SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Supplementary Table 1. Definitions of
advertisement

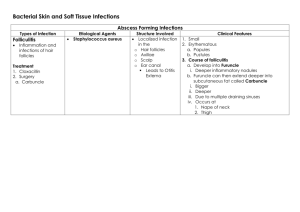
SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Supplementary Table 1. Definitions of device-related infection in the included studies. Study ID Definition Muers 1981 Oral temperature of 37.5°C on ≥2 occasions on or after the 3 rd postoperative day with evidence of acute inflammation and of pus or bacteria in the generator pouch; or frank pus in the generator pocket. Erosion with secondary infection was excluded. Ramsdale 1984 Pocket infection: oral temperature of ≥37.5°C on ≥2 occasions on or after the 3rd postoperative day associated with acute inflammation around the generator and/or pus in the generator pocket. Superficial wound infection: indurated discharging and nondischarging wound edges without evidence of pocket infection, requiring antibiotic treatment but not generator replacement. Bluhm 1984 Presence of purulent substance and/or increased local temperature, redness, pain and swelling. 2728272828 Bluhm 1986 Purulent secretion; or ≥2 inflammatory signs of local temperature rise, redness, pain and swelling together with a positive culture; or all 4 inflammatory signs without positive culture. Erosion of generator/lead was excluded. Glieca 1987 Fever (>37.5°C) with local signs of inflammation or purulent secretion at the pocket site. Positive cultures were found in all cases. Mueller 1990 Criteria proposed by Choo et el.: 1) Inflammation and abscess formation at the implant site. 2) Erosion of the pacing system with secondary infection. 3) Fever and positive blood cultures without any other source of infection. Positive cultures from the infected site essential for the diagnosis of infection. Bru 1991 Local signs of inflammation at the pocket associated with ≥1of the following: positive cultures, purulent secretion or general signs of infection. Lüninghake 1993 Microbiologically proven infection and local aseptic inflammation. Mounsey 1994 Septicaemia, pocket abscess, or erosion of the pulse generator or electrode through the skin; all requiring a repeat operation. Chauhan 1994 Criteria proposed by Choo et al. Aggarwal 1995 Pocket infection requiring generator/lead removal. Superficial infection requiring only antibiotics was excluded. Kron 2003 Device infections requiring hospitalization or prolongation of hospitalization with or without explantation and administration of intravenous antibiotics. Bertaglia 2006 Major infective complications: septicemia, endocarditis, pocket abscess, or pocket erosion. Klug 2007 1) Fistula, abscess, or purulent collection at the site of the implanted material; 2) impending/frank erosion associated with fever or with a major Duke criterion; 3) systemic infection related to CIED: Duke criteria. Oliveira 2009 Superficial infection: local inflammation and pus in the surgical incision without evidence of pocket extension or systemic manifestation. Pocket infection without systemic manifestation: purulent discharge with microorganisms demonstrated by culture from the surgical wound or pocket with ≥2 of the following: pain, warmth, erythema, or local fluctuance. Systemic infection: pocket infection with ≥2of the following: fever, hypothermia, tachycardia, tachypnea, leukocytosis, leukopenia. Romeyer-Bouchard Definition of Mayo Cardiovascular Infections Study Group. 2010 Krahn 2011 Major pocket infections usually requiring intervention; minor incisional infections. Metais 2011 Surgical site infection: pus discharge from the wound within 1 year after implantation, irrespective of microorganism identification or deep infection of the surgical site. CIED-endocarditis or infection of the leads was confirmed by transesophageal echocardiography in case of any suspicious biological or clinical symptoms. Landolina 2011 NR MacFadden 2012 Major pocket infections usually requiring intervention; minor incisional infections. Uslan 2012 CDC definition for surgical site infections including deep and superficial surgical site infections exclusive of stitch abscesses. Bloom 2006 Infection requiring device explantation. Sohail 2007 Definition of Mayo Cardiovascular Infections Study Group: pocket infection: local signs of inflammation (erythema, warmth, fluctuance, wound dehiscence, tenderness, purulent drainage, or erosion of generator or lead through skin) and positive cultures; or positive blood cultures without any other source of bacteremia and resolution of bacteremia after device extraction. Endocarditis: valvular or lead vegetations in echocardiography or Duke criteria for infective endocarditis. Marschall 2007 CDC definition for surgical site infections (superficial incisional, deep incisional, or organ space infections). Lekkerkerker 2008 Definition of Mayo Cardiovascular Infections Study Group. Gould 2008 Pocket infections requiring lead extraction and incisional infections treated medically. Nery 2010 Modified Mayo Clinic group definition including superficial wound infections. Sohail 2011 Definition of Mayo Cardiovascular Infections Study Group. Raad 2012 Pocket infection: local warmth, erythema, swelling, edema, pain, or discharge from the device pocket. Unexplained bloodstream infection or sepsis in a patient with CIED. Lead-related endocarditis: vegetations in transesophageal echocardiography or positive Duke criteria. Hercé 2013 ≥1 of the following criteria requiring explantation of the device: positive culture from the explanted material; local signs of inflammation (abscess, fistula, discharge), with or without general signs of infection (fever, elevated CRP, leukocytosis) or positive blood culture; presence of lead or valvular vegetations in echocardiography; repeated septic pulmonary embolism, suggestive of device-related infection. Rao 1974 NR Mugica 1977 Abscess formation. Hartstein 1978 Purulent secretion at the generator site with positive cultures. Wunderly 1990 Local erythema, tenderness or swelling at the generator site and positive wound cultures or purulent drainage with a positive wound gram stain. Trappe 1995 Local signs of inflammation (warmth, erythema, purulent drainage), general signs of inflammation (fever [>37.5°C], leukocytosis, a shift of the differential blood count to the left, elevated serum CRP) and positive blood cultures. Spinler 1998 Presence of fever (>100.4 F), leukocytosis (WBC>104/mm3) and other signs and symptoms dependent on the site of infection, with or without positive aspirate or blood cultures. Smith 1998 NR Harcombe 1998 Late (>6 weeks after implantation) infective complications according to Choo et al. Kiviniemi 1999 Criteria proposed by Choo et al. Higgins 2000 NR Mela 2001 NR Wiegand 2004 NR Al-Khatib 2005 NR Gil 2006 Fever (> 37.8°C) or any sign of infection (warmth, erythema, tenderness, purulent drainage) around the pocket or surgical wound. Catanchin 2007 1) Pocket infection: clinical signs with or without positive cultures, abscess formation and wound breakdown. 2) Lead infection: clinical features with or without positive blood cultures or vegetations in echocardiography. Dasgupta 2007 Pocket infection requiring device extraction. Ito 2009 Infective endocarditis (definition not reported). Pakarinen 2010 1) Device system infection (pocket infection or fever associated with positive blood cultures without an infectious focus elsewhere). 2) Superficial wound infection. Cengiz 2010 1) Pocket infection. 2) Systemic infection (valvular or lead vegetations in echocardiography or modified Duke criteria for endocarditis). Borleffs 2010 Infectious pocket-related causes of surgical reintervention: 1) pocket infection (confirmed invasion of pathogenic microorganisms within the ICD pocket); 2) decubic ulcer (impending or frank erosions without apparent infectious manifestations). Margey 2010 Definition of Mayo Cardiovascular Infections Study Group. Bloom 2011 1) Superficial incisional surgical site infection according to CDC. 2) Deep incisional or organ/space (generator pocket) surgical site infection. 3) Endocarditis: modified Duke criteria. Johansen 2011 A record of ‘infection’, ‘mechanical protrusion’, ‘erosion’, or ‘wound pain’ treated with device removal. Charytan 2011 ICD-9 diagnosis 996.61. Device infections were further validated by evidence of intravenous antibiotic use, hospitalization, device or lead removal within 30 days, or subsequent death. Tompkins 2011 Definite infection of the pocket or lead (positive cultures) or development of bacteremia/ sepsis within 60 days of implantation. Lyman 2011 NR Armaganijan 2012 NR Schuchert 2013 NR Peterson 2013 NR Palmisano 2013 1) Systemic infection: valvular or lead vegetations in echocardiography or modified Duke criteria for infective endocarditis. 2) Pocket infection: swelling, redness, and discharge in the pocket and bacterial growth in wound cultures without evidence of systemic infection. CIED cardiac implantable electronic device, NR not reported, CDC centers for disease control and prevention, CRP C-reactive protein, WBC white blood cells, ICD implantable cardioverter-defibrillator, ICD-9 international classification of diseases (ninth revision) Supplementary Table 2. Microbiology of device-related infections. Study ID Na Microorganism b Muers 1981 33 9 Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus): 44%; Staphylococcus epidermidis (S. epidermidis): 11%; negative: 44% Ramsdale 1984 34 21 S. aureus: 19%; Clostridium welchii: 5%; polymicrobial: 5%; negative: 24%; no specimen: 48% Bluhm 1984 27 8 S. aureus: 25%; S. epidermidis: 38%; unknown: 38% Glieca 1987 30 12 S. aureus: 25%; S. epidermidis: 67%; Escherichia coli (E. coli): 8% Mueller 1990 45 3 S. epidermidis: 100% Lüninghake 1993 31 15 S. aureus: 7%; negative: 93% Mounsey 1994 32 13 S. aureus: 31%; S. epidermidis: 8%; Enterococcus faecalis: 8%; skin flora: 31%; E. coli: 8%; negative: 15% Bertaglia 2006 36 15 S. aureus: 7%; negative: 33%; unknown: 60% Klug 2007 39 42 S. aureus: 14%; S. epidermidis: 29%; CoNS: 21%; Corynebacterium: 2%; Morganella morganii: 2%; Staphylococcus schleiferi: 2%; E. coli: 2%; polymicrobial: 7%; negative/unknown: 19% Oliveira 2009 29 13 S. aureus: 62% (MRSA: 12.5%; MSSA: 87.5%); S. epidermidis: 23%; Staphylococcus simulans: 8%; CoNS: 8% Romeyer-Bouchard 13 S. aureus: 54% (MSSA 100%); CoNS: 15%; Gram-negative: 8%; negative: 23% Metais 2011 44 7 S. aureus: 29% (MRSA: 50%; MSSA: 50%); S. epidermidis: 29%; CoNS: 29%; unknown: 14% Uslan 2012 47 14 S. aureus: 14%; CoNS: 14%; negative: 36%; Serratia marcescens: 7%; E. coli: 7%; Acinetobacter 2010 46 baumannii: 7%; Citrobacter koseri: 7%; Propionibacterium acnes: 7% Sohail 2007 15 29 S. aureus: 38% (MRSA: 18%; MSSA: 82%); CoNS: 31%; Gram-negative: 3%; Candida albicans: 3%; Aspergillus fumigates: 3%; Peptostreptococcus magnus: 3%; polymicrobial: 7%; negative: 10% Marschall 2007 51 19 S. aureus: 11%; CoNS: 11%; Serratia marcescens: 5%; negative: 11%; no specimen: 63% Lekkerkerker 2008 75 S. aureus: 25%; CoNS: 29%; other bacteria: 11%; polymicrobial: 13%; negative: 15%; no specimen: 6% 24 S. aureus: 21%; CoNS: 13%; Viridans group streptococci: 4%; Serratia marcescens: 4%; Pseudomonas 50 Nery 2010 52 species: 4%; negative: 54% Sohail 2011 14 68 S. aureus: 47% (MRSA: 28%; MSSA: 72%); CoNS: 25%; polymicrobial: 7%; Serratia marcescens: 6%; Propionibacterium species: 4%; Enterococcus species: 1%; Pseudomonas aeruginosa: 1%; negative: 7% Raad 2012 53 18 S. aureus: 11%; S. epidermidis: 28%; CoNS: 6%; Morganella morganii: 6%; Proteus mirabilis: 6%; negative: 28%; unknown: 17% Hercé 2013 49 35 S. aureus: 34%; other: 29%; negative: 37% Rao 1974 71 3 S. aureus: 33%; E. coli: 33%; polymicrobial: 33% Mugica 1977 40 S. aureus: 61.5%; S. epidermidis: 33.5%; negative: 5.5% Hartstein 1978 64 9 S. aureus: 33%; S. epidermidis: 44%; Micrococcus: 11%; polymicrobial: 11% Wunderly 1990 76 8 S. aureus: 38%; S. epidermidis: 25%; Corynebacterium species: 25%; negative: 13% Trappe 1995 75 13 S. aureus: 46%; CoNS: 31%; Pseudomonas species: 15%; Streptococcus pyogenes: 8% Spinler 1998 11 9 S. aureus: 44% (MSSA: 100%); CoNS: 33%; Pseudomonas aeruginosa: 11%; negative: 11% Smith 1998 73 19 S. aureus: 26%; CoNS: 26%; Staphylococcus (not otherwise specified): 5%; fungi: 11%; corynebacteria: 69 5%; Bacillus fragilis: 5%; negative: 21% Harcombe 1998 63 18 S. aureus: 11%; S. epidermidis: 44%; Staphylococcus xylous: 5%; Enterobacter: 5%; Clostridium fallox: 5%; Pseudomonas aeruginosa: 5%; polymicrobial: 28% Mela 2001 68 21 S. aureus: 38%; CoNS: 19%; Propionibacterium: 5%; polymicrobial: 29%; negative: 10% Gil 2006 62 10 S. aureus: 10%; CoNS: 30%; Streptococcus agalactiae: 10%; polymicrobial: 40%; negative: 10% Catanchin 2007 58 39 S. aureus: 38% (MRSA: 13%; MSSA: 87%); CoNS: 21% (methicillin-resistant: 13%); Gram-negative bacillus: 3%; Gram-positive coccus: 3%; negative: 36% Cengiz 2010 59 57 S. aureus: 12% (MRSA: 29%; MSSA: 71%); S. epidermidis: 11% (methicillin-resistant: 33%); Staphylococcus hominis: 4%; Bacillus subspecies: 2%; Enterobacter cloacae: 4%; Acinetobacter haemolyticus: 2%; Pseudomonas aeruginosa: 2%; negative/ unknown: 65% Margey 2010 e 57 39 S. aureus: 36% (MRSA: 14%; MSSA: 86%); CoNS: 21%; Streptococcus species: 8%; Gram-negative: 5%; negative: 38% Bloom 2011 84 3 CoNS: 33%; negative: 67% Tompkins 2011 74 7 S. aureus: 57% (MRSA: 75%; MSSA: 25%); Enterococcus: 29%; polymicrobial: 14% CoNS coagulase-negative Staphylococcus, MRSA methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, MSSA methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus a b Number of infections with available microbiological data. Identified from pocket, lead or blood cultures. Supplementary Table 3. Pooled effect estimates for potential risk factors predisposing to CIED infection. Factor Studies Totals Statistical Pooled estimate (N) (N) Method Age 11 6295 WMD -1.27 [-3.08, 0.55] Male gender 16 18770 OR BMI ≥ 25 3 367 Body weight 2 ASA ≥ 3 P value Heterogeneity P I2 0.17 0.67 0 1.12 [0.89, 1.41] 0.35 0.50 0 OR 1.04 [0.63, 1.72] 0.87 0.36 2.01 453 WMD -2.69 [-6.69, 1.31] 0.19 0.77 0 2 380 OR 0.93 [0.24, 3.58] 0.91 0.94 0 Smoking 2 1820 OR 0.48 [0.11, 2.08] 0.32 0.82 0 Diabetes mellitus 18 11839 OR 2.08 [1.62, 2.67] <0.000001 0.37 6.83 Renal insufficiency a 5 2033 OR 3.02 [1.38, 6.64] 0.006 70.50 Host-related factors 0.01 ESRD b 8 3045 OR 8.73 [3.42, 22.31] Serum Creatinine 4 612 WMD Cirrhosis 2 291 Atrial fibrillation 6 CAD 0.00001 0.11 41 12.78 [-9.78, 35.33] 0.27 0.02 68.33 OR 1.94 [0.28, 13.53] 0.51 0.38 0 872 OR 1.12 [0.63, 1.98] 0.69 0.10 45.77 6 968 OR 1.26 [0.92, 1.73] 0.15 0.73 0 Previous MI 2 1948 OR 1.08 [0.41, 2.89] 0.87 0.06 72.19 CABG 3 363 OR 0.87 [0.54, 1.40] 0.56 0.74 0 CHF 6 1277 OR 1.65 [1.14, 2.39] 0.008 0.73 0 NYHA class ≥ 2 3 2447 OR 2.47 [1.24, 4.91] 0.01 0.61 0 Ejection fraction 4 2837 WMD -0.78 [-3.32, 1.76] 0.55 0.74 0 Prosthetic valve 4 649 OR 1.42 [0.72, 2.81] 0.31 0.53 0 PAD 2 1948 OR 0.88 [0.31, 2.50] 0.81 0.28 16.06 Cerebrovascular disease 2 1948 OR 1.07 [0.30, 3.79] 0.91 0.06 71.36 COPD 6 2810 OR 2.95 [1.78, 4.90] 0.00003 0.91 0 Malignancy 6 1555 OR 2.23 [1.26, 3.95] 0.006 0.48 0 Autoimmune disease 2 291 OR 1.44 [0.42, 4.90] 0.56 0.32 0 Skin disorders 4 6810 OR 2.46 [1.04, 5.80] 0.04 0.34 9.73 Fever prior to implantation 3 6652 OR 4.27 [1.13, 16.12] 0.03 0.23 33.01 Oral anticoagulants 9 8527 OR 1.59 [1.01, 2.48] 0.04 0.06 45.89 Antiplatelet therapy 4 6748 OR 1.37 [0.83, 2.28] 0.22 0.54 0 Heparin bridging 2 6373 OR 1.87 [1.03, 3.41] 0.04 0.71 0 Corticosteroid use 10 3432 OR 3.44 [1.62, 7.32] 0.001 0.36 9.46 Immunosuppressive drug use c 2 291 OR 1.85 [0.63, 5.46] 0.27 0.49 0 Permanent CVC 3 1181 OR 5.74 [0.94, 34.93] 0.06 0.15 47.18 History of device infection 4 463 OR 7.84 [1.94, 31.60] 0.004 0.17 40.10 Antibiotic prophylaxis 16 14166 OR 0.32 [0.18, 0.55] d 0.00005 <0.001 62.61 Device replacement/ 26 21214 OR 1.98 [1.46, 2.70] 0.00001 0.006 45.88 Generator change 20 12134 OR 1.74 [1.22, 2.49] 0.002 0.02 43.64 Lead dislodgement/ 5 1755 OR 6.37 [2.93, 13.82] 0.000003 0.30 17.63 Hematoma 12 14228 OR 8.46 [4.01, 17.86] <0.000001 0.001 63.66 Temporary pacing 10 10683 OR 2.31 [1.36, 3.92] 0.002 34.75 Procedure-related factors revision/upgrade repositioning 0.13 Procedure duration 9 4850 WMD 9.89 [0.52, 19.25] 0.04 0.008 61.59 Inexperienced operator e 2 1715 OR 2.85 [1.23, 6.58] 0.01 0.47 0 ICD device 14 16594 OR 1.19 [0.84, 1.68] 0.32 0.27 16.53 CRT device 9 13308 OR 1.92 [0.90, 4.10] 0.09 0.09 42.29 Dual-chamber device 14 45224 OR 1.45 [1.02, 2.05] 0.04 0.04 44.3 ≥2 leads 6 1146 OR 2.02 [1.11, 3.69] 0.02 0.17 35.61 Abdominal generator pocket 7 4017 OR 4.01 [2.48, 6.49] <0.000001 0.67 0 Presence of epicardial leads 3 623 OR 8.09 [3.46, 18.92] 0.000001 0.98 0 Presence of abandoned leads 2 291 OR 1.82 [0.86, 3.83] 0.12 0.51 0 Device-related factors WMD weighted mean difference, OR odds ratio, BMI body mass index, ASA American Society of Anesthesiologists, ESRD end-stage renal disease, CAD coronary artery disease, MI myocardial infarction, CABG coronary artery bypass grafting, CHF congestive heart failure, NYHA New York Heart Association, PAD peripheral artery disease, COPD chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, CVC central venous catheter, ICD implantable cardioverter defibrillator, CRT cardiac resynchronization therapy. a Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) <60 ml/min or creatinine clearance (CrCL) <60 ml/min GFR≤ 15 ml/min or hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis c Immunosuppressive drugs other than corticosteroids d The pooled effect estimate from randomized studies was 0.26 [0.13, 0.52] e <100 previous procedures b Supplementary Table 4. Sensitivity analysis excluding studies that included superficial wound infections and studies with inadequate definition of CIED infection. Factor Studies Totals Statistical Pooled estimate (N) (N) Method Age 4 1457 WMD -0.07 [-2.82, 2.68] Male gender 10 14444 OR BMI ≥ 25 2 291 Body weight 2 Diabetes mellitus P value Heterogeneity P I2 0.96 0.32 14.34 1.26 [0.95, 1.66] 0.10 0.91 0 OR 0.94 [0.44, 2.01] 0.87 0.17 45.78 453 WMD -2.69 [-6.69, 1.31] 0.19 0.77 0 12 9082 OR 2.00 [1.52, 2.64] 0.0000009 0.45 0 Renal insufficiency a 4 593 OR 2.64 [1.17, 5.97] 0.02 0.01 74.26 ESRD b 6 981 OR 6.27 [2.86, 13.75] 0.000005 0.66 0 Serum Creatinine 3 558 WMD 20.70 [-7.55, 48.94] 0.15 0.05 67.13 Cirrhosis 2 291 OR 1.94 [0.28, 13.53] 0.51 0.38 0 Atrial fibrillation 5 818 OR 1.33 [0.79, 2.25] 0.28 0.21 32.52 Host-related factors CAD 6 968 OR 1.26 [0.92, 1.73] 0.15 0.73 0 CABG 3 363 OR 0.87 [0.54, 1.40] 0.56 0.74 0 CHF 4 515 OR 1.60 [1.08, 2.36] 0.02 0.52 0 Prosthetic valve 2 291 OR 1.14 [0.45, 2.92] 0.78 0.26 20 COPD 3 363 OR 3.35 [1.73, 6.50] 0.0004 0.92 0 Malignancy 6 1555 OR 2.23 [1.26, 3.95] 0.006 0.48 0 Autoimmune disease 2 291 OR 1.44 [0.42, 4.90] 0.56 0.32 0 Skin disorders 4 6810 OR 2.46 [1.04, 5.80] 0.04 0.34 9.73 Fever prior to implantation 2 6391 OR 5.39 [1.18, 24.61] 0.03 0.2 40.47 Oral anticoagulants 6 7200 OR 1.64 [0.99, 2.71] 0.05 0.06 52.85 Antiplatelet therapy 3 6694 OR 1.44 [0.82, 2.54] 0.21 0.36 1.87 Corticosteroid use 7 2105 OR 5.28 [2.29, 12.18] 0.0001 0.38 6.65 Immunosuppressive drug usec 2 291 OR 1.85 [0.63, 5.46] 0.27 0.49 0 Permanent CVC 3 1181 OR 5.74 [0.94, 34.93] 0.06 0.15 47.18 History of device infection 4 463 OR 7.84 [1.94, 31.60] 0.004 0.17 40.10 Antibiotic prophylaxis 15 13727 OR 0.37 [0.21, 0.64] 0.0004 0.01 51.02 Device replacement/ 17 17539 OR 2.00 [1.39, 2.89] 0.0002 0.01 50.02 Generator change 16 11063 OR 1.74 [1.15, 2.63] 0.009 0.02 46.83 Lead dislodgement/ 4 1659 OR 8.71 [3.86, 19.64] 0.0000002 0.60 Hematoma 8 8575 OR 9.78 [3.70, 25.84] 0.000004 0.003 68.12 Temporary pacing 7 8843 OR 2.05 [1.02, 4.12] 0.04 0.05 Procedure duration 4 1961 WMD 9.92 [-8.94, 28.78] 0.30 0.001 81.58 Inexperienced operator d 2 1715 OR 2.85 [1.23, 6.58] 0.01 0.47 0 ICD device 7 9469 OR 0.93 [0.65, 1.33] 0.69 0.70 0 CRT device 4 8629 OR 3.79 [0.71, 20.30] 0.12 0.007 75.19 Dual-chamber device 10 11300 OR 1.70 [1.11, 2.59] 0.01 0.1 39.39 ≥2 leads 4 468 OR 2.03 [0.94, 4.37] 0.07 0.06 60.56 Abdominal generator pocket 2 291 OR 2.18 [0.93, 5.10] 0.07 0.96 0 Presence of epicardial leads 3 623 OR 8.09 [3.46, 18.92] 0.000001 0.98 0 Presence of abandoned leads 2 291 OR 1.82 [0.86, 3.83] 0.51 0 Procedure-related factors revision/upgrade 0 repositioning 52.28 Device-related factors 0.12 WMD weighted mean difference, OR odds ratio, BMI body mass index, ESRD end-stage renal disease, CAD coronary artery disease, CABG coronary artery bypass grafting, CHF congestive heart failure, COPD chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, CVC central venous catheter, ICD implantable cardioverter defibrillator, CRT cardiac resynchronization therapy. a Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) <60 ml/min or creatinine clearance (CrCL) <60 ml/min GFR≤ 15 ml/min or hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis c Immunosuppressive drugs other than corticosteroids d <100 previous procedures b Supplementary Table 5. Sensitivity analysis including only prospective studies. Factor Studies Totals Statistical Pooled estimate P value Heterogeneity Method P I2 Host-related factors Age 5 3852 WMD -2.04 [-5.19, 1.10] 0.20 0.70 0 Male gender 8 14965 OR 1 [0.70, 1.42] 0.98 0.36 8.87 Diabetes mellitus 7 9815 OR 1.88 [1.19, 2.98] 0.007 0.74 0 NYHA class ≥ 2 2 2393 OR 2.77 [1.26, 6.05] 0.01 0.43 0 Ejection fraction 2 952 WMD -0.83 [-4.06, 2.40] 0.62 0.38 0 COPD 2 2393 OR 2.30 [0.97, 5.48] 0.06 0.36 0 Skin disorders 2 6519 OR 2.60 [0.88, 7.70] 0.08 0.63 0 Fever prior to implantation 2 6580 OR 5.34 [1.002, 28.43] 0.05 0.20 38.05 Oral anticoagulants 3 7271 OR 1.18 [0.44, 3.11] 0.75 0.12 53.50 Antiplatelet therapy 2 6622 OR 1.19 [0.62, 2.28] 0.61 0.38 0 Corticosteroid use 3 1349 OR 2.10 [0.47, 9.32] 0.33 0.91 0 Antibiotic prophylaxis 11 10864 OR 0.29 [0.13, 0.63] 0.002 0.001 66.35 Device replacement/ 8 8793 OR 0.95 [0.49, 1.87] 0.89 0.07 47.13 Procedure-related factors revision/upgrade Generator change 6 2139 OR 0.91 [0.37, 2.22] 0.83 0.06 52.26 Lead dislodgement/ 4 1659 OR 7.03 [2.49, 19.85] 0.0002 0.22 32.17 Hematoma 6 9715 OR 9.33 [2.84, 30.69] 0.0002 <0.001 78.12 Temporary pacing 4 8683 OR 3.29 [1.87, 5.80] 0.00004 0.43 Procedure duration 6 4508 WMD 13.04 [-0.64, 26.73] 0.06 0.02 63.41 Inexperienced operator a 2 1715 OR 2.85 [1.23, 6.58] 0.01 0.47 0 ICD device 4 8676 OR 1.01 [0.5, 2.03] 0.98 0.68 0 CRT device 4 9016 OR 1.82 [0.86, 3.86] 0.12 0.56 0 Dual-chamber device 7 12102 OR 1.28 [0.73, 2.25] 0.38 0.15 37.19 Abdominal generator pocket 2 2268 OR 5.03 [1.96, 12.91] 0.0008 0.31 3.75 repositioning 0 Device-related factors WMD weighted mean difference, OR odds ratio, NYHA New York Heart Association, COPD chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, ICD implantable cardioverter defibrillator, CRT cardiac resynchronization therapy. a <100 previous procedures Supplementary Table 6. Assessment of publication bias for factors examined by at least 5 studies. Funnel plot Egger’s test Bias? P value Age No Male gender Risk factor Trim and Fill method Studies OR [95% CI], trimmed (N) before/after trim and fill 0.19 0 NA Yes 0.12 4 1.12 [0.89, 1.41] / 1.07 [0.86, 1.35] Diabetes No 0.5 0 NA Renal insufficiency Yes 0.27 1 3.02 [1.38, 6.64] / 2.64 [1.25, 5.60] ESRD No 0.63 0 NA Atrial fibrillation No 0.51 0 NA CAD No 0.10 0 NA CHF No 0.94 0 NA COPD Yes 0.45 3 2.95 [1.78, 4.90] / 2.38 [1.56, 3.63] Malignancy Yes 0.85 1 2.23 [1.26, 3.95] / 2.05 [1.18, 3.57] Oral anticoagulants No 0.14 0 NA Corticosteroid use No 0.54 0 NA Antibiotic Yes 0.004 5 0.32 [0.18, 0.55] / 0.52 [0.28, 0.96] No 0.28 0 NA No 0.26 0 NA prophylaxis Device replacement/ revision/upgrade Generator change Lead dislodgement/ No 0.54 0 NA Hematoma No 0.64 0 NA Temporary pacing No 0.59 0 NA Procedure duration No 0.90 0 NA ICD device No 0.65 0 NA CRT No 0.34 0 NA Dual-chamber device Yes 0.19 5 1.45 [1.02, 2.05] / 1.07 [0.74, 1.56] ≥2 leads Yes 0.42 3 2.02 [1.1, 3.69] / 1.17 [0.58, 2.37] Abdominal generator Yes 0.41 1 4.01 [2.48, 6.49] / 3.65 [2.31, 5.77] repositioning pocket OR odds ratio, 95% CI 95% confidence interval, NA not applicable, ESRD end-stage renal disease, CAD coronary artery disease, CHF congestive heart failure, COPD congestive obstructive pulmonary disease, ICD implantable cardioverter-defibrillator, CRT cardiac resynchronization therapy. Supplementary Table 7. Assessment of the methodological quality of randomized studies that examined the effectiveness of antibiotic prophylaxis. Study ID Random sequence Allocation Blinding Incomplete outcome generation concealment Muers 1981 High risk High risk No Low risk Ramsdale 1984 Low risk Unclear No Unclear Bluhm 1984 Unclear Unclear No Low risk Bluhm 1986 Unclear Unclear Double-blind Low risk Glieca 1987 Unclear Unclear No Unclear Lüninghake 1993 Unclear Unclear No Unclear Mounsey 1994 Unclear Unclear No Low risk Oliveira 2009 Unclear Unclear Double-blind Low risk data SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1. Microbiology of CIED infection.