Vertical Matrix Grade 5
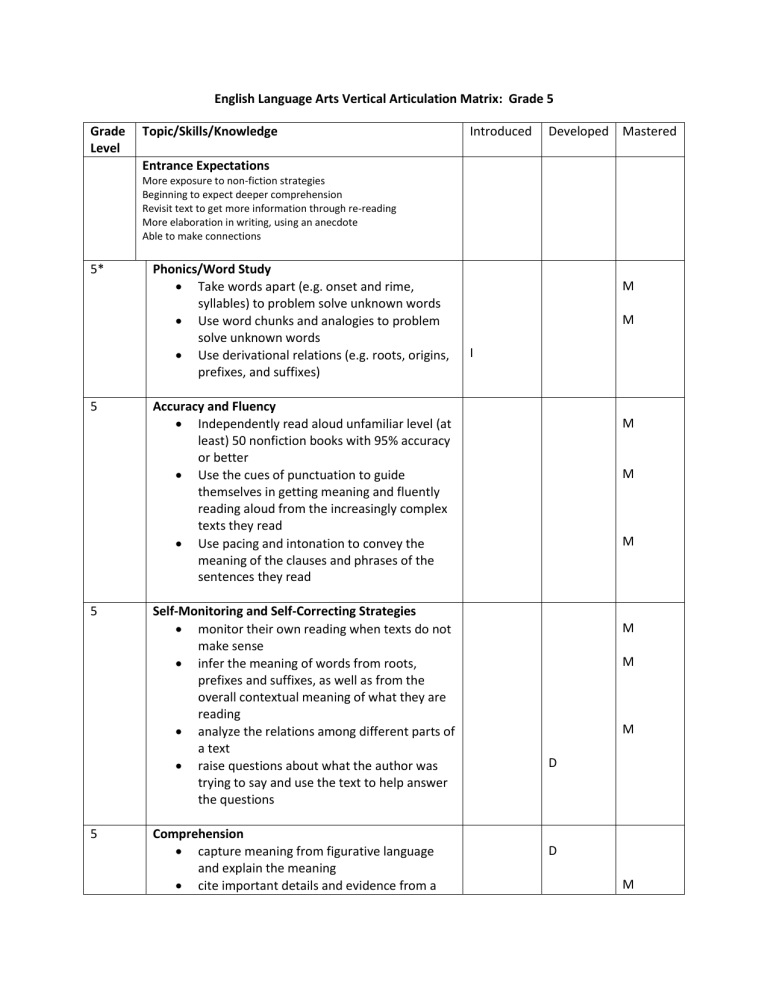
English Language Arts Vertical Articulation Matrix: Grade 5
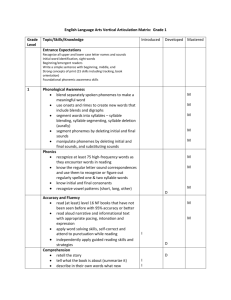
Grade
Level
Topic/Skills/Knowledge
5*
5
5
5
Introduced Developed Mastered
Entrance Expectations
More exposure to non-fiction strategies
Beginning to expect deeper comprehension
Revisit text to get more information through re-reading
More elaboration in writing, using an anecdote
Able to make connections
Phonics/Word Study
Take words apart (e.g. onset and rime, syllables) to problem solve unknown words
Use word chunks and analogies to problem solve unknown words
Use derivational relations (e.g. roots, origins, prefixes, and suffixes)
Accuracy and Fluency
Independently read aloud unfamiliar level (at least) 50 nonfiction books with 95% accuracy or better
Use the cues of punctuation to guide themselves in getting meaning and fluently reading aloud from the increasingly complex texts they read
Use pacing and intonation to convey the meaning of the clauses and phrases of the sentences they read
Self-Monitoring and Self-Correcting Strategies
monitor their own reading when texts do not make sense
infer the meaning of words from roots, prefixes and suffixes, as well as from the overall contextual meaning of what they are reading
analyze the relations among different parts of a text
raise questions about what the author was trying to say and use the text to help answer the questions
Comprehension
capture meaning from figurative language and explain the meaning
cite important details and evidence from a
I
D
D
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
5 text to support thinking
compare one text to another they have read or heard or seen (T-T ; T-W)
discuss why an author might have chosen particular words
say how a story relates to something in reallife experience (T-S)
discuss the interrelationships of story elements (e.g. characters, plot, setting, events, theme)
use structure of informational text to retrieve information (e.g. text features)
analyze the causes, motivations, sequences, results of events, and point of view
use reasoning and information from within and outside the text to examine arguments
describe in their own words what new information they gained from a nonfiction text and how it relates to their prior knowledge
follow instructions or directions they encounter in the more complicated functional texts they are now reading
identify main idea and supporting details
apply these comprehension strategies: visualizing, questioning, predicting, making connections, inferring, determining importance, synthesis
Independent and Assisted Reading, Being Read To
read 30 books a year, independently or with assistance, and regularly participate in discussions of their reading with another student, a group or an adult
read and hear texts read aloud from a variety of genres
read multiple books by the same author and be able to identify differences and similarities among them
reread some favorite books or parts of longer books, gaining deeper comprehension and knowledge of author’s craft
listen to and discuss at least one chapter read to them every day
discuss underlying themes or messages when interpreting fiction
identify and discuss recurring themes across
I
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
D
D
D
5
5
5 works
evaluate literary worth and participate informatively in peer talk about selecting books to read
examine the reasons for a character’s actions, accounting for situation and motive
select “Just Right” books with teacher guidance
Discussing Books & Responding to Literature
note and talk about author’s craft: word choice, beginnings and endings, plot, and character development
use comparisons and analogies to explain ideas
ask other students questions requiring them to support their claims or arguments
indicate when their own or others’ ideas need further support or explanation
Vocabulary
Determine or clarify the meaning of unknown and multiple-meaning words and phrases based on grade 5 reading and content, choosing flexibly from a range of strategies.
Demonstrate understanding of figurative language, word relationships, and nuances in word meanings.
Acquire and use accurately grade-appropriate general academic and domain-specific words and phrases, including those that signal contrast, addition, and other logical relationships (e.g., however, although, nevertheless, similarly,
moreover, in addition).
Writing: Habits & Processes
Write daily
Generate their own topics and spend the necessary amount of time to revisit and refine their writing
Routinely rework, revise, edit and proofread their work
Consciously appropriate specific elements of a favorite author’s to refine the quality of
D
M
M
M
D
D
D
D
D
M
M
M
M
M
M
5
5
5 their own work (Mentor Texts)
Apply criteria for state rubric or genre specific rubrics
Over the course of the year polish 8-10 pieces of writing
Writing: Narrative Writing
Create believable characters through the precise choice of detail
Create a sequence of events that unfolds naturally
Develop characters through their actions, thoughts and feelings
Develop an engaging plotline (setting, problem, events, solution)
Focus and develop story events
Expand or ‘stretch out’ story events
Craft a strong lead
Craft a memorable ending
Craft sentence variety
Develop real or imagined experiences or events using effective technique, descriptive details, and clear event sequences
Writing: Functional Writing
Engage the reader by establishing a context
for the piece
Identify the topic
Provide a guide to action
Show the steps in a action in considerable detail
Include relevant information
Use language that is straightforward and clear
May use illustrations detailing steps in the process
Writing: Responding to Literature
Support an interpretation by making specific reference to the text
Compare two works by an author
Discuss several works that have a common idea or theme
Make connections between the text and their own ideas and lives
D
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
M
5*
5
Writing: Informational
Introduce the topic, sometimes providing a context
Have an organizational structure that is useful to the reader
Communicate the ideas, insights or theories that have been elaborated on or illustrated through facts, details, quotations, statistics and information
Use diagrams, charts or illustrations as appropriate to the text
Have a concluding sentence or section
Employ a straightforward tone of voice
Writing: Language Use & Conventions
Style and Syntax:
Use appropriately a variety of sentence structures to show relationships of ideas
(simple, compound, complex with transitions)
Incorporate transitional words and phrases appropriate to thinking
Embed phrases and powerful vocabulary that make their writing lively and graphic
Use varying sentence patterns and lengths to slow reading down, speed it up, create mood
Embed literary language where appropriate
Reproduce sentence structures found in various genres they are reading
Spelling:
Notice when words do not look correct and use strategies to correct the spelling (for example, experiment with alternative spellings, look the word up in the dictionary or word list)
Correctly spell all familiar high-frequency words
Correctly spell most inflectional endings, including plurals and verb tenses
Use correct spelling patterns and rules such as consonant doubling, dropping e and changing y to i
Correctly spell most derivational words (for example, -tion, -ment, -ly)
Vocabulary and Word Choice:
Use words from their speaking vocabulary in
M
M
M
M
M
M
D
D
D
D
D
D
their writing, including words they have learned from reading and class discussion
Make word choices that reveal they have a large enough vocabulary to exercise options in word choice (for example, more precise and vivid words)
Extend their writing vocabulary by using specialized words related to their topic or setting of their writing (i.e., the names of the breeds of dogs if they are writing about dogs)
Punctuation, Capitalization, and Other Conventions:
Apply grade level rules of punctuation as stated in grammar scope and sequence found in LA Resource Binder
Apply grade level rules of capitalization as stated in grammar scope and sequence found in LA Resource Binder
Use a variety of sentence types, comma structures, and parts as stated in grammar scope and sequence found in LA Resource
Binder
Apply various parts of speech appropriately as stated in grammar scope and sequence found in LA Resource Binder
D
D
M
M
M
M