Learning space - Accessible Technology
advertisement

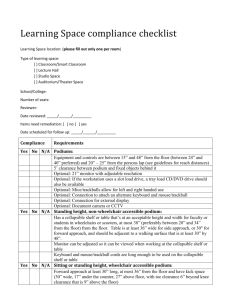
Learning spaces accessibility guidelines Introduction The following are guidelines for equipment, podiums, signage, and other elements in learning spaces (areas whose primary purpose is for students to receive instruction) on campus which contain technology. These guidelines were developed to adhere to the Temple University Accessibility of Information and Technology policy: Any information and technology — including, but not limited to, computers and ancillary equipment, instructional materials, software, videos, multimedia, telecommunications, or webbased content or products — developed, procured, maintained, or used in carrying out university activities must be compliant with Sections 504 and 508 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973, as amended, the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990, as amended, and other related local, state, and federal laws, as well as other related university policies. Although these are guidelines, the University adheres to ICC/ANSI A117.1.2009, and IBC 2012 Chapter 11 guidelines for accessible building construction and renovation. In addition, accessible learning space must comply with industry standards, and must comply with the applicable laws, such as 2010 ADA Standards for Accessible Design and the Rehabilitation Act of 1973, as amended. Some relevant sections of these laws and statutes are referenced at the end of this document. Definitions: Learning space: a classroom, lecture hall, studio space, seminar room, and auditorium/theater space, including those used for lab instruction. Computer lab based classrooms Any learning spaces with computers at the student desks should adhere to these standards as well as the Computer Lab Accessibility Guidelines. Requirements for accessible learning space with technology The University has an inventory of accessible learning spaces. If a school does not have an accessible learning space as part of its assigned inventory it must work with the Central University Scheduling Office to schedule an accessible learning space when demand arises, or proactively remediate an existing space. As the university does not have any centrally scheduled studio space, programs that require studio space for instruction must provide for accessible studio space when the demand arises. Accessible learning spaces must be capable of supporting instructors and students with disabilities, and must be physically accessible (that is, the route to the accessible learning space and the accessible learning space itself, along with ancillary items such as room signage and controls, must be accessible according to applicable local, state and federal disabilities law as well as with 2010 ADA Standards for Accessible Design.) Instructors with disabilities must be scheduled to teach in these accessible learning spaces as a priority. If this poses an undue burden, other accommodations will be contemplated, as appropriate. If there are scheduling needs that the designated school or college space cannot accommodate, they should request appropriate space through the Central University Scheduling Office. Any newly created learning space, must be accessible according to applicable local, state and federal disabilities law as well as with 2010 ADA Standards for Accessible Design and any university policies and guidelines. Podiums All podiums in accessible learning spaces should meet the following requirements. Alternate designs for the podiums are acceptable provided they meet the specifications below or are approved by the Accessible Technology Compliance Committee. Access to controls, peripherals and ports (USB, audio, media, including drive trays) are between 15” and 48” from the floor (between 24” and 40” preferred) and 20" to 25" from the center of where the person’s lap is expected to be. Side reach distances (obstructed and non-obstructed): Forward reach (obstructed and non-obstructed): 11/11/2013 2 The podium must have at least 60” space between it and the wall (or other fixed structure) behind it. Sitting or standing height, wheelchair accessible podium 8” min 27” min 9” 17” – 25” 27" minimum clearance under work surface for knee space 11/11/2013 6” max Top of work surface is from28" to 34" above the floor 3 The podium in accessible learning spaces should have a forward approach that is at least 30” long, and at most 36” from the floor, and must have knee and toe space under the podium (at least 30” wide, and extending 17” under the counter with a height of 27” above the floor, which a toe clearance of 6” beyond the knee clearance at a height of 9” above the floor). Standing height non-wheelchair accessible podium Standing height podiums in accessible learning spaces that are not wheelchair accessible (for example, pedestal style podiums) should have a collapsible shelf, or table next to the podium, that’s at an acceptable height and width for faculty or students in wheelchairs or scooters, at most 38” (preferably between 28” and 34” from the floor) from the floor, and at least 36” wide for side approach or at least 30” wide for forward approach, and should be adjacent to a walking surface that is at least 30” by 48”. The monitor should be adjustable so that the full screen can be viewed when sitting at the collapsible shelf or table. The Keyboard and mouse should have long enough cords that they can be used left and right handed on the shelf or table. Optional components Connections for an external display for low vision students Connections to attach an alternate keyboard and mouse/trackball (note: due to security restrictions, assistance will be required to install the drivers) The monitor on the podium should have a 21 inch display. If the workstation on the podium uses a slot load drive, a tray load CD/DVD drive should also be available. Mice and trackballs allow for left and right handed use. Document camera or CCTV: (MagniLink U Split) Control Panels Control panels in accessible learning spaces used to operate the equipment in the podium or in the room typically come in two form factors: touch panels; push buttons. Touch control panels have a backlit display that is operable by touch, similar to a tablet. Push button control panels are a series of physical buttons. Both types of control panels should meet the following accessibility guidelines: Control panels in accessible learning spaces which are not mounted on podiums must be reachable and viewable by someone in a wheelchair (see ADA Standards section 308.2 for forward reach distances and section 308.3 for side reach distances). Control panels in accessible learning spaces mounted on podiums must be reachable according to the reach distances specified in the podiums section for equipment controls. Touch control panels Touch control panels in accessible learning spaces should have audible prompts and an alternate layout that is usable by blind/low vision instructors. Touch control panels in accessible learning spaces should have high contrast. 11/11/2013 4 Push button control panels Push button control panels in accessible learning spaces should have braille labels next to the button for the function and shall be usable by people with disabilities without requiring an enduser to attach assistive technology to the product. Note: If instructions are available in braille detailing the button function and layout with cross reference to the braille label, then braille labels do not have to reflect the purpose of the control, and not every button has to be labeled if they are grouped together in the same control panel, and are tactilely discernible from one another. For example, in a control panel with the following layout: SysOn SysOff Laptop1 Laptop2 RackPC RackVid VolUp VolDn Adjust Mute HelpMe Cancel A braille label "A" should be placed next to VolUp, and a document provided which details the function of each button and their placement relative to "A". (Note: a braille labeler is available from Classroom Technology Support, and DRS.) Signs and documentation Signs in accessible learning spaces should be printed in with the following attributes: Minimum 18 point sans serif fonts (see ADA Standards for specifics regarding fonts and spacing) High contrast colors (i.e. black on white, or Temple cherry and white) Capital letters No italics, oblique angles, scripts, or other decorations Braille (either on the same sign, or on a different sign) If accessibility symbols are used, they should be the international accessibility symbols. Signs with tactile characters (Braille) should be positioned so that the baseline of the lowest character is 48” above the floor and the baseline of the top character is a maximum of 60” from the floor. Visual characters must be at least 40 inches from the floor. Braille is only required for permanent signage, such as building signage. Documentation should be available in both print and braille, and should be positioned no more than 48”above the floor. An alternative to putting braille on signs is to have a HTML or Word document available on the desktop labeled 'policies and guidelines.' Electronic copies of the documentation are an acceptable alternative to braille documents. 11/11/2013 5 Class Captures Accessible learning spaces that are configured with class capture should use an accessible solution such as Echo360 or MediaSite. Software The following software is recommended for use on accessible podiums and carts: Screen reader software: JAWS Learning Systems Tool: Read and Write Gold Screen magnification: ZoomText (with speech) Browser plugins: o MathPlayer To defray costs, a solution such as KeyServer could be used to provide adaptive software in all learning spaces without incurring additional licensing costs. JAWS, Read and Write Gold, and ZoomText are available with networked licenses and can be installed on any machine on campus. It is recommended that drivers for the following braille displays be added to the computers in learning spaces as well: • • • • • • Freedom Scientific 's Focus braille display: HumanWare 's braille Note: HumanWare 's brailliant and brailleconnect HIMS JAWS drivers for the Braille EDGE HIMS JAWS drivers for the Braille Sense HIMS JAWS drivers for the SyncBraille Please submit a TUhelp request, or contact accessibility@temple.edu to obtain access to the networked versions of JAWS, Read and Write Gold, and Zoomtext. Whiteboards Fixed height whiteboards should be hung 60” high from the center of the board; however adjustable height whiteboards should be mounted according to manufacturer specifications. Pull cords for manual screens Rooms with screens which utilize pull cords should also contain a pole (such as the Da-Lite Pull Rod 74689) to retrieve the pull cord if end of the cord is outside of the required reach ranges (15" to 48" from the floor). Assistive Listening Devices Assisted listening devices work with t-coils, and have both bands available. The number of assisted listening devices meets or exceeds the minimum number required according to the following table: 11/11/2013 6 Seating Capacity Minimum Number of Required Assistive Listening Devices 50 or less 2 51 to 200 2, plus 1 per 25 seats over 50 seats (or fraction thereof) 201 to 500 2, plus 1 per 25 seats over 50 seats (or fraction thereof) Accessible Carts If certain technology needs cannot be met, a request for accessible learning space cannot be fulfilled through the Central University Scheduling Office, school/colleges should request an accessible technology cart at least 48 hours before it is needed1. An accessible cart has access to controls, peripherals and ports (USB, audio, media, including drive trays) between 15” and 48” from the floor (between 24” and 40” preferred) from the floor and 20" to 25" from the center of where the person’s lap is expected to be. All software listed in the software section is installed on the carts. There are a sufficient number of accessible carts compliant with these standards which are available in the event of a request for an accommodation. Recommendations for all learning spaces Recommended Software: Microsoft Office (with Voice Dictation options installed) Adobe Acrobat Reader (with accessibility options activated) Windows Media Player (with captioning turned on by default) Screen magnification software built into Operating System is available for end users to activate Speech recognition software built into Windows is available for end users to activate Text-to-speech software built into Operating System is available for end users to activate Allow users to adjust keyboard settings: o Key repeat rate o Keystroke delay o Sticky keys Legal & statutory references This section contains references to several laws and statues that are common to accessible learning spaces with technology. However, each accessible learning space may have unique equipment or physical spaces that are subject to laws not referenced in this section. 1 Classroom Technology Support requests 48 hours advance notice for a cart, as last minute requests cannot always be fulfilled. 11/11/2013 7 The relevant sections of Section 508 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973 may include: subpart B 1194.26 for workstations and subpart B 1194.25 for control panels. Relevant sections of the 2010 ADA Standards for Accessible Design may include: 219 Assistive Listening Systems 304 Turning Space 305 Clear Floor or Ground Space 306 Knee and Toe Clearance 308 Reach Ranges 309 Operable Parts 703 Signs 802 Wheelchair Spaces, Companion Seats, and Designated Aisle Seats 11/11/2013 8