Lecture #58 – The Shoulder: Special Tests Notes Special tests
advertisement

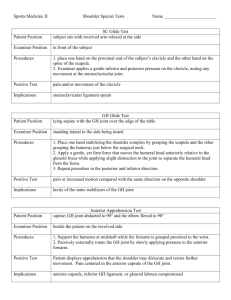
Lecture #58 – The Shoulder: Special Tests Special tests Categories Ligamentous Stability tests Pathology Biceps tendon Labral Tear Impingement Neurovascular Ligamentous tests Piano key test Patient position: standing or seated Examiner position: anterior or lateral to patient Examiner action: o Hand #1 – gentle stabilization of humeral head o Hand #2 – of clavicle (piano key) Positive: excessive motion at AC joint, pain, ↑ in symptoms Pathology: AC ligament sprain Modification: “Tap” on clavicle (Fx Test) AC shear/compression test Patient position: standing or seated w/arm at side Examiner position: lateral to patient o Hands – cupping the AC joint with interlocking fingers Heel on distal clavicle with fingers over the AC Heel on scapular spine with fingers over the AC Examiner action: gentle squeezing heels together Positive: excessive at AC joint, pain, ↑ in symptoms Pathology: AC ligament sprain Apprehension test Patient position: supine (edge of table) o GH Joint to 90° & elbow flex to 90° Examiner position: lateral to patient o Hand #1 – distal humerus or elbow o Hand #2 – distal forearm or wrist Examiner action: o Support shoulder at 90° ABD o Slow rotation of shoulder Positive: look or action of apprehension by patient o Pain centered in anterior shoulder Pathology: Anterior capsule, ligaments, or labrum injury o Humeral head has potentially previously o Do NOT perform if assessment is obvious Relocation test Patient position: supine (edge of table) o Shoulder at 90° ABD, and elbow flex to 90° Notes Examiner position: lateral to patient o Hand #1 – distal humerus or elbow o Hand #2 – distal forearm or wrist Examiner action: o Slow ER of shoulder until pain or apprehension is felt o is applied to anterior humeral head Positive: apprehension ↓ with posterior force Pathology: GH ligament sprain (anterior) or capsular laxity Stability tests Sulcus sign Patient position: standing or seated w/arm at side Examiner position: anterolateral to patient Examiner action: o Hand 1 – Supporting scapula o Hand 2 – firm traction of distal humerus Positive: gapping between and humeral head o Just humeral head moves in this test Pathology: GH ligament and/or capsule sprain (superior) Wall push-up test Patient position: standing arm’s length from wall Examiner position: posterior & lateral to patient Patient action: o Patient performs push-ups against wall o Younger & stronger patients may perform normal push-ups Positive: border of scapula lifts off the thorax o Usually in 5-10 reps Pathology: muscle weakness o Long Thoracic Nerve Injury Rotator cuff pathology tests Drop arm test Patient position: standing or seated Examiner position: anterior or lateral to patient Patient action: passive shoulder ABD o Can perform actively Examiner action: o Asks patient to slowly lower arm (added resistance as needed) Positive: inability to return arm to side slowly or severe pain Pathology: Tear of the rotator cuff o Usually tendon Full can test Patient position: standing or seated Examiner position: anterior to patient Patient action: o ABD to 90° in the plane of the scapula w/examiner resistance o Lecture #58 – The Shoulder: Special Tests Examiner action: o Isometric manual resistance to ABD Positive: weakness and/or pain with resistance Pathology: supraspinatus impingement, strain, or inflammation Gerber lift-off test Patient position: standing with dorsum of hand on lumbosacral joint Examiner position: lateral to patient Patient action: o Active IR of arm (“ ”) Positive: weakness and/or pain with inability to lift hand off back Pathology: strain/weakness Biceps tendon tests Speed’s test Patient position: standing/sitting in anatomical position (palms forward) Examiner position: anterior or lateral to patient o Hand #1 – stabilize shoulder w/palpation of bicipital groove o Hand #2 – distal and anterior forearm Action: resist active of shoulder Positive: pain and/or tenderness at bicipital groove Pathology: biceps tendinitis (tenosynovitis) Labral tests O’Brien’s test Patient position: seated or standing o GH joint flexed to 90o and Horiz. ADD 15o from front o Full humeral and pronated forearm Examiner position: anterior to patient o One hand place over superior aspect of patient’s distal forearm Examiner Action: o Pushes downward on forearm o Test repeated with humerus ER and forearm supinated Positive: Pain experienced with arm in but is ↓ during Pathology: labral tear ( ) Impingement tests Neer impingement test Patient position: seated or standing in anatomical position (palms forward) Examiner position: anterolateral to patient o Hand #1 – stabilize posterior shoulder o Hand #2 - forearm Action: forearm pronation, IR & forced passive of shoulder Positive: pain, apprehension by patient, inability to move, etc. Pathology: (supraspinatus, subacromial bursa, biceps tendon) Notes Hawkins-Kennedy test Patient position: seated or standing in anatomical position (palms forward) Examiner position: anterolateral to patient o Hand #1 – distal humerus/elbow o Hand #2 – distal forearm Action: o Passive flexion of shoulder and elbow to 90° o Followed by forced Positive: pain, apprehension by patient, inability to move, etc. Pathology: impingement syndrome Neurovascular tests Brachial plexus stretch test Patient: seated and relaxed Examiner: standing anterior to patient Action: examiner forces and shoulder depression o Hand #1 side of head o Hand #2 lateral aspect of shoulder Positive: reproduction or ↑ in Sx & Sy (pain) to side being stretched Pathology: brachial plexus lesion o Pain on side compressed = nerve Do not perform if cervical fracture or dislocation is suspected Roo’s test Patient position: standing looking forward Examiner position: Posterior to patient Patient Action: o ABD to 90˚, Elbow flexed to 90º (90-90 position) o hands slowly for 3 minutes Positive: Unable to maintain position, suffers pain, weakness of arm, numbness, tingling Pathology: Syndrome o Compression of artery between clavicle and first rib Stretch reflexes Strike the tendon with a reflex hammer o Use your thumb to protect the tendon and focalize the force of the hammer Observe for the stretch reflex Repeat 3-6 times for consistency o Biceps brachii reflex o reflex o Triceps brachii reflex