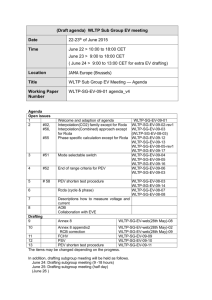
DraftingUnit

Christian Snead Subject: Life Skills 8
Unit Title: Drafting
Number of Lessons: 5 - 6 Time in weeks: 1.1
Rationale: To teach students the
basic
design concepts and their application to real-world design situations and to accurately represent objects in accordance to industry standards.
Students will be introduced to:
geometric concepts
fundamentals of graphic representation and presentation
the relationship between real objects, 3-D visualizations (object space), and 2-D representations (paper space)
accurate description of the size and shape of an object, using the principles of projection
relating and understanding of drafting and design to personal, economic and societal considerations.
Students will be able to:
determine the relative size and shape of surfaces as well as solids, using multi-view and pictorial representation
create finished drawings of complex three-dimensional objects and spaces on two-dimensional surfaces
Overview: This unit is a direct lead in from our previous unit of Introduction to technology education, where the design process (IDEAL) was introduced.
Prerequisite Concepts and Skills: basic drawing skills
Teacher preparation required: handouts, former students samples
Resources: http://myclass.peelschools.org/sec/11/28370/Lessons/Technical%20Drawing%20Lessons/Orth ographic%20Projection%20Lesson%20revised.pdf
Cross –Curricular Connections: Math (scale drawings, geometric concepts, arithmetic, conversion and estimating techniques) and Art (computer aided drafting CAD graphical techniques to mentally visualize 3D objects).
UDL and DI strategies: For enrichment, students will be encouraged to use various computer software programs to create more elaborate drawings. Also, students who struggle with the
1
basic drafting concepts or have difficulty with fine motor control will have adaptations made to the assignments.
Overview of Lessons:
Lesson #1
Introduction to Drafting and the basic drafting tools
(65 mins.)
Core Lesson Concepts:
* What is drafting?
* Why and when do we use drafting?
* Where is drafting used in our society?
PLO’s in lesson - Students will be introduced to:
basic design concepts and their application to real-world design situations
basic geometric concepts used in drafting
basic tools used in drafting (T square, protractor, ruler, compass, paper, pencil)
the relationship between real objects, 3-D visualizations (object space), and 2-D representations (paper space)
Instructional Objectives and Teaching Strategies:
*Introduce the concept of drafting to students.
*Familiarize students with tools required for drafting
Lesson Activities:
Materials specific to this lesson:
*Class discussion around where and how drafting applies in our lives.
*Discuss where drafting fits into the design process
*Students work on task (letter practice sheet)
Assessment Strategies:
Formative Assessment – students participate in class discussion and begin to explore how drafting impacts their world. Students also complete lettering practice sheet.
Hand out – letter practice sheet
Drawing board
Drafting tools: T square, protractor, ruler, compass, pencils
2
Lesson #2 and #3
Title block, lines and angles
(130 mins. 2 classes)
Core Lesson Concepts:
* Introduce the title block and measurement concepts
* Introduce the basic lines used in drafting: guide line, object line, hidden line, and centre line, dimension line, extension line
*Explain why and when the drafting lines are needed in drafting
PLO’s in lesson: Students will be introduced to:
basic design concepts and their application to real-world design situations
basic tools used in drafting (T square, protractor, ruler, compass, paper, pencil)
the relationship between real objects, 3-D visualizations (object space), and 2-D representations (paper space)
Instructional Objectives and Teaching Strategies:
*Introduce the title block, and drafting lines to the students
*Teach the various measurements and degrees in drafting
*Demonstrate how to make accurate angles using drafting tools
*Familiarize students with tools required for drafting
Lesson Activities:
Materials specific to this lesson:
*white board in classroom
*handout with drafting angles, title block, and drafting lines
*T square, ruler, protractor, ruler, paper, pencils
Assessment Strategies:
students participate in class discussion
students complete sheet with protractor angles title block and reproduce the drafting lines.
Hand out – drafting angles and drafting lines
Drawing board
Drafting tools: T square, protractor, ruler, compass, pencils
3
Lesson #4
Introduction to Orthographic Drawing
(65 mins)
Core Lesson Concepts:
* Introduce a multi-view drawing (orthographic drawings)
* Explain where, when, why and how orthographic drawings are used.
PLO’s in lesson: Students will be introduced to:
comprehensive and conventional representation of objects for the purposes of production (i.e., details + assembly = simple to intermediate working drawings)
• scale representation of:
− complex 3-D details in orthographic
− simple objects in pictorial
Instructional Objectives and Teaching Strategies:
*Students will look at how to understand and view a multi-view drawing. Students will be able to accurately point out and a draw the side view, top view and front view of an object.
Teacher explains principles of orthographic drawing.
Teacher shows students the sample of the door stop orthographic drawing.
Students have an opportunity to handle the door stop
Students work on reproducing the orthographic drawing of the door stop – they can used the hand out as their guide.
Lesson Activities:
Materials specific to this lesson:
*white board in classroom
*door stop (to be reproduced in orthographic drawing)
*paper and pencil and drafting tools (T-square, ruler)
*handout with orthographic picture of door stop, which students use as a guide
*handout of definitions and 3D picture of Porsche 911
Assessment Strategies:
students participate in class discussion
students complete sheet with protractor angles title block and reproduce the door stop object correctly. Teacher marks drawings on criterion referenced assessment rubric.
4
Lesson #5
Introduction to Isometric Drawing
(65 mins)
Core Lesson Concepts:
* Introduce an isometric drawing
* Explain where, when, why and how isometric drawings are used.
PLO’s in lesson: Students will be introduced to:
accurate description of the size and shape of an object, using the principles of projection
clear communication of the relative size and shape of surfaces as well as solids, using multi-view and pictorial representation
creation of finished drawings of complex three-dimensional objects and spaces on two-dimensional surfaces
Instructional Objectives and Teaching Strategies:
*Students will look at how to understand and view an isometric drawing.
Teacher explains principles of isometric drawing. Teacher reinforces concepts of orthographic drawings introduced in last lesson and shows how isometric drawings are an extension of this.
Teacher shows students the sample of the door stop isometric drawing.
Students work on reproducing the isometric drawing of the door stop – they can used the hand out as their guide.
Lesson Activities:
Materials specific to this lesson:
*white board in classroom
*door stop (to be reproduced in isometric drawing)
*paper and pencil and drafting tools (T-square, ruler)
*handout with isometric picture of door stop, which students use as a guide
Assessment Strategies:
students participate in class discussion
students complete sheet with protractor angles title block and reproduce the door stop object correctly. Teacher marks drawings on criterion referenced assessment rubric.
5