Topic 7: Heredity and Reproduction
advertisement
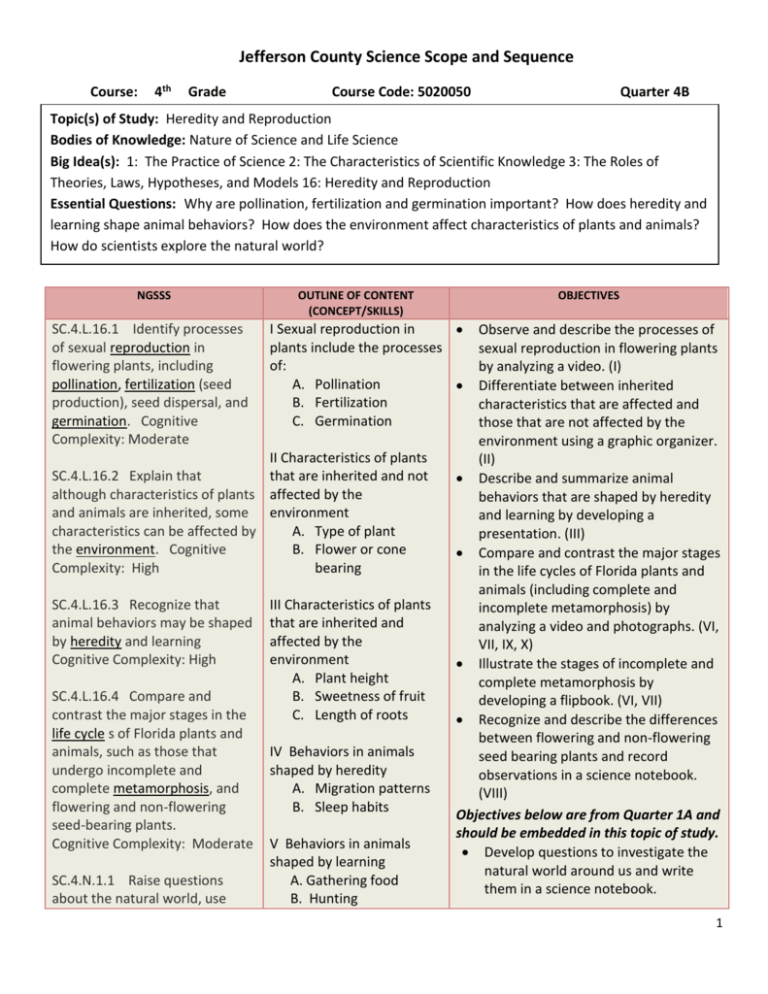
Jefferson County Science Scope and Sequence Course: 4th Grade Course Code: 5020050 Quarter 4B Topic(s) of Study: Heredity and Reproduction Bodies of Knowledge: Nature of Science and Life Science Big Idea(s): 1: The Practice of Science 2: The Characteristics of Scientific Knowledge 3: The Roles of Theories, Laws, Hypotheses, and Models 16: Heredity and Reproduction Essential Questions: Why are pollination, fertilization and germination important? How does heredity and learning shape animal behaviors? How does the environment affect characteristics of plants and animals? How do scientists explore the natural world? NGSSS SC.4.L.16.1 Identify processes of sexual reproduction in flowering plants, including pollination, fertilization (seed production), seed dispersal, and germination. Cognitive Complexity: Moderate OUTLINE OF CONTENT (CONCEPT/SKILLS) I Sexual reproduction in plants include the processes of: A. Pollination B. Fertilization C. Germination II Characteristics of plants SC.4.L.16.2 Explain that that are inherited and not although characteristics of plants affected by the and animals are inherited, some environment characteristics can be affected by A. Type of plant the environment. Cognitive B. Flower or cone Complexity: High bearing SC.4.L.16.3 Recognize that animal behaviors may be shaped by heredity and learning Cognitive Complexity: High SC.4.L.16.4 Compare and contrast the major stages in the life cycle s of Florida plants and animals, such as those that undergo incomplete and complete metamorphosis, and flowering and non-flowering seed-bearing plants. Cognitive Complexity: Moderate SC.4.N.1.1 Raise questions about the natural world, use OBJECTIVES III Characteristics of plants that are inherited and affected by the environment A. Plant height B. Sweetness of fruit C. Length of roots IV Behaviors in animals shaped by heredity A. Migration patterns B. Sleep habits V Behaviors in animals shaped by learning A. Gathering food B. Hunting Observe and describe the processes of sexual reproduction in flowering plants by analyzing a video. (I) Differentiate between inherited characteristics that are affected and those that are not affected by the environment using a graphic organizer. (II) Describe and summarize animal behaviors that are shaped by heredity and learning by developing a presentation. (III) Compare and contrast the major stages in the life cycles of Florida plants and animals (including complete and incomplete metamorphosis) by analyzing a video and photographs. (VI, VII, IX, X) Illustrate the stages of incomplete and complete metamorphosis by developing a flipbook. (VI, VII) Recognize and describe the differences between flowering and non-flowering seed bearing plants and record observations in a science notebook. (VIII) Objectives below are from Quarter 1A and should be embedded in this topic of study. Develop questions to investigate the natural world around us and write them in a science notebook. 1 Jefferson County Science Scope and Sequence appropriate reference materials that support understanding to obtain information (identifying the source), conduct both individual and team investigations through free exploration and systematic investigations, and generate appropriate explanations based on those explorations. Cognitive Complexity: High SC.4.N.1.4 Attempt reasonable answers to scientific questions and cite evidence in support. Cognitive Complexity: High SC.4.N.1.6 Keep records that describe observations made, carefully distinguishing actual observations from ideas and inferences about the observations. Cognitive Complexity: High VI Incomplete metamorphosis in animals refers to the insects that go through 3 stages to change the way they look: grasshoppers, cockroaches, and dragonflies. VII Complete metamorphosis in animals refers to the insects that go through 4 stages to change the way they look: beetles and moths. VIII Major stages of life cycle for plants A. Flowering B. Non flowering IX Life cycles of common Florida plants Conduct an investigation and record observations in a science notebook. Compare and contrast observations made by different groups using a graphic organizer. Discuss reasons why differences may exist among various lab teams. Recognize that scientists question and check each other’s work through role play. Describe how different approaches to science are not always a rigid step by step process, but can include observations by analyzing a video. Use proof (empirical evidence) to support explanations and document in a science notebook. Describe the different types of models (2D, 3D, computer simulations). Explain why models are important but are also limited in what they can represent. X Life Cycles of common Florida animals SC.4.N.1.7 Recognize and explain that scientists base their explanations on evidence. Cognitive Complexity: Moderate SC.4.N.1.8 Recognize that science involves creativity in designing experiments. Cognitive Complexity: Moderate SC.4.N.2.1 Explain that science focuses solely on the natural world. Cognitive Complexity: Moderate TEACHER TRANSITION INTO NEXT TOPIC OF STUDY Now that we know about the patterns and life cycles of plants and animals let's learn about patterns of interdependence among organisms. SC.4.N.3.1 Explain that models can be three dimensional, two dimensional, an explanation in 2 Jefferson County Science Scope and Sequence your mind, or a computer model. Cognitive Complexity: Moderate MACC.4.MD.1.1: Know relative sizes of measurement units within one system of units including km, m, cm; kg, g; lb, oz.; l, ml; hr, min, sec. Within a single system of measurement, express measurements in a larger unit in terms of a smaller unit. Record measurement equivalents in a two column table. For example, know that 1 ft is 12 times as long as 1 in. Express the length of a 4 ft snake as 48 in. Generate a conversion table for feet and inches listing the number pairs (1, 12), (2, 24), (3, 36), ... MACC.4.MD.2.4: Make a line plot to display a data set of measurements in fractions of a unit (1/2, 1/4, 1/8). Solve problems involving addition and subtraction of fractions by using information presented in line plots. For example, from a line plot find and interpret the difference in length between the longest and shortest specimens in an insect collection. LACC.4.RI.1.3: Explain events, procedures, ideas, or concepts in a historical, scientific, or technical text, including what happened and why, based on specific information in the text. LACC.4.RI.2.4: Explain events, procedures, ideas, or concepts in a historical, scientific, or technical text, including what happened and why, based on specific information in the text. LACC.4.RI.2.4: Determine the 3 Jefferson County Science Scope and Sequence meaning of general academic and domain-specific words or phrases in a text relevant to a grade 4 topic or subject area. LACC.4.RI.4.10: By the end of year, read and comprehend informational texts, including history/social studies, science, and technical texts, in the grades 4–5 text complexity band proficiently, with scaffolding as needed at the high end of the range. LACC.4.SL.1.1: Engage effectively in a range of collaborative discussions (one-on-one, in groups, and teacher-led) with diverse partners on grade 4 topics and texts, building on others’ ideas and expressing their own clearly. a. Come to discussions prepared, having read or studied required material; explicitly draw on that preparation and other information known about the topic to explore ideas under discussion. b. Follow agreed-upon rules for discussions and carry out assigned roles. c. Pose and respond to specific questions to clarify or follow up on information, and make comments that contribute to the discussion and link to the remarks of others. d. Review the key ideas expressed and explain their own ideas and understanding in light of the discussion. LACC.4.W.3.8: Recall relevant information from experiences or gather relevant information from print and digital sources; take notes and categorize information, and provide a list of sources. LACC.4.W.3.9: Draw evidence from 4 Jefferson County Science Scope and Sequence literary or informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research. a. Apply grade 4 Reading standards to literature (e.g., “Describe in depth a character, setting, or event in a story or drama, drawing on specific details in the text [e.g., a character’s thoughts, words, or actions].”). b. Apply grade 4 Reading standards to informational texts (e.g., “Explain how an author uses reasons and evidence to support particular points in a text”). 5