Digital to Analogue conversion – the R
advertisement

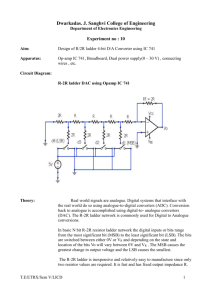
Unit 7: Electrical devices LO3: Understand how to use signal conditioning techniques and signal conversion devices Digital to Analogue conversion – the R-2R ladder Learner activity sheet Activity 1 Digital to analogue converters are circuits or devices that convert a digital input into an analogue signal. They are typically used to interface a microprocessor or microcontroller to an output device or actuator. In this activity, you are going to investigate one particular type of analogue to digital conversion circuit called the R-2R ladder. The R-2R ladder circuit is shown below, and consists of a combination of resistors (values R and 2R) and an operational amplifier (op amp) used as a summing amplifier. The circuit will convert a digital input (at terminals A, B C and D) to a corresponding analogue voltage output at output of the op amp. The gain of the op amp is set using resistors RF and RI, and if RF = RI the gain is 1. Version 1 Begin the activity by investigating how the circuit works. An explanation of how the circuit works can be found at the following website (although you may find others): http://www.circuitsgallery.com/2012/04/digital-to-analog-converter-using-r-2r.html 𝐴𝑛𝑎𝑙𝑜𝑔𝑢𝑒 𝑂𝑢𝑡𝑝𝑢𝑡 (𝑉) = − 𝑅𝐹 𝐷 𝐶 𝐵 𝐴 ( + + + ) 𝑅𝐼 2 4 8 16 Example: If Logic 0 = 0V and Logic 1 = 10 V, and RF = RI = 1K then with digital inputs (A, B, C, D) = 0101 𝐴𝑛𝑎𝑙𝑜𝑔𝑢𝑒 𝑂𝑢𝑡𝑝𝑢𝑡 (𝑉) = − 1𝐾 0 10𝑉 0 10 𝑉 ( + + + ) 1𝐾 2 4 8 16 = −(2.5 𝑉 + 0.625 𝑉) = −3.125 𝑉 Version 1 Activity 2 Construct the circuit for the R-2R ladder shown in Activity 1. Alternatively, you may simulate the circuit using circuit simulation software. Equipment you will need: Op Amp (741) Resistors (R = 1K, RF = 1K, RI = 1K) – to make 2R you will need 2 x 1K resistors in series Breadboard or veroboard Connecting wire Power supply (with positive and negative outputs) Multimeter (or oscilloscope) to measure output voltage You will also need to provide digital inputs to terminals A, B, C and D corresponding to Logic 1 and Logic 0. You could use toggle switches to connect the terminals to the positive voltage from the power supply (+VCC) or 0V (zero volts) to represent Logic 1 and Logic 0 respectively. Version 1 Investigate operation of the circuit by tabulating output voltage for binary combinations of digital inputs. Insert calculated output voltage, and the voltage measured. A B C D 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 Output Output Voltage Voltage (calculated) (measured) Continue the table to include all combinations of digital inputs to A, B, C and D. Plot a graph of binary input vs. output voltage. You may do this using graph paper or a spreadsheet. Answer the following questions: 1. Does the circuit perform as expected – comment on the shape of the graph? Version 1 2. Do the measured values of output voltage agree with the calculated values – and if not, why? 3. How could the circuit be extended to include further digital inputs? 4. How is the R-2R ladder principle used in the design of commercial Digital to Analogue converter integrated circuits? Version 1