Problem Set 3, Fall 2015 Student Name: 8 points total Note: Please
advertisement

Problem Set 3, Spring 2016
Student Name:
8 points total
Note: Please show all work.
1. Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an autosomal recessive disorder. Normally, both parents must be
carriers of the CF gene in order for the child to inherit the disorder. In 1998, Arthur Beaudet of
the Baylor College of Medicine saw a very unusual CF patient. Testing revealed the following:
1) the mother was a CF carrier
2) the father had two wild-type alleles
3) both of the patient's chromosomes that contained the CF gene had come from her
mother.
It was determined that nondisjunction must have occurred in both oogenesis of the mother
and spermatogenesis of the father to create the patient's odd combination of alleles. Diagram
the 2 nondisjunction events that occurred in meiosis of the father and of the mother. Then
show which two gametes fused to produce the CF patient's phenotype.
2. A man has an extra toe on each foot as a result of a dominant trait that he inherited from his
mother. His mother's mother and his mother also had the trait. The man falls in love with a
ten-toed beauty and their first child, a boy, has a normal number of toes.
A. Draw a pedigree for this family and show all genotypes.
B. What is the chance that their next child will have 12 toes like it's father?
1
Problem Set 3, Spring 2016
Student Name:
8 points total
1/2
If it’s X-linked dominant then all daughers and no sons will be affected,
so probability is still 1/2.
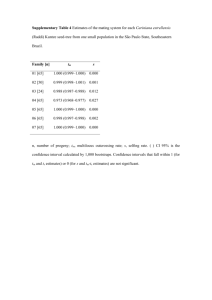
3. In the pedigree shown, individual III-1 died at age 2 of a rare metabolic disorder.
XAY
XAXa
XAY
XAXa
A. What is/are the possible modes of
I
A–
A–
A–
A–
inheritance?
1
2
3
4
X-linked recessive or autosomal recessive
AXa
AY
X
X
II
Aa
Aa
1
2
B. Indicate the genotypes of each individual
in the pedigree, based on the pattern of
XaY
XAXA or
XAXA or
inheritance you listed in part A (if you
III
a
a
aa
listed more than one, choose your favorite)
1
3
A–2
A–
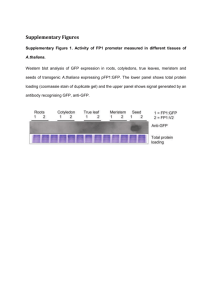
4. A rare disease affects individuals as shown. From the pedigree, this trait is most likely to be
inherited as an
autosomal dominant or
XdY
XDXd
X-linked dominant trait.
dd
Dd
Assign genotypes to all
individuals for each
XdY
XdXd
XDXd
XDY
XdXd
pattern of inheritance. If
dd
dd
Dd
Dd
dd
multiple genotypes are
possible, please list
them all.
XdXd
dd
XdXd
dd
XdY
dd
2
XdY
dd
XDXd
Dd
XdY
dd
Problem Set 3, Spring 2016
Student Name:
8 points total
5. Joe is colorblind. Colorblindness is X-linked and recessive. His wife Susie has normal vision
with no family history of the disease. What are the chances of their having a colorblind son?
Daughter? Can any of their children be carriers? If so, what proportion and what gender(s)?
Cross is XcbY X XCBXCB => XCBXcb and XCBY So no children affected and all daughters but no
sons carry (Carrier is someone with mutation but no symptoms, typically heterozygote for a
recessive mutation.)
6. While studying guinea pigs in South America, you notice that there are two true breeding
populations in your area. One has long hair and light eyes, and the other has short hair and
dark eyes. You cross guinea pigs from population 1 with population 2. The F1 progeny all have
long hair and dark eyes. You cross the F1 progeny to produce F2's and obtain the following
results:
308 long hair, light eyes L–dd
901 long hair, dark eyes L–D–
287 short hair, dark eyes llD–
104 short hair, light eyes lldd
1600 total
A. What are the genoytpes of the F2 guinea pigs?
B. If you cross long-haired, light-eyed F2 progeny with short-haired, light-eyed F2
progeny, what is the probability of obtaining short-haired, light-eyed offspring? What is
the probability of obtaining long-haired, dark-eyed offspring?
1/3 LLdd X lldd =>Lldd
2/3 Lldd X lldd =>1/2 Lldd and ½ lldd
P{short, light} = ½(2/3) = 1/3
P{long, dark} = 0
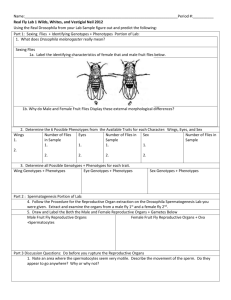
7. The genetic disorder citronosis makes people crave grapefruit. Results of a pedigree analysis
of citronosis are shown below:
3
Problem Set 3, Spring 2016
8 points total
Student Name:
I
1
2
II
1
2
3
4
6
5
III
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
A. What is the most likely pattern of inheritance for citronosis?
X-linked dominant
B. List the most likely genotype for the following individuals:
I-1
X CX c
II-2 XCY
III-2 XCXc
III-5 XcY
8. After studying a lizard species on a Pacific island, you conclude that there are two truebreeding strains: strain A is green and has a spikey tail and strain B is blue and has a smooth
tail. A cross between a female of strain A and a male of strain B produces all green, smoothtailed offspring. A cross between the F1's results in the following progeny at the frequencies
indicated.
Note: ratio of green
female: green male:
XBXB or b P–
Green, smooth-tailed females
3/8
blue male is 2:1:1,
XBY P–
Green, smooth-tailed males
3/16
suggesting X linkage.
XbY P–
Blue, smooth-tailed males
3/16
ratio of smooth:spikey
XBXB or b pp
Green, spikey-tailed females
1/8
is 3:1 regardless of
XBY pp
Green, spikey-tiled males
1/16
gender.
XbY pp
Blue, spikey-tailed males
1/16
A. What are the genotypes of the original strains and what are the genotypes of the F2
progeny? Originals strains are XBXB pp and XbY PP; F2 progeny are listed above.
4
8
Problem Set 3, Spring 2016
Student Name:
8 points total
B. What phenotypes will offspring have from a cross of blue, spikey-tailed F2 males
with original strain B females?
Cross is XbYpp X XbXbPP will produce XbYPp X XbXbPp, so all progeny are blue and
smooth tailed.
5