Mrs. Hughes EM Spectrum & Waves Name: Date: ______ Core
advertisement

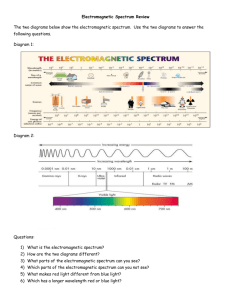
Mrs. Hughes Date: ________ EM Spectrum & Waves Name: __________________ Core #: ________ Electromagnetic Spectrum Waves Powerpoint Slides: 2. Electromagnetic Radiation (energy) comes from the ______________________. * Energy from the sun (152 million km away) reaches earth in _________minutes. Travelling at the speed of light 300,000 km per second 3. Electromagnetic Spectrum Waves: long wavelengths = _______________ waves short wavelengths = ______________ waves 4. The sun's energy reaches the Earth in _____________________________ waves (ie. x-rays, light rays, gamma rays) – S waves 5. Two types of waves: a) Compressional waves - such as ________________waves; require a medium to transfer energy. b) Transverse waves - such as ____________________ waves - can transfer energy in a vacuum, without a medium. 6. Wave Characteristics: Label- Crest, Trough, Amplitude, wavelength, & Rest position (or equilibrium poition) 7. ______________________= the number of wave crests that pass a point during one second. Measured in _____________ (Hz =cycles per second). * Note: as wavelength increases, frequency ________________________. 8. ______________________= amount of energy transferred (hint: dimmer switch). The larger the amplitude the (higher or lower) the energy. 9. Electromagnetic Spectrum: Wonders? 10. Radio waves = Wavelength longer than 30cm (AM radio appx. 1km) Uses: _____________________________________________________ * Your radio captures radio waves emitted by radio stations (stations accelerate electrons in a circuit with an antenna). Electrons wiggling back & forth create an EM wave * So many senders & receivers international regulations on frequencies * In space, radio waves are created by electrons accelerating away from supernova explosions, by some galaxies, by clouds of gas where stars are forming, and by rotating collapsed dead stars (neutron stars). Astronomers used radio waves from space to detect the presence of a black hole. 11. Microwaves = 1mm – 30cm Uses: *______________________ – cause water molecules to vibrate enthusiastically (heat) *_______________________- Wifi & Bluetooth * by astronomers to learn about the structure of nearby galaxies 12. Infared Radiation = 1 millionth meter – 0.1 mm (point of a pin) * Slightly less energy than visible light * Produced by the vibration of atoms within molecules – we perceive this as heat Uses: * _____________Photographs – houses; diseased areas on the surface of the human body * __________________________________ for TV 13. Visible Light = size of a bacterium Lowest energy visible light we see = _____________________(750nm) Highest energy visible light we see = _____________________(450nm) 14. Ultraviolet = size of a virus (10nm) * Slightly more energy and shorter wavelength than your eyes can detect * Some insects can detect near UV light Uses: * _________________________: long exposure = damage to skin & eyes * _________________________: Counterfeit money & black light paint 15. X-Rays = 10nm-0.01nm (size of a water molecule) * Discovered in 1895 & put to use in ____________________imaging * More energetic & shorter wavelength than UV so they pass right through matter that appears opaque to our eyes. * Used to measure thickness in _________________________. 16. Gamma Rays = 0.01nm – 0.0001nm (smaller than an atom) * Short wavelengths & more energy * Blocked only by thick heavy metals (lead & concrete) * Can damage living tissue & DNA * Sometimes used to kill cancer cells & irradiate medical equipment & food to destroy bacteria * On earth, most come from nuclear reactions & decay of radioactive materials * Astronomers use these rays to study unusual events in distant galaxies (pulsars, quasars, hypernovae) 17. Foot: can only be viewed in X-ray, UV, Visible, and Infared a) Observations? Infared: Visible: Ultraviolet (UV): X-ray: 18. Moon: a) Observations? Radio: Microwave; Infared: Visible: Ultraviolet (UV): X-ray: Gamma ray: 20. Let’s take a closer look at the Electromagnetic Spectrum 1. What do you notice? 2. What uses Infrared radiation? 3. What is UV protection on Sunscreen? 4. What type of radiation has the longest wavelength and lowest energy? 5. What type of radiation has the shortest wavelength and the highest energy? 6. What types of radiation have higher energy than visible light? Which have lower energy than visible light?