eq09
advertisement

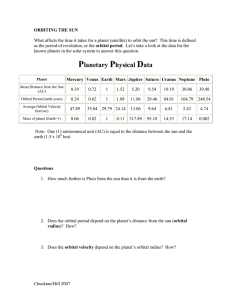
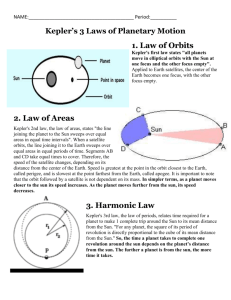
GRAVITATION Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion 1. The path of each planet around the Sun is an ellipse with the Sun at one focus. 2. Each planet moves so that all imaginary lines drawn from the Sun to the planet sweeps out equal areas in equal periods of time. 3. The ratio of the squares of the periods of revolution of planets is equal to the ratio of the cubes of their orbital radii. r M G radius of orbit [m] mass of planet or large massive object such as the Sun Universal Gravitation Constant G = 6.67x10-11 N.m2.kg-1 T period of revolution of planet or satellite [s] vorb orbital velocity of planet or satellite [m.s-1] vesc escape velocity of space craft or satellite [m.s-1] Kepler’s 3rd Law r 3 GM T 2 4 2 vorb2 r13 r2 3 T12 T2 2 3 1 2 1 r2 T2 3 r r 22 T T2 vorb1 M r1 T1 3 r2 2 T2 T1 r1 Orbital period T 2 r vorb geostationary satellite T = 24 h Orbital velocity is the velocity of an object in an orbit around a massive object. The motions GM of the planets around the Sun are elliptical in shape. vorb r Equation Mindmap eq09: Doing Physics on Line 1 Escape velocity of a projectile launched from the surface of a planet (or moon) is the minimum velocity with which the projectile must leave the surface in order to escape from the effects of the planet’s gravity (this occurs at an infinite distance from the planet) vesc 2GM r If vlaunch < vesc object returns to surface or goes into orbit around the massive object. Equation Mindmap eq09: Doing Physics on Line 2