SITE: Puzzles of the Earth http://library
advertisement
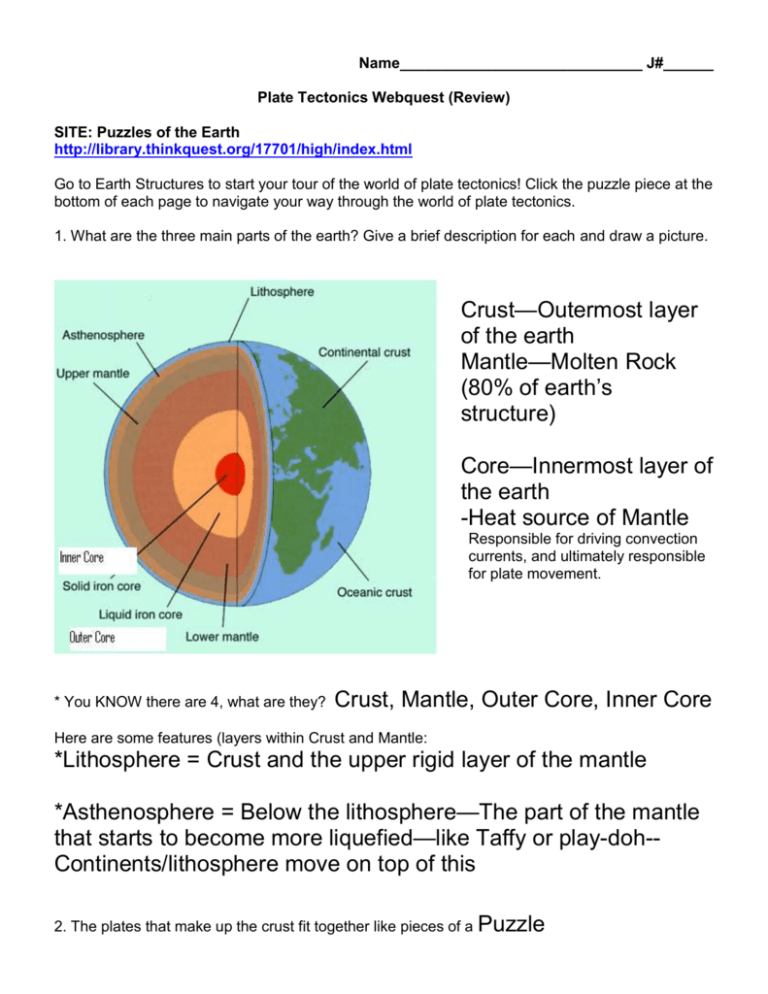
Name_____________________________ J#______ Plate Tectonics Webquest (Review) SITE: Puzzles of the Earth http://library.thinkquest.org/17701/high/index.html Go to Earth Structures to start your tour of the world of plate tectonics! Click the puzzle piece at the bottom of each page to navigate your way through the world of plate tectonics. 1. What are the three main parts of the earth? Give a brief description for each and draw a picture. Crust—Outermost layer of the earth Mantle—Molten Rock (80% of earth’s structure) Core—Innermost layer of the earth -Heat source of Mantle Responsible for driving convection currents, and ultimately responsible for plate movement. * You KNOW there are 4, what are they? Crust, Mantle, Outer Core, Inner Core Here are some features (layers within Crust and Mantle: *Lithosphere = Crust and the upper rigid layer of the mantle *Asthenosphere = Below the lithosphere—The part of the mantle that starts to become more liquefied—like Taffy or play-doh-Continents/lithosphere move on top of this 2. The plates that make up the crust fit together like pieces of a Puzzle 3. Which plate do we live on? North American (Hint: Earth Map) 4. We live on the earth’s outermost layer. What is it called? Crust 5. Match each description using a C for continental plates or O for oceanic plates. O Crust that "carries" the ocean C Crust that "carries" the continents; may also contain oceans C Less dense and tends not to subduct. *What does subduct mean? Sink O More dense and tends to be subducted. 6. How do plates move? Write a description using the terms magma, plates, and convection currents. COMPARE to a lava lamp! Tectonic Plates (pieces of the lithosphere) float on molten rock (magma). Near the core, magma in the mantle is heated, which causes convection (transfer of heat through liquids) in the magma (in the mantle). Currents rise and fall due to density (less dense rises and spreads, which cools and then falls because it is more dense.) This pushes against the lithosphere and moves the crust; creating crunching and pulling across the globe! If you’ve ever watched a lava lamp, you’ve seen convection currents at work. 1. Heat (from the light bulb) warms up a colored liquid/wax at the base of the lamp. 2. The colored liquid rises, because hot liquids are less dense than cool ones. 3. As the blobs of hot liquid move away from the heat source, they cool off, become more dense again, and sink back to the bottom. This cycle of movement is called a convection current. 7. What happens at a convergent boundary? Explain and draw a diagram! *There are 3 types of convergent boundaries. 2 Plates collide- crust destroyed 8. What happens in each situation? Continental plate meets oceanic plate –subduction (one sinks under the other)trench and then beyond the trench lies continental volcanic arcs Two continental plates meet –mountains uplift Two oceanic plates meet – Subduction-trench and then beyond the trench lies volcanic island arcs 9. What happens at a divergent boundary? Explain and draw a diagram! 2 plates moving away from each other *there are 2 types of divergent boundaries (oceanic-oceanic and continentalcontinental) 10. What is sea-floor spreading? New crust forms where two plates move away from each other **Oceanic-Oceanic Divergent Boundaries. 11. Describe transform plate movement. Explain and draw a diagram! earthquake Friction/ 12. What are three geographic features that may be found at plate boundaries? Mountain Volcano Trench SITE: ZOOM Plate Tectonics http://www.enchantedlearning.com/subjects/astronomy/planets/earth/Continents.shtml 1. Who first proposed the idea of continental drift? Alfred Wegener 2. What did he name the gigantic supercontinent that existed 200 million years ago? Pangaea 3. When did it begin to break up? Jurassic Period 4. What were the names of the two smaller supercontinents created by the break up? Gondwanaland and Lauraisa 5. How fast are the plates moving? 1 to10 cm per year Try the Plate Tectonics Quiz http://www.enchantedlearning.com/subjects/astronomy/activities/radiobuttonquiz/Tectonicspz.shtml








