Quiz #1

R
EFRACTION
R
EVIEW
1. _____ A swimmer (in a lake whose surface is perfectly calm) looks upward through the water at the setting sun. His view of the sun will make it appear a. lower than it really is b. higher than it really is c. the same as viewed above water d. smaller than it really is
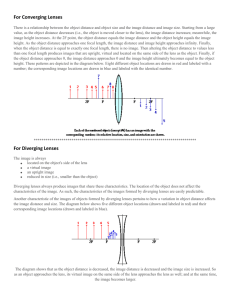
2. _____ The figure below shows the path of a portion of a ray of light as it passes through three different materials.
The figure is drawn to scale. What can be concluded concerning the refractive indices of these three n
1 n
2 n
3 materials? a. n b. n
1
< n
2
< n
3
< n
2
< n
3
1 c. n d. n
3
2
< n
1
< n
< n
1
< n
2
3
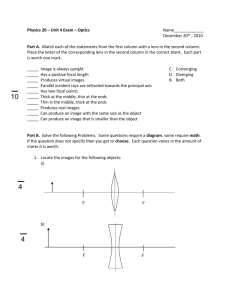
3. _____ For which piece of glass in the diagram below is the ray diagram correct?
A.
B.
4. _____ A ray of light, initially traveling in a vacuum, is incident on the surface of a flat transparent material as shown in the diagram to the right. Part of the light is reflected at the surface and part is refracted. The angle between
C.
the reflected ray and the refracted ray is a. less than 40° b. between 40° and 50° c. between 50° and 100° d. between 100° and 140° e. more than 140°
For the next two questions, light rays are passing from water into different substances, as shown:
D.
E.
f
A B C D
5. _____ Which substance has the highest index of refraction?
6. _____ In which substance is the speed of light almost unchanged?
7. _____ A diver is 1.2 m beneath the surface of a still pond of water. At what angle must the diver shine a beam of light toward the surface in order for the light to horizontally across the water? a. 41° b. 49° c. 59° d. 63°
8. _____ When an object is placed 25 cm from a lens, a real image is formed. Which conclusion is incorrect ? a. The image is upright. b. The lens is a converging lens. c. The image may be reduced or enlarged. d. The image distance can be less than 25 cm. e. The focal length of the lens is less than 25 cm.
9. _____ When an object is placed 15 cm from a lens, a virtual image is formed. Which conclusion is incorrect ? a. The lens may be a converging or diverging lens. b. If the image is upright the lens must be a diverging lens. c. If the image is reduced, the lens must be a diverging lens. d. If the lens is a diverging lens, the image distance must be less than 15 cm. e. If the lens is a converging lens, the focal length must be greater than 15 cm.
10. _____ An object is placed 20 cm from a diverging lens. A reduced image is formed. Which is necessarily true? a. The image is inverted. c. The image distance must be greater than 20 cm. b. The image could be real. d. The focal length of the lens may be less than 20 cm.
11. _____ An object is placed between f and 2f in front of a converging lens. The real image on the other side of the lens will be: a. inverted and smaller b. upright and larger c. inverted and larger d. the same size e. upright and smaller
The following two questions pertain to the situation described below:
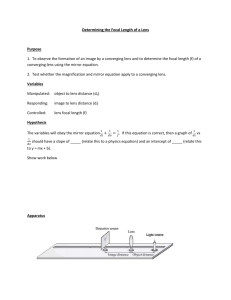
The figure below is a scaled diagram of an object and a lens. One focal point of the lens, F is shown.
Object
A B
F
C D E
12. _____ At which of the labeled points will the image be formed? a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E
13. _____ The lens is then immersed in a fluid that has an index of refraction that is larger than that of the lens. Which is true concerning this new situation? a. The image will be real. c. The image will be enlarged relative to the object. b. The image will be inverted. d. The image will be formed on the same side of the lens as the object.
14. _____ If the focal length of a converging lens is 12 cm, at what distance from the lens should an object be placed so that the resulting image formed is larger (choose all that apply)? a. 5 cm b. 10 cm c. 15 cm d. 20 cm e. 25 cm
15. _____ If the focal length of a diverging lens is 12 cm, at what distance from the lens should an object be placed so that the resulting image formed is virtual (choose all that apply)? a. 5 cm b. 10 cm c. 15 cm d. 20 cm e. 25 cm
16. _____ If the focal length of a converging lens is 12 cm, at what distance from the lens should an object be placed so that the resulting image formed is virtual (choose all that apply)? a. 5 cm b. 10 cm c. 15 cm d. 20 cm e. 25 cm
17. _____ When a ray of light passes from water into air at an angle slightly less than the critical angle, the angle of refraction is: a. 0° b. equal to the angle of incidence c. a little less than 90° d. a little less than the e critical angle
18. _____ In the diagram to the right, which path would the light take if i were less than the critical angle?
19. _____ In the diagram to the right, which path would the light take if i were greater than the critical angle?
20. _____ A ray of light originates in medium A and is incident upon medium B . glass air
i c d
For which set of values of the indices of refraction for A and B is total internal reflection not possible? n
A a. 1.36 n
B
1.00 a b b. 1.26 c. 2.54 d. 1.28 e. 1.12
1.15
1.63
1.36
1.06
21. _____ A beam of light in a glass prism is totally internally reflected. If the index of refraction of the glass is 1.5, a possible value of the angle of incidence could be: a. 40° b. 50° c. 60° d. “a” or “b” e. “b” or “c”
22. _____ In the demonstration where a laser beam was directed into a stream of water, it stayed in the stream, not leaving it until the stream landed in a catch basin. How was the light able to be trapped in the stream even though the water was transparent? a. The angle of incidence from the water to the air was greater than the critical angle. b. The angle of incidence from the water to the air was less than the critical angle. c. The optical density of the water was greater than the that of the air around it. d. The optical density of the water was less than the that of the air around it. e. “a” and “c” f “a” and “d” g. “b” and “c” h. “b” and “d”
23. _____ Which is the eye component responsible for farsightedness in virtually all older people? d. retina a. cornea b. lens c. fovea
24. _____ Why is it difficult to focus on an object in dim light? a. The choroids in humans are black, absorbing all incident light. b. The fovea contains only cones and no rods. c. Available light is too strongly absorbed by the cornea. d. The iris is limited in its ability to increase aperture size.
25. _____ A boy has a near point of 75 cm. Which statement below is true? a. He is nearsighted and requires diverging lenses to correct her vision. b. He is nearsighted and requires converging lenses to correct her vision. c. He is farsighted and requires diverging lenses to correct her vision. d. He is farsighted and requires converging lenses to correct her vision.
26. _____ A girl has a far point of 25 cm. Which statement below is true? a. She is nearsighted and requires diverging lenses to correct her vision. b. She is nearsighted and requires converging lenses to correct her vision. c. She is farsighted and requires diverging lenses to correct her vision. d. She is farsighted and requires converging lenses to correct her vision.
27. _____ After staring at the secondary color, yellow, and then looking at a white surface, why will you see blue? a. The yellow cones have been fatigued b. The red cones have been fatigued c. The green cones have been fatigued d. Both “a” and “b” e. Both “a” and “c” f. Both “b” and “c”
28. The transparent block below has an index of refraction of 1.70. Trace the given rays through the block until they have emerged back into the air.
29. Make ray diagrams to locate the full images. Mark these images with an “I.”
2f
2f
2f f f f f f f
2f
2f
2f
30. A 10-cm tall object is 20 cm away from a lens like the one you used in the Lens Labette. It produces an image that is twice the size of the object. a. What is the focal length of the lens? b. Now make a scale ray diagram using the object distance above and the focal length you just calculated. When you have located the image with your diagram, measure is distance and then compare it to the image distance you used as a given in part “a.” c. If the same object were in the same position in front of a lens that had the same focal length as the one above, but was a diverging lens, how tall would the image be? Do this first with the lens equation and then with a scale ray diagram. d. Now assume that the object is 6.0 cm in front of the original converging lens. How tall will the resulting image be? Do this first with the lens equation and then with a scale ray diagram.
Honors Physics only beyond this point
31. A 1.0-cm tall object is placed 20 cm to the left of a converging lens with the focal length 15 cm. A concave mirror with a focal length of 10 cm is located 75 cm to the right of the lens. What is the height of the image produced by the lens/mirror combination?
32. A candle is located 25.00 cm to the left of a converging lens (f = 20.00 cm). A second identical lens is placed to the right of the first lens, such that the image formed by the combination has twice the size and the same orientation as the original candle. Find the distance between the lenses.
33. A 4-cm high object is placed 30 cm to the left of a converging lens that has a focal length of 10 cm .
A second converging lens is placed 20 cm to the right of the first lens. Determine the focal point of the second lens if an image is formed 13.3 cm to the right of the first lens.
34. An object is placed 36 cm from a set of three lenses. The first is a converging lens with a 24 cm focal length. The next lens is 18 cm from the first lens. It is a diverging lens with a focal length of 18 cm. The last lens is 9.0 cm beyond the second lens. It is a converging lens with a 12 cm focal length. Find the position of the image.