3 Use place value understanding to round multi-digit whole numbers to any place. When students are asked to round large numbers, they first need to identify which digit is in the appropriate place. Example: Round 76,398 to the nearest 1000. Topic 5 – 6 days Major cluster 4.OA.3 Solve multistep word problems posed with whole numbers and having whole-number I Can: 4.NBT.3 Round numbers up to the millions place 4.NBT.3 Explain why a number is rounded to a given place. 4.NBT.3 Demonstrate understanding of place value using a drawing, chart, table, diagram, etc… I Can: Step 1: Since I need to round to the nearest 1000, then the answer is either 76,000 or 77,000. Step 2: I know that the halfway point between these two numbers is 76,500. Step 3: I see that 76,398 is between 76,000 and 76,500. Step 4: Therefore, the rounded number would be 76,000. Students need many opportunities solving multistep story problems using all four operations. An interactive whiteboard, document camera, drawings, words, answers using the four operations, including problems in which remainders must be interpreted. Represent these problems using equations with a letter standing for the unknown quantity. Assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies including rounding. 4.OA.3 Write an equation to solve the word problem using a letter to Example: represent the missing number. Chris bought clothes for school. She bought 3 shirts for $12 each and a skirt for $15. How much money did Chris spend on her new school clothes? 3 x $12 + $15 = a Major cluster Topic 6 numbers, and/or objects may be used to help solve story problems. Fluency: Multiplying 1Digit Numbers 4.NBT.5. Multiply a whole number of up to four digits by a one-digit whole number, and multiply two two-digit numbers, using strategies based on place value and the properties of operations. Illustrate and explain the calculation by using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models. Major cluster I Can: 4.NBT.5 Apply the properties of operations to multiply numbers 4.NBT.5 Multiply a 2 digit number by a 1 digit number 4.NBT.5 Multiply a 3 – and 4-digit number by a 1-digit number 4.NBT.5 Illustrate and explain multiplication using rectangular arrays Students who develop flexibility in breaking numbers apart have a better understanding of the importance of place value and the distributive property in multi-digit multiplication. Students use base ten blocks, area models, partitioning, compensation strategies, etc. when multiplying whole numbers and use words and diagrams to explain their thinking. They use the terms factor and product when communicating their reasoning. Multiple strategies enable students to develop fluency with multiplication and transfer that understanding to division. Use of the standard algorithm for multiplication is an expectation in the 5th grade. This standard refers to place value understanding, which extends beyond an algorithm or procedure for rounding. The expectation is that students have a deep understanding of place value and number sense and can explain and reason about the answers they get when they round. Students should have numerous experiences using a number line and a hundreds chart as tools to support their work with rounding. Product Array Factor Rounding 4.OA.3 Solve multistep word problems posed with whole numbers and having I Can: whole-number answers using the four operations, including problems 4.OA.3 Solve a word problem involving multiplication of in which remainders must be interpreted. Represent these problems one digit numbers with 2using equations with a letter standing for the unknown quantity. ,3-, and 4- digit numbers Assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies including rounding. 4.OA.4 Write and equation from a situation using a variable. Major cluster 4.OA.4 Decide if an answer is reasonable. Students need many opportunities solving multistep story problems using all four operations. An interactive whiteboard, document camera, drawings, words, numbers, and/or objects may be used to help solve story problems. 4.NBT.3 Use place value understanding to round multi-digit whole numbers to any place. Major cluster Topic 7 I Can: 4.NBT.3 Use place value to round. 4.NBT.3 Use place value understanding in order to determine what place value to round to. Example: 4.NBT.3 refers to place value understanding, which extends beyond an algorithm or procedure for rounding. The expectation is that students have a deep understanding of place value and number sense and can explain and reason about the answers they get when they round. Students should have numerous experiences using a number line and a hundreds chart as tools to support their work with rounding. Number Sense: Multiplying by 2-Digit Numbers 4.NBT.5. I Can: Multiply a whole number of up to four digits by a one-digit whole number, and multiply two two-digit numbers, using strategies based on place value and the properties of 4.NBT.5 Apply the properties of operations. Illustrate and explain the calculation by using equations, rectangular operations to multiply numbers arrays, and/or area models. 4.NBT.5 Multiply a 2 digit number by a multiple of 10 Equation The standards for this Unit are the same as for the previous Unit. However, this Unit introduces multiplying with 2-digit numbers with a concentration on multiplying with multiples of 10 as a means of estimation. Students who develop flexibility in breaking numbers Factors Product Major cluster 4.NBT.5 Illustrate and explain multiplication using rectangular arrays apart have a better understanding of the importance of place value and the distributive property in multi-digit multiplication. Students use base ten blocks, area models, partitioning, compensation strategies, etc. when multiplying whole numbers and use words and diagrams to explain their thinking. They use the terms factor and product when communicating their reasoning. Multiple strategies enable students to develop fluency with multiplication and transfer that understanding to division. Use of the standard algorithm for multiplication is an expectation in the 5th grade. This standard refers to place value understanding, which extends beyond an algorithm or procedure for rounding. The expectation is that students have a deep understanding of place value and number sense and can explain and reason about the answers they get when they round. Students should have numerous experiences using a number line and a hundreds chart as tools to support their work with rounding. Example: 4.NBT.3 Use place value understanding to round multi-digit whole numbers to any place. I Can: 4.NBT.3 Use place value to round. 4.NBT.3 Use place value Round Compatible numbers understanding in order to determine what place value to round to. Major cluster 4.OA.3 Solve multistep word problems posed with whole numbers and having whole-number answers using the four operations, including problems in which remainders must be interpreted. Represent these problems using equations with a letter standing for the unknown quantity. Assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies including rounding. Major cluster I Can: 4.OA.3 Write an equation to solve the word problem using a letter to represent the missing number. 4.OA.3 Determine if an answer makes sense, based on the problem. 4.OA.3 Justify my answers using mental math and estimation 4.NBT.3 refers to place value understanding, which extends beyond an algorithm or procedure for rounding. The expectation is that students have a deep understanding of place value and number sense and can explain and reason about the answers they get when they round. Students should have numerous experiences using a number line and a hundreds chart as tools to support their work with rounding. Example: On a vacation, your family bikes an average of 23 miles a day for 12 days. How many miles did they travel total? Some typical estimation strategies for this problem: Student 1: I first thought about 23 and 12. I used compatible numbers and thought of them as 20 and 10. I multiplies two and one together and got 2 and then I added two zeros at the end. I got 200. Student 2: I rounded 12 to 10 and multiplied 23 by 10 and got 230. The assessment of estimation strategies should only have one reasonable answer (200 or 230), or a range (between 200 and 250). Problems will be structured so that all acceptable estimation strategies will arrive at a reasonable answer. Topic 8 Fluency: Multiplying by 2-Digit Numbers 4.NBT.5. Multiply a whole number of up to four digits by a one-digit whole number, and multiply two two-digit numbers, using strategies based on place value and the properties of operations. Illustrate and explain the calculation by using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models. Major cluster I Can: 4.NBT.5 Apply the properties of operations to multiply numbers 4.NBT.5 Multiply a 2 digit number by a 10 4.NBT.5 Illustrate and explain multiplication using rectangular arrays This Unit has more emphasis on actual multiplication of 2-digit numbers than did the previous unit. The last unit focused on estimation as a way of students deciding if an answer was reasonable. This asks them to multiply and then uses their estimation skills to decide if an answer is reasonable. This standard calls for students to extend their understanding of place value related to multiplying and dividing by multiples of 10. In this standard, students should reason about the magnitude of digits in a number. Students should be given opportunities to reason and analyze the relationships of numbers that they are working with. Example: Rounding Commutative Property Compatible Distributive Property How is the 2 in the number 582 similar to and different from the 2 in the number 528? 4.OA.3 Solve multistep word problems posed with whole numbers and having whole-number answers using the four operations, including problems in which remainders must be interpreted. Represent these problems using equations with a letter standing for the unknown quantity. Assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies including rounding. Major cluster I Can: 4.OA.3 Write an equation to solve the word problem using a letter to represent the missing number. 4.OA.3 Determine if an answer makes sense, based on the problem. 4.OA.3 Justify my answers using mental math and estimation Example: On a vacation, your family bikes an average of 23 miles a day for 12 days. How many miles did they travel total? Some typical estimation strategies for this problem: Student 1: I first thought about 23 and 12. I used compatible numbers and thought of them as 20 and 10. I multiplies two and one together and got 2 and then I added two zeros at the end. I got 200. Student 2: I rounded 12 to 10 and multiplied 23 by 10 and got 230. The assessment of estimation strategies should only have one reasonable answer (200 or 230), or a range (between 200 and 250). Problems will be structured so that all acceptable estimation strategies will arrive at a reasonable answer.