Virginia Mathematics Checkpoint Assessment
advertisement

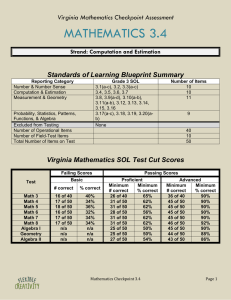
Virginia Mathematics Checkpoint Assessment MATHEMATICS 5.4 Strand: Computation and Estimation Standards of Learning Blueprint Summary Reporting Category Number & Number Sense Computation & Estimation Measurement & Geometry Grade 5 SOL 5.1, 5.2(a-b), 5.3(a-b) 5.4, 5.5(a-b), 5.6, 5.7 5.8(a-e), 5.9, 5.10, 5.11, 5.12(a-b), 5.13(a-b) 5.14, 5.15, 5.16(b-d), 5.17, 5.18(a-d), 5.19 5.16(a) Probability, Statistics, Patterns, Functions, & Algebra Excluded from Testing Number of Operational Items Number of Field-Test Items Total Number of Items on Test Number of Items 7 13 12 18 50 10 60 Virginia Mathematics SOL Test Cut Scores Failing Scores Test Math 3 Math 4 Math 5 Math 6 Math 7 Math 8 Algebra I Geometry Algebra II Basic # correct % correct 16 of 40 17 of 50 18 of 50 16 of 50 17 of 50 17 of 50 n/a n/a n/a 40% 34% 36% 32% 34% 34% n/a n/a n/a Passing Scores Proficient Minimum Minimum # correct % correct 26 of 40 65% 31 of 50 62% 31 of 50 62% 28 of 50 56% 31 of 50 62% 31 of 50 62% 25 of 50 50% 25 of 50 50% 27 of 50 54% Mathematics Checkpoint 5.4 Advanced Minimum Minimum # correct % correct 36 of 40 90% 45 of 50 90% 45 of 50 90% 45 of 50 90% 45 of 50 90% 46 of 50 92% 45 of 50 90% 44 of 50 88% 43 of 50 86% Page 1 Checkpoint Items 1. Directions: After showing your thinking, circle the box you want to select. Find the estimated product. Select the correct estimation from the boxes below. 4,253 x 19 = 80,807 80,000 Mathematics Checkpoint 5.4 90,000 Page 2 2. Directions: After showing your thinking, circle the box you want to select. Find the estimated quotient. Select the correct estimation from the boxes below. 34 639 27 30 Mathematics Checkpoint 5.4 20 Page 3 3. Directions: After showing your thinking, circle the box you want to select. Max and his brother were playing a video game. Max had a total score of 45,910 points. His score was 29,899 points higher than his brother’s score. What was Max’s brother’s score? 24,181 points 16,011 points Mathematics Checkpoint 5.4 20,831 points Page 4 4. Directions: After showing your thinking, write your answer in the box. The car dealership just received a new shipment of cars. There were already 129 cars on the lot. The shipment brought in an additional 63 cars. If the manager wanted to divide all the cars into 6 equal rows, how many cars would be in each row? cars Mathematics Checkpoint 5.4 Page 5 5. Directions: After showing your thinking, write your answer in the box. The store owner knew that for back-to-school sales she would need to order extra notebooks. Usually she orders 3 cases of notebooks each month. Each case holds 125 notebooks. To prepare for the back-to-school sales, the store owner ordered an additional 6 cases in the month of August. How many total notebooks did the store owner have to sell in August? notebooks Mathematics Checkpoint 5.4 Page 6 6. Directions: After showing your thinking, circle the box you want to select. The marching band director always places the band members in rows to march. Last year there were 149 marching band members. 26 of those members graduated and are no longer in the band. This year there are an additional 47 new members who joined the band. If the marching band director puts the members into 4 equal rows, how many members would be left over? 3 2 Mathematics Checkpoint 5.4 1 Page 7 7. Directions: After showing your thinking, write your answer in the box. Solve. (4,567 + 6,892) – 3,872 = Mathematics Checkpoint 5.4 Page 8 8. Directions: After showing your thinking, write your answer in the box provided below. Solve. (5,894 x 52) – 4,569 = Mathematics Checkpoint 5.4 Page 9 Checkpoint Solutions SOL 5.4 The student will create and solve single-step and multistep practical problems involving addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division with and without remainders of whole numbers. Essential Knowledge and Skills a. Select appropriate methods and tools from among paper and pencil, estimation, mental computation, and calculators according to the context and nature of the computation in order to compute with whole numbers b. Create single-step and multistep problems involving the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division with and without remainders of whole numbers, using practical situations c. Estimate the sum, difference, product, and quotient of whole number computations d. Solve single-step and multistep problems involving addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division with and without remainders of whole numbers, using paper and pencil, mental computation, and calculators in which 1. sums, differences, and products will not exceed five digits 2. multipliers will not exceed two digits 3. divisors will not exceed two digits 4. dividends will not exceed four digits e. Use two or more operational steps to solve a multistep problem. Operations can be the same or different Item Answer/Solution SOL/EKS Code 1 80,000 5.4c 2 20 5.4c 3 16,011 points 5.4d 4 32 5.4d 5 1,125 5.4d 6 2 5.4d 7 7,587 5.4e 8 301,919 5.4e Essential Knowledge and Skills Estimate the sum, difference, product, and quotient of whole number computations Estimate the sum, difference, product, and quotient of whole number computations Solve single-step and multistep problems involving addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division with and without remainders of whole numbers, using paper and pencil, mental computation, and calculators Solve single-step and multistep problems involving addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division with and without remainders of whole numbers, using paper and pencil, mental computation, and calculators Solve single-step and multistep problems involving addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division with and without remainders of whole numbers, using paper and pencil, mental computation, and calculators Solve single-step and multistep problems involving addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division with and without remainders of whole numbers, using paper and pencil, mental computation, and calculators Use two or more operational steps to solve a multistep problem. Operations can be the same or different Use two or more operational steps to solve a multistep problem. Operations can be the same or different Mathematics Checkpoint 5.4 Page 10