File - Mrs. Glazebrook
advertisement
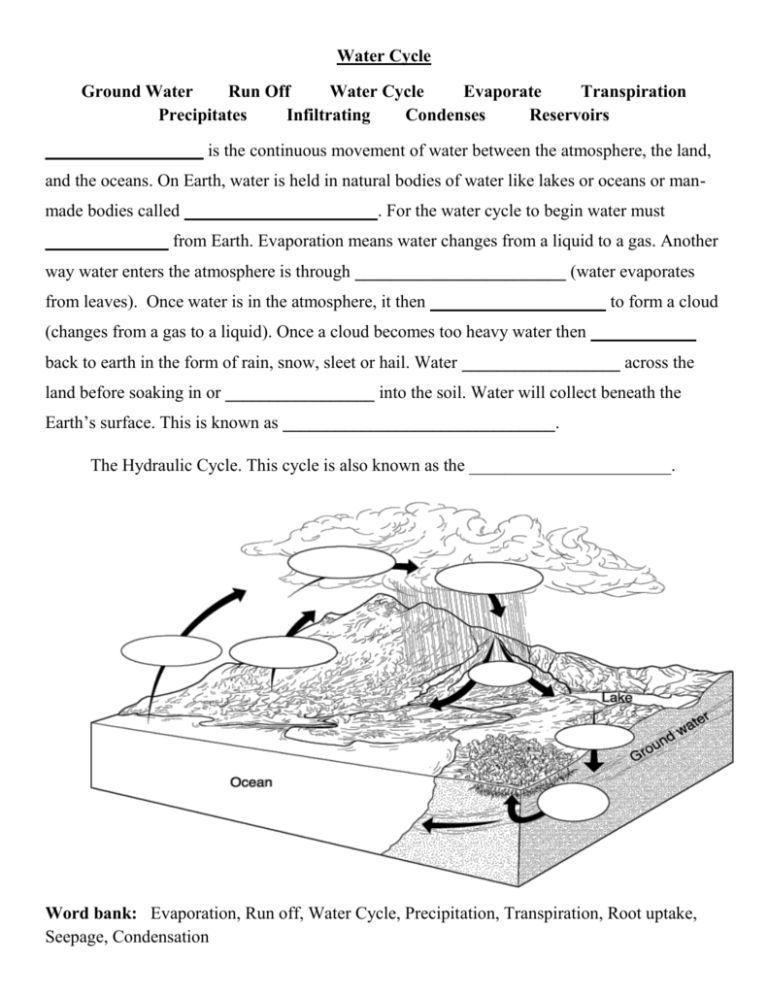
Water Cycle Ground Water Run Off Water Cycle Evaporate Transpiration Precipitates Infiltrating Condenses Reservoirs __________________ is the continuous movement of water between the atmosphere, the land, and the oceans. On Earth, water is held in natural bodies of water like lakes or oceans or manmade bodies called ______________________. For the water cycle to begin water must ______________ from Earth. Evaporation means water changes from a liquid to a gas. Another way water enters the atmosphere is through ________________________ (water evaporates from leaves). Once water is in the atmosphere, it then ____________________ to form a cloud (changes from a gas to a liquid). Once a cloud becomes too heavy water then ____________ back to earth in the form of rain, snow, sleet or hail. Water __________________ across the land before soaking in or _________________ into the soil. Water will collect beneath the Earth’s surface. This is known as _______________________________. The Hydraulic Cycle. This cycle is also known as the _______________________. Word bank: Evaporation, Run off, Water Cycle, Precipitation, Transpiration, Root uptake, Seepage, Condensation Carbon – oxygen Cycle: Decomposing Bacteria Combusting Carbon Sinks Photosynthesis Carbon Dioxide Consumed Carbon is found in all life and in the Earth’s atmosphere. Plants, through __________________, convert carbon dioxide to carbohydrates (sugars), and release oxygen as a by-product. In turn plants are _______________________ (eaten) by other organisms. Once these organisms die, ________________________ break down the dead organism and release _______________________ back into the atmosphere. Trees, oceans and lakes act as __________________________; they trap large amounts of carbon and release it back into the atmosphere slowly over time. Humans disrupt the carbon cycle by burning or _____________________ organic materials. Word Bank: Cellular Respiration, Decomposition, Photosynthesis, Fossil Fuels, Combustion Nitrogen Cycle: Denitrification Nitrogen Cycle Amino Acids Lightning Ammonia Decomposing Bacteria Nitrogen Fixation Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria Proteins The ________________________ is the pathway for moving nitrogen between biotic and abiotic factors on Earth. Nitrogen is essential for the formation of _____________________ and ________________________ in all living organisms. The atmosphere is 78% nitrogen (N2). Animals cannot use nitrogen gas. Instead bacteria in the soil called ____________________________________ convert the atmospheric nitrogen into __________________ or nitrate. This process is called ______________________________. _______________________ can also cause nitrogen fixation. Once in the soil, plants absorb the nitrogen through their roots and then organisms eat the plants. When organisms die, ___________________________ release the nitrogen from the bodies back into the atmosphere in a process called ____________________________. Word Bank: Gas, Nitrogen, Nitrogen Fixation, Death and Decay, Nitrogen in Soil, Bacteria, Waste Phosphorus Cycle Bacteria Leaching Phosphorus Cycle Weathering Dies Waste Absorb The _____________________ originates from the ground. Phosphorus is released the ground by the ________________________ and ______________________ of rocks. Plants then _________________ the phosphorus through their roots. Organisms consume the plants and excrete ______________________ in the form of urine and feces. Phosphorus is also release when an organism _______________________. Decomposing _____________________ the break down the dead organism or waste products. Finally, the Phosphorus is released back into the soil to either create new rocks or be reabsorbed into plants. The _____________________ Cycle Word Bank: Death and Decay, Bacteria, Root absorption, Consumption, Phosphorus Human Impact Overview THREAT GREENHOUSE EFFECT ACID RAIN OZONE DEPLETION AIR POLLUTION WATER POLLUTION SOIL DEGRADATION/ DEPLETION HABITAT DESTRUCTION CAUSE POSSIBLE RESULTS Water Cycle Ground Water Run Off Water Cycle Evaporate Transpiration Precipitates Infiltrating Condenses Reservoirs Water Cycle is the continuous movement of water between the atmosphere, the land, and the oceans. On Earth, water is held in natural bodies of water like lakes or oceans or man-made bodies called Reservoirs. For the water cycle to begin water must Evaporate from Earth. Evaporation means water changes from a liquid to a gas. Another way water enters the atmosphere is through Transpiration (water evaporates from leaves). Once water is in the atmosphere, it then Condenses to form a cloud (changes from a gas to a liquid). Once a cloud becomes too heavy water then Precipitates back to earth in the form of rain, snow, sleet or hail. Water Runs Off across the land before soaking in or Infiltrating into the soil. Water will collect beneath the Earth’s surface. This is known as Ground Water. The Hydraulic Cycle. This cycle is also known as the water cycle Word bank: Evaporation, Run off, Water Cycle, Precipitation, Transpiration, Root uptake, Seepage, Condensation Carbon – oxygen Cycle: Decomposing Bacteria Combusting Carbon Sinks Photosynthesis Carbon Dioxide Consumed Carbon is found in all life and in the Earth’s atmosphere. Plants, through photosynthesis, convert carbon dioxide to carbohydrates (sugars), and release oxygen as a by-product. In turn plants are consumed (eaten) by other organisms. Once these organisms die, decomposing bacteria break down the dead organism and release carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere. Trees, oceans and lakes act as carbon sinks; they trap large amounts of carbon and release it back into the atmosphere slowly over time. Humans disrupt the carbon cycle by burning or combusting organic materials. Word Bank: Cellular Respiration, Decomposition, Photosynthesis, Fossil Fuels, Combustion Nitrogen Cycle: Denitrification Nitrogen Cycle Amino Acids Lightning Ammonia Decomposing Bacteria Nitrogen Fixation Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria Proteins The Nitrogen cycle is the pathway for moving nitrogen between biotic and abiotic factors on Earth. Nitrogen is essential for the formation of amino acids and proteins in all living organisms. The atmosphere is 78% nitrogen (N2). Animals cannot use nitrogen gas. Instead bacteria in the soil called Nitrogen Fixing bacteria convert the atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia or nitrate. This process is called Nitrogen Fixation. Lightning can also cause nitrogen fixation. Once in the soil, plants absorb the nitrogen through their roots and then organisms eat the plants. When organisms die, decomposing bacteria release the nitrogen from the bodies back into the atmosphere in a process called Denitrification. Word Bank: Gas, Nitrogen, Nitrogen Fixation, Death and Decay, Nitrogen in Soil, Bacteria, Waste Phosphorus Cycle Bacteria Leaching Phosphorus Cycle Weathering Dies Waste Absorb The phosphorus cycle originates from the ground. Phosphorus is released the ground by the weathering and leaching of rocks. Plants then absorb the phosphorus through their roots. Organisms consume the plants and excrete waste in the form of urine and feces. Phosphorus is also release when an organism dies. Decomposing bacteria the break down the dead organism or waste products. Finally, the Phosphorus is released back into the soil to either create new rocks or be reabsorbed into plants. The _____________________ Cycle Word Bank: Death and Decay, Bacteria, Root absorption, Consumption, Phosphorus Human Impact Overview THREAT GREENHOUSE EFFECT CAUSE Burning fossil fuels and clearing forests increases amount of carbon dioxide in atmosphere POSSIBLE RESULTS Melts polar ice caps, causes overall drastic changes in climate throughout the world ACID RAIN Burning fossil fuels makes rain more acidic Acid rain destroys forests and poisons the environment OZONE DEPLETION Chemicals eat away the ozone layer Increases chances of skin cancer AIR POLLUTION Burning wood and fossil fuels releases chemicals in the air Increases health issues WATER POLLUTION Waste, trash, and chemicals contaminate water sources Threatens life in water ways and drinking water SOIL DEGRADATION/ DEPLETION Soil erosion, pesticides and over use destroy soil Threat to farming HABITAT DESTRUCTION Poisoning lakes and destroying forests Threatens living species and upsets nature’s balance









