1.Background
advertisement

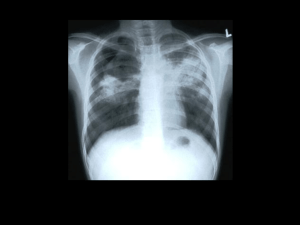
MINISTRY OF HEALTH UKRAINE Vinnytsya National Medical University them. Pirogov "Approved" upon methodical conference Department of the rate of tuberculosis Clinical Allergy and Immunology Head of Department Professor B. Puhlyk _________________________ (signature) „_29___”__avgusta 2013 р. GUIDELINES INDIVIDUAL WORK OF STUDENTS WHILE PREPARING FOR THE PRACTICAL LESSON AND WORK IN THE CLASSROOM Academic discipline Module number 1 Subject classes Course Faculty Phthisiology Phthisiology Pulmonary tuberculosis combined with professional dust diseases. Tuberculosis in patients with HIV / AIDS. Ambulatory diagnosis. 4 th of Medicine Vinnytsya – 2013 1.Background Tuberculosis - an infectious disease, which is based on the formation of caseous necrotic changes in the lungs or other organs. Some groups, professional activities which are connected with harmful factors are at increased risk of contracting tuberculosis. These patients often are forms that occur with a covert, asymptomatic clinical course, or there are certain diagnostic difficulties to detect tuberculosis against changes in the lungs due to the influence of occupational factors. These patients often are forms that occur with a covert, asymptomatic clinical course, or there are certain diagnostic difficulties to detect tuberculosis against changes in the lungs due to the influence of occupational factors. In regard to the timely detection of tuberculosis and the appointment of an adequate treatment regimen should be able to properly collect complaints data history of life and disease, conduct physical and Radiological Examination required. Koniotuberkulosis - pulmonary tuberculosis combined with professional dust disease of the lungs. In recent years Ukraine simultaneously developing two socially dangerous epidemic diseases - tuberculosis and HIV / AIDS, which often affect the same groups. Tuberculosis is the most common opportunistic disease was the main cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with AIDS. Among HIV-infected and AIDS patients the most common opportunistic infection is tuberculosis. HIV infection increases the risk of active tuberculosis and, conversely, tuberculosis adversely affect the course of HIV infection. WHO experts believe that the incidence of HIV / AIDSassociated tuberculosis is a sensitive indicator of HIV prevalence in the general population. According to the literature summarized above 30% of HIV-infected people suffering from tuberculosis and about 30-40% of ill die from tuberculosis. Due to the deterioration of the epidemiological situation of tuberculosis in Ukraine and worldwide, increasing morbidity and mortality from tuberculosis, ineffective TB control activities in Ukraine implemented DOTS therapy DOTS therapy (Directly Observed Treatment Short-course - strictly controlled treatment short course chemotherapy). 2. Learning Objectives: The task of the teacher - to teach students basic diagnostic stages of diagnosis koniotuberculosis. With the participation of the teacher, students must: 1. Familiar with the method of collecting history, especially attracting attention in professional history and clinical symptoms and physical methods of examination (percussion, auscultation, palpation) TB patients. 2. To study the radiological implications of different forms of pulmonary tuberculosis. 3. To study the radiological implications silikosis, antrokosis, asbestosis. 4. Determine the required level of laboratory diagnosis, to be able to evaluate this spirometry, ECG abnormalities. 5. Master the stages of the diagnostic process. 6. Teach students the proper collection of complaints, medical history and life, hold on "subjective test to determine the X-ray shadow of the main pathological characteristic of tuberculosis. In addition, the student must know certain social groups (drug addicts, prostitutes), which primarily require screening for tuberculosis. Future Specialist must have the ability to explain the necessity renhenolohichnoho or laboratory testing for tuberculosis, know the basic steps to test and pissing konsultuvnnya, possess basic rules of ethics and deontology in the diagnosis of HIV / AIDS-associated tuberculosis. 7. Determination of basic principles, objectives, methods and conditions of DOTS therapy. Future specialist must possess basic questions about diagnosis and treatment of TB patients through DOTS system. 3. Basic knowledge, skills necessary for studying the topic (interdisciplinary integration) The names of previous subjects 1. Human Anatomy 2. Normal physiology 3. Physiopathology 4. Pathologic anatomy . 5. Microbiology, Virology and Immunology 6. Pharmacology 7. General hygiene Received skills . General plan of structure of the lungs. The structure of the membrane wall air ways. Value for breathing organism. Ventilation of the lungs and alveoli, its uneven in different regions of the lungs. . General pathology, respiratory pathology. Ways of penetration and distribution of mycobacteria in humans Tuberculosis. Etiology and pathogenesis. Productive granulomatous inflammation. Structure specific granulomas in tuberculosis. Changes in lung parenchyma arising in koniozah. Study of infectious process. Mycobacteria (the causative agent of tuberculosis), its structure, properties, resistance. Types of MBT and their epidemiological significance. Pharmacokinetics of drugs. TB antibiotics and chemotherapy, classification, dosage, methods of administration. Concept of occupational hazards and diseases. Rising incidence of tuberculosis among health care workers. Fundamentals of nutrition, physical education and hardening in the prevention of tuberculosis. 4. Tasks for independent work in preparation for employment. The list of basic terms, parameters, characteristics, which the student must learn in preparation for the Session: Term Pneumokoniosis: silikoz, silikatoz (asbestosis, talkoz, cement) metalokoniozy (Berlioz, siderosis, alyuminlz, barytoz) karboniozy (anthracosis, hrafitoz, soot pneumoconiosis), pneumoconiosis from smishanoho dust penvmokoniozy from orhanchnichnohor dust (cotton, corn, cork, trostnikovoyi) 2. Complaints in patients Coney tuberculosis. 3. "Fireplace" 4.. Infiltration 5. Dissemination 6. . Active detection of HIV / AIDS-associated TB. 7. Passive detection of HIV / AIDS-associated tu-TB 8. . DOTS therapy 9. Category 10. The effectiveness of therapy Definition Group of diseases that are characterized by changes in the pulmonary system by getting outside certain dusting compounds. Intoxication syndrome. Bronhoplevrapulmonary syndrome. Shadow to 1 cm Shadow than 1 cm Centers shadows that capture 3 or more segments. Diagnosis of tuberculosis in patients with HIV / AIDS infection in the registration of new cases of HIV infection in the annual preventive screening patients rest of this contingent. Diagnosis of tuberculosis in patients with HIV / AIDS infection in facing the health facility with symptoms similar to tuberculosis. Controlled treatment short course chemotherapy. The set of patients by type of tuberculosis Termination bacteria, healing cavities collapse, positive radiological speaker disappearance of signs of intoxication and clinics bronchopulmonary syndrome. Theoretical question for the class: Теоретичні питання до заняття: 1. The main epidemiological indicators in Ukraine and abroad. 2. Recent developments in the treatment of tuberculosis. 3. The main objectives, principles and objectives of DOTS therapy.4 4. . Terms implementation of DOTS therapy. 5. Concept adapted DOTS treatment in Ukraine. 6. The effectiveness of DOTS therapy. 7. Main clinical features of the course of tuberculosis in patients with AIDS 8. Features of the collection and the life history of the disease in patients with HIV / AIDSassociated tuberculosis. 9. The main clinical symptoms of tuberculosis in patients with HIV / AIDS. 10. Radiographic methods (fluorography plain film, tomogram). 11. Basic radiological syndromes in respiratory diseases. 12. Use of tuberculin for the diagnosis of tuberculosis in patients with AIDS. 13. Features of the collection and the life history of the disease in patients koniotuberculosis. 14. The main clinical symptoms in patients koniotuberculosis. 15. Radiographic methods (fluorography plain film, tomogram) at koniotuberculosis. 16. Basic radiological syndromes in k koniotuberculosis. 17. Stages diagnosis " koniotuberculosis " Practical studies performed in preparation 4.3.1. Fill in the table Task Key answer List the laboratory methods for detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. 2. What bacterioscopic detection methods MBT ? 3. What do you know types of mycobacteria? 4. What are the ways of human infection with TB? 5. What are the most characteristic changes hemogram with active tuberculosis? 6. What is tuberculin? 7. What are the results of the Mantoux test you know? 8. What methods of radiologic diagnosis you know?: 9. What is DOTS strategy? 10. What are the basic principles of the aims and objectives of DOTS? 1. 11. Which category of patients includes DOTS system for standard treatment? for the Session: 12. What schemes DOTS therapy exist for certain categories of patients? 13. What provides adapted to the conditions of Ukraine DOTS strategy for the diagnosis and treatment of TB? 14. What is the role of general practitioners in the early detection of tuberculosis? 15. What complaints comprises intoxication syndrome? 16. What complaints comprises bronhopleuralpulmonary syndrome? 17. What are the ways HIV you know? 18. What are the main clinical features of the course of tuberculosis in AIDS patients? 19. What properties have enlarged peripheral lymph gland tuberculosis patients with HIV / AIDS? 20. What forms koniotuberkulosis you know? 21. What complaints from a patient koniotuberculosis? 22. What features collection that the history of life in patients with koniotuberculosis? 23. What are the major changes spirohrami in patients with koniotuberculosis 24. What the methods of X-ray diagnosis koniotuberculosis you know? 4.3.2. Solve test tasks: 1. How many fractions in the right lung? A. Two V. * Three C. Ten D. Eleven 2. What is the focal shadow? A. * Shadow to 1 cm B. Shadow than 1 cm S. Shadow 2 cm 3.What is coughing up blood? A. Isolation of more than 100 ml of blood per day V. * Select up to 50 ml of blood per day C. Selection of more than 50 ml of blood per day 4. What are the main method of X-ray examination to detect cavities in the lungs? A. X-ray B. Plain radiographs in the direct projection S. * tomogram D. Bronhografiya 5. Practical tasks performed on classes: 5.1. Run gathering complaints, medical history, occupational history, history of life. 5.2. Carry out inspection, palpation, percussion and auscultation of a patient with tuberculosis. 5.3. Describe survey radiographs of the chest cavity in a straight projection. 5.4. Аn assessment of the results of laboratory testing, ECG data, spirohramy. 5.5. denitify changes in parameters hemogram in patients with active tuberculosis. 5.6.To be able to palpate increased peripheral lymph gland. 5.7. Be able to identify positive symptoms Franko, Vederhofera. 5.8. Learn to read radiographs, tomograms with signs of primary TB. 5.9. Categorize the patient to the standard treatment regimen based on the results of X-ray and laboratory examinations. 5.10. A standard scheme for DOTS therapy system for certain categories of patients. 5.11. Learning basic diagnostic steps in establishing a diagnosis of HIV / AIDSassociated tuberculosis. 5.12. Run gathering complaints, medical history, occupational history, history of life. 5.13. Describe survey radiographs of the chest cavity of a patient with direct projection koniotuberculosis. Content topics: 1. Vyzel A.A., Hurylyova 2. Occupational illness. M.E/ "Tuberculosis." Moscow, 6. Materials for self-control and the final level of learning material: №№ Завдання 1. The patient on examination found the lag of the chest in breathing, bulging intercostal spaces, sharply reduced voice Відповідь 2001. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. tremor on this side, lower respiratory rumors. What do you expect to see on radiographs of the chest? The patient koniotuberculosis lungs. Suddenly, after a severe attack of coughing, chest pain appeared, which gradually increases. What this could mean and what test should be done? An examination of the patient revealed a shift of the trachea toward the midline of the body. Who was described this symptom and what processes in the lungs it can cause? In Miner at x-ray of the lungs revealed syndrome dissemination. What kind of disease to think about in the first place and that more tests should be done to elucidate the origin of dissemination? From what method should begin in a hospital X-ray screening for lung koniotuberculosis: and / fluorography; b / fluoroscopy; in / radiography; g / imaging; d / elektro-X-ray Which segments of the lung often localized tuberculosis processes? What may appear radiographically change root lungs koniotuberculosis? Define radiographic term focus: A / shadow within the segment; b / shade smaller than 1 cm; in / shade more than 1 cm; g / availability clarification sizes up to 1 cm in the center of the eclipse. What pathological processes lead to a shift of the mediastinum (with unilateral lesions): a/ towards destruction; b / in the opposite direction What are the main radiological syndromes in koniotuberculosis lungs? What is the minimum radiographic examinations should be used to detect cavities? and / Plain radiography; b / imaging; in / fluorography; g / bronchoscopy; d / lateral radiography 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 The patient appeared hemoptysis, increased body temperature. What radiographic examination and in which order should I do? On what type of violations going on spirohramy in patient koniotuberculosis lungs and what type of dyspnea is most typical of these patients? Patient D, a strong cough, hemoptysis. Last month he lost 5 kg. What auxiliary examination methods necessary for diagnosis? How does the X-ray phase collapse? At what stages of development koniotuberculosis observed changes in the roots of the lungs? What is an invasive method to confirm the diagnosis koniotuberculosis? What are the basic principles of the DOTS strategy? What are the main criteria for categories of patients under the DOTS system. A patient with disseminated tuberculosis with collapse and there is bacteria. Which category should include the patient? The patient appeared relapse of tuberculosis. Which category should include this patient? At the end of the intensive phase of treatment the patient achieved a positive X-ray dynamics, termination of bacteria. What further tactics patient? What is the abbreviation with anti-TB drugs? specify regimen therapy according 1,2,3 categories. After being discharged from the hospital the patient is recommended to continue 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 treatment at the place of residence. Who is responsible for the out pathient treatment? A patient who is registered with the center for prevention and control of AIDS present cough for two months. Do I need to perform X-ray examination of the chest, where the survey was carried out 4 months ago? In a patient with HIV infection present bronchopulmonary syndrome. On radiographs of pathological changes were detected. Do I need to perform in this case of sputum for MBT? In a patient with HIV infection present bronchopulmonary syndrome. On radiographs of pathological changes were detected, MBT (-) three times. What should be the doctor's tactics in this case? In a patient with HIV infection in the lungs x-ray revealed a round shadow. What kind of disease to think about in the first place and that more tests should be done to elucidate the etiology of the shadows? What are the contraindications to perform tuberculin exist in patients with HIV / AIDS? What changes are possible in the hemogram in patients with HIV / AIDSassociated TB? What changes in immunogram possible in patients with HIV / AIDS-associated TB? What agents can cause inflammation in the lungs of patients with AIDS? Literature. Summary 1. "Tuberculosis" I.T. P"yatnochka. Ternopil. "Ukraine"., 2005. 2. Pylypchyk MS, Petrenko VI , Phthisiology. Textbook. Kyiv: High School, 1998. – 296 p. 3. Savula MM, AJ Ladny Tuberculosis. Textbook. Ternopil 'Ukrmedknyha ", 1999. 323 p. 4. NV Putov, GB Fedoseev "Guide to pulmonolohyy", 1964.-455 p. 5. Tuberculosis respiratory organs / Ed. A.H.Homenko. - Moscow: Medicine, 1988. 576 p.


![Working Group on New Diagnostics Quiz []](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/005832552_1-2f3950d800e81be53089eed30c91f80b-300x300.png)
