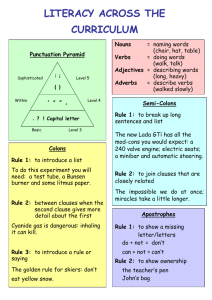
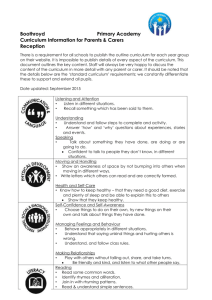
RF, L and SL Learning Targets
advertisement

Grade 3 Foundational Skills/Language/Speaking & Listening Learning Targets-2014-15 7-26-14 Year Long Learning Targets These are standards that do not have a particular emphasis in one or more quarters. They should be addressed throughout the school year. RF3.b Decode words with common Latin suffixes RF3.d Read grade-appropriate irregularly spelled words. RF4.c Students will evaluate their understanding of the text and use strategies for self-correction. SL1.a Come to discussions prepared, having read or studied required material; explicitly draw on that preparation and other information known about the topic to explore ideas under discussion. SL1.b Follow agreed-upon rules for discussions (e.g., gaining the floor in respectful ways, listening to others with care, speaking one at a time about the topics and texts under discussion.) SL6 Speak in complete sentences when appropriate to task and situation in order to provide requested detail or clarification. L1.c Use abstract nouns (e.g. childhood) L2.g Consult reference materials, including beginning dictionaries, as needed to check and correct spellings. L2.f Use spelling patterns and generalizations (e.g., word families, position-based spellings, syllable patterns, ending rules, meaningful word parts) in writing words. L3.b Recognize and observe differences between the conventions of spoken and written standard English. L4.a Use direct definition context clues to determine the meaning of an unknown word or phrase L4.d Use glossaries or beginning dictionaries, both print and digital, to determine or clarify the precise meaning of key words and phrases in all content areas. L5.b Identify real-life connections between words and their use (e.g. describe people who are friendly or helpful.) L5.c Distinguish shades of meaning among related words that describe states of mind or degrees of certainty (e.g., knew, believed, suspected, heard, wondered.) L6 Acquire and use accurately grade-appropriate conversational, general academic and domain-specific words and phrases, including those that signal spatial and temporal relationships (e.g., After dinner that night we went looking for them.) Student Learning Targets- Quarter 1 RF3.a Identify and know the meaning of the common derivational suffixes that create adjectives – -al, -ary, -able, -ly, -y, -ful. RF3.a Begin using the derivational suffixes that create adjectives in both oral sentences and in writing. RF4.a Read grade level text with accuracy SL1.c Ask questions to orally check understanding of information presented and stay on topic. SL4 Orally report on a text, tell a story, or recount an experience with appropriate facts L1.a L1.b L1.d L1.e L1.f L1.g L1.h L1.i L1.i L1.j L2.a L2.c L2.d L2.e L3.a L4.b L5.a Explain the function of subject and object nouns and verbs in general and their function in both oral and written sentences. Form and use regular plural nouns using the suffix –s in written sentences Form and use regular verbs using the suffixes –s and –es in written sentences Form and use present tense verbs *Ensure subject-verb and pronoun-antecedent agreement for present tense in oral and written sentences. Form and use comparative and superlative adjectives and adverbs using –er and -est Use coordinating conjunctions – and, but, or - in oral sentences. Create and use simple sentences both orally and in writing Create and use orally compound subjects and verbs. Form individual letters correctly using cursive writing or joined italics Orally identify the words to be capitalized in a title Orally identify which words in a text are dialogue Interpret the concept of possessives by recognizing what the noun owns. Use conventional spelling for high-frequency and short vowel words that double the ending consonant before adding a suffix. Use words that express shades of meaning in oral conversation Determine the meaning of a new word formed when the suffixes -s, -es, -al, -ary, -able, -ly, -y, and –ful are added Understand the difference between the literal and figurative meanings of commonly used idioms. Third Grade 2014-15 *-Beginning in grade 3, these skills and understandings are particularly likely to require continued attention in higher grades as they are applied to increasingly sophisticated writing and speaking. Grade 3 Foundational Skills/Language/Speaking & Listening Learning Targets-2014-15 7-26-14 Year Long Learning Targets These are standards that do not have a particular emphasis in one or more quarters. They should be addressed throughout the school year. RF3.b Decode words with common Latin suffixes RF3.d Read grade-appropriate irregularly spelled words. RF4.c Students will evaluate their understanding of the text and use strategies for self-correction. SL1.a Come to discussions prepared, having read or studied required material; explicitly draw on that preparation and other information known about the topic to explore ideas under discussion. SL1.b Follow agreed-upon rules for discussions (e.g., gaining the floor in respectful ways, listening to others with care, speaking one at a time about the topics and texts under discussion.) SL6 Speak in complete sentences when appropriate to task and situation in order to provide requested detail or clarification. L1.c Use abstract nouns (e.g. childhood) L2.g Consult reference materials, including beginning dictionaries, as needed to check and correct spellings. L2.f Use spelling patterns and generalizations (e.g., word families, position-based spellings, syllable patterns, ending rules, meaningful word parts) in writing words. L3.b Recognize and observe differences between the conventions of spoken and written standard English. L4.a Use direct definition context clues to determine the meaning of an unknown word or phrase L4.d Use glossaries or beginning dictionaries, both print and digital, to determine or clarify the precise meaning of key words and phrases in all content areas. L5.b Identify real-life connections between words and their use (e.g. describe people who are friendly or helpful.) L5.c Distinguish shades of meaning among related words that describe states of mind or degrees of certainty (e.g., knew, believed, suspected, heard, wondered.) L6 Acquire and use accurately grade-appropriate conversational, general academic and domain-specific words and phrases, including those that signal spatial and temporal relationships (e.g., After dinner that night we went looking for them.) Student Learning Targets- Quarter 2 RF3.a RF3.a RF3.a RF3.a RF3.c RF4.a Identify and know the meaning of these prefixes - pre-, disBegin using the prefixes – pre-, dis- – in both oral sentences and in writing. Identify and know the meaning of common derivational suffixes that create nouns – -er, -ess, -ness, -ary, -y. Begin using the derivational suffixes that create nouns in both oral sentences and in writing. Identify new syllable type – consonant –le Read grade-level text with accuracy, purpose, and understanding SL1.c SL1.d SL2 SL3 SL4 Ask questions to check understanding of information presented, stay on topic, and link their comments to the remarks of others. Explain their own ideas and understanding in light of the discussion. Determine the main ideas and supporting details of a text read aloud. Ask and answer questions about information from a speaker Report orally on a text, tell a story, or recount an experience with appropriate facts and relevant, descriptive details, speaking clearly at an understandable pace L1.a L1.e L1.f L1.g L1.h L1.i L1.i L1.j Explain the function of subject and object pronouns and adjectives in general and their function in both oral and written sentences. Form and use past tense verbs *Ensure subject-verb agreement for past tense in oral and written sentences. Form and use comparative and superlative adjectives using more. Use coordinating conjunctions – and, but, or, - in written sentences Create and use complex sentences both orally and in writing Create and use compound subjects and verbs in writing. Join individual letters correctly using cursive writing or joined italics to form connected words Third Grade 2014-15 *-Beginning in grade 3, these skills and understandings are particularly likely to require continued attention in higher grades as they are applied to increasingly sophisticated writing and speaking. Grade 3 Foundational Skills/Language/Speaking & Listening Learning Targets-2014-15 L1.k L2.a L2.c L2.d L2.e L3.a L4.b L4.c L4.c L5.a 7-26-14 Use reciprocal pronouns - each other, one another – correctly in oral sentences Capitalize the appropriate words in a title in writing Correctly copy dialogue with quotation marks and commas from text Form and use singular noun possessives correctly in written sentences Use conventional spelling for high-frequency and silent e words that drop the e before adding a suffix. Use words and phrases that express shades of meaning in oral conversation and in writing. Determine the meaning of a new word formed when the prefixes – pre-, dis- and suffixes -er, -ess, -ness, -ary, -y are added. Know the meaning of the roots – fract and scrib/script/scribe. Use known roots – fract and scrib/script/scribe – to determine the meaning of an unknown word with the same root. Be able to explain the literal and figurative meanings of commonly used idioms Third Grade 2014-15 *-Beginning in grade 3, these skills and understandings are particularly likely to require continued attention in higher grades as they are applied to increasingly sophisticated writing and speaking. Grade 3 Foundational Skills/Language/Speaking & Listening Learning Targets-2014-15 7-26-14 Year Long Learning Targets These are standards that do not have a particular emphasis in one or more quarters. They should be addressed throughout the school year. RF3.b Decode words with common Latin suffixes RF3.d Read grade-appropriate irregularly spelled words. RF4.c Students will evaluate their understanding of the text and use strategies for self-correction. SL1.a Come to discussions prepared, having read or studied required material; explicitly draw on that preparation and other information known about the topic to explore ideas under discussion. SL1.b Follow agreed-upon rules for discussions (e.g., gaining the floor in respectful ways, listening to others with care, speaking one at a time about the topics and texts under discussion.) SL6 Speak in complete sentences when appropriate to task and situation in order to provide requested detail or clarification. L1.c Use abstract nouns (e.g. childhood) L2.g Consult reference materials, including beginning dictionaries, as needed to check and correct spellings. L2.f Use spelling patterns and generalizations (e.g., word families, position-based spellings, syllable patterns, ending rules, meaningful word parts) in writing words. L3.b Recognize and observe differences between the conventions of spoken and written standard English. L4.a Use direct definition context clues to determine the meaning of an unknown word or phrase L4.d Use glossaries or beginning dictionaries, both print and digital, to determine or clarify the precise meaning of key words and phrases in all content areas. L5.b Identify real-life connections between words and their use (e.g. describe people who are friendly or helpful.) L5.c Distinguish shades of meaning among related words that describe states of mind or degrees of certainty (e.g., knew, believed, suspected, heard, wondered.) L6 Acquire and use accurately grade-appropriate conversational, general academic and domain-specific words and phrases, including those that signal spatial and temporal relationships (e.g., After dinner that night we went looking for them.) Student Learning Targets- Quarter 3 RF3.a RF3.a RF3.a RF3.a RF3.c RF4.a RF4.b Identify and know the meaning of these prefixes - non-, over-. Begin using the prefixes – non-, over- – in both oral sentences and in writing. Identify and know the meaning of the common derivational suffixes that create adverbs and verbs – -ly, -ize, -ate. Begin using the derivational suffixes that create adverbs and verbs in both oral sentences and in writing. Use the six syllable types to decode unknown two syllable words. Read grade-level text with purpose and understanding. Read grade-level prose and poetry orally with accuracy SL1.c SL1.d SL2 SL3 SL5 SL5 Ask questions to check understanding of information presented, being able to stay on topic and link their comments to the remarks of others. Explain their own ideas and understanding of the topic under discussion. Determine the main ideas and supporting details of a text read aloud or information presented in diverse media and formats, including visually, quantitatively, and orally. Ask and answer questions orally about information from a speaker, offering appropriate elaboration and detail. Create audio recordings of stories or poems to demonstrate fluid reading. Create and add visual displays, when appropriate, to emphasize or enhance certain facts or details of topics under discussion. L1.a L1.b L1.d L1.e L1.f L1.g L1.h L1.i Explain the function of adverbs in general and their function in both oral and written sentences. Form and use irregular plural nouns in written sentences Form and use irregular verbs (e.g., catch, hear, teach, etc.) in both oral and written sentences. Form and use future tense verbs *Ensure subject-verb agreement for future tense in oral and written sentences. Form and use comparative and superlative adverbs using most. Use subordinating conjunctions – after, because, before, if, once, since, unless, when, and while - to produce sentences orally. Master the creation and use of complex sentences orally and in writing. Third Grade 2014-15 *-Beginning in grade 3, these skills and understandings are particularly likely to require continued attention in higher grades as they are applied to increasingly sophisticated writing and speaking. Grade 3 Foundational Skills/Language/Speaking & Listening Learning Targets-2014-15 L1.j L1.k L2.b L2.c L2.d L2.e L3.a L4.b L4.c L4.c L5.a 7-26-14 Join connected words correctly using cursive writing or joined italics to form sentences with correct spacing. Use reciprocal pronouns - each other, one another – correctly in oral and written sentences Correctly write addresses using commas where appropriate Write simple dialogue in narratives using the form He said, “…..” Form and use plural possessive nouns ending in –s’, and –es’ correctly in written sentences Use conventional spelling for high-frequency and words that change the ‘y to an i’ before adding a suffix. Choose words and phrase that express shades of meaning for effect in oral conversation Determine the meaning of a new word formed when the prefixes – non-, over- and suffixes -ing, -ly, -ize, -ate - are added Know the meaning of the roots – spect, fac, and mit. Use known roots – spect, fac, and mit – to determine the meaning of an unknown word with the same root Recognize idioms in text and describe the literal and figurative meanings of them Third Grade 2014-15 *-Beginning in grade 3, these skills and understandings are particularly likely to require continued attention in higher grades as they are applied to increasingly sophisticated writing and speaking. Grade 3 Foundational Skills/Language/Speaking & Listening Learning Targets-2014-15 7-26-14 Year Long Learning Targets These are standards that do not have a particular emphasis in one or more quarters. They should be addressed throughout the school year. RF3.b Decode words with common Latin suffixes RF3.d Read grade-appropriate irregularly spelled words. RF4.c Students will evaluate their understanding of the text and use strategies for self-correction. SL1.a Come to discussions prepared, having read or studied required material; explicitly draw on that preparation and other information known about the topic to explore ideas under discussion. SL1.b Follow agreed-upon rules for discussions (e.g., gaining the floor in respectful ways, listening to others with care, speaking one at a time about the topics and texts under discussion.) SL6 Speak in complete sentences when appropriate to task and situation in order to provide requested detail or clarification. L1.c Use abstract nouns (e.g. childhood) L2.g Consult reference materials, including beginning dictionaries, as needed to check and correct spellings. L2.f Use spelling patterns and generalizations (e.g., word families, position-based spellings, syllable patterns, ending rules, meaningful word parts) in writing words. L3.b Recognize and observe differences between the conventions of spoken and written standard English. L4.a Use direct definition context clues to determine the meaning of an unknown word or phrase L4.d Use glossaries or beginning dictionaries, both print and digital, to determine or clarify the precise meaning of key words and phrases in all content areas. L5.b Identify real-life connections between words and their use (e.g. describe people who are friendly or helpful.) L5.c Distinguish shades of meaning among related words that describe states of mind or degrees of certainty (e.g., knew, believed, suspected, heard, wondered.) L6 Acquire and use accurately grade-appropriate conversational, general academic and domain-specific words and phrases, including those that signal spatial and temporal relationships (e.g., After dinner that night we went looking for them.) Student Learning Targets- Quarter 4 RF3.a RF3.a RF3.a RF3.c RF4.a RF4.b Identify and know both meanings of the prefixes – in-, im-, – in both oral sentences and in writing. Begin using the prefixes – in-, im-, – in both oral sentences and in writing. Master the use of the common derivational suffixes in both oral sentences and in writing. Use the six syllable types to decode unknown multi-syllable words. Read grade-level text with purpose and understanding. Read grade level prose and poetry with accuracy, appropriate rate, and expression SL1.c Ask questions to check understanding of information presented, being able to stay on topic and link their comments to the remarks of others. SL1.d Explain their own ideas and understanding of the topic under discussion. SL1.c Ask questions to check understanding of information presented, being able to stay on topic and link their comments to the remarks of others. SL1.d Explain their own ideas and understanding of the topic under discussion. SL4.a Plan and deliver an informative/explanatory oral presentation on a topic that: organizes ideas around major points of information, follows a logical sequence, includes supporting details, uses clear and specific vocabulary, and provides a strong conclusion. SL5 Create audio recordings of stories or poems to demonstrate fluid reading at an understandable pace. SL5 Create and add visual displays, when appropriate, to emphasize or enhance certain facts or details of topics under discussion or presentation. L1.b Master the use of irregular plural nouns in written sentences L1.d Form and use irregular verbs in written sentences L1.e Master the use of past, present, and future verb tenses L1.f *Ensure subject-verb agreement for tenses in oral and written sentences. Third Grade 2014-15 *-Beginning in grade 3, these skills and understandings are particularly likely to require continued attention in higher grades as they are applied to increasingly sophisticated writing and speaking. Grade 3 Foundational Skills/Language/Speaking & Listening Learning Targets-2014-15 L1.g L1.h L1.i L1.j L2.c L2.d L2.e L3.a L4.b L4.c L4.c L5.a 7-26-14 Form and use comparative and superlative adjectives and adverbs using –er, –est, more, and most, choosing between them correctly, depending on what is to be modified. Use subordinating conjunctions – after, because, before, if, once, since, unless, when, and while - to produce sentences orally and in writing. Create and use compound sentences orally and in writing (e.g. I went to the store and I bought some bread.; She went to the movies but he went to the park.). Write sentences correctly using cursive writing or joined italics to form paragraphs with correct spacing, margins, and indentations. Write more complex dialogue Form and use possessives correctly for irregular plural nouns in written sentences. Use conventional spelling for high-frequency, other studied words, and words that have spelling changes when suffixes are added (elf, wolf, shelf, etc..) Choose words and phrase that express shades of meaning for effect in oral conversation and in writing Determine the meaning of a new word formed when the prefixes – in-, im-, - are added Know the meaning of the roots – vid/vis. Use known roots – vid/vis – to determine the meaning of an unknown word with the same root Recognize idioms in text and describe the literal and figurative meanings of them Third Grade 2014-15 *-Beginning in grade 3, these skills and understandings are particularly likely to require continued attention in higher grades as they are applied to increasingly sophisticated writing and speaking. Grade 3 Foundational Skills/Language/Speaking & Listening Learning Targets-2014-15 7-26-14 Review Standards from Prior Grades RF3.a Identify and know the meaning of these prefixes - re-, un-. RF3.a Begin using the prefixes – re-, un- – in both oral sentences and in writing. RF3.c Identify syllable types – closed, VCE, open, r-controlled, and vowel team. L1.b Form and use regular plural nouns using the suffix –es for words ending in s, x, ch, and sh in written sentences L1.d Form and use regular past tense verbs using the suffix –ed in written sentences L1.d Identify the difference between regular and irregular verbs. L1.i Distinguish a complete sentence from a sentence fragment. L2.e Form and use verbs with suffixes –ed and –ing. L4.c Use a known root – multi and graph – to determine the meaning of an unknown word with the same root. Suggestions Roots meanings and examples multi – meaning many or much - multiple, multiply, multifold, multimedia, multilingual, multiplex, multitude graph – meaning to write or draw - autograph, graphite, graphic, telegraph, photograph fract – meaning to break – fracture, fraction, infraction, refract scrib/script/scribe – meaning to write – scribble, inscription, prescribe, manuscript, describe, description, prescription, subscription, transcribe, inscribe, scripture spect – meaning to look or watch – inspection, inspect, spectator, suspect, prospect, spectacle, specimen, respect, expect mit – meaning to send – submit, intermittent, transmit, missile, mission, admit, transmission, emit, remit, commit, permit, omit fac – meaning to do or make – factory, manufacture, facsimile, benefactor vid/vis – meaning to see – video, televise, television, visible, vision, evidence, evident, provide, revise, supervise Irregular Verb examples become, begin, bring, keep, leave, take, draw, forgive, freeze, give, etc. Prefix meanings and examples Re- - meaning again or back – reimburse, return Un- - meaning not – unknown, unhappy, unfriendly Pre- - meaning before – pregame, pretest Dis- - meaning not or apart – disagree, discord, Non- - meaning not – nonfiction, nonsense, nonfat Over- - meaning over – overlook, overall, overgrown In-, Im- - meaning not – inefficient, impossible, injustice, invalid, immeasurable In-, Im- - meaning in – impression, inmate, immigration, instyle Third Grade 2014-15 *-Beginning in grade 3, these skills and understandings are particularly likely to require continued attention in higher grades as they are applied to increasingly sophisticated writing and speaking. Grade 3 Foundational Skills/Language/Speaking & Listening Learning Targets-2014-15 7-26-14 Derivational Suffix meanings and examples Words that change to Adjectives -al – meaning relating to – accidental, personal, professional -ary – meaning relating to – imaginary, secondary -able – meaning capable of – taxable, comfortable, readable -ly – meaning like or manner of – brotherly, sisterly, monthly -y – meaning inclined to – easy, messy, chewy -ful – meaning full of – careful, forgetful, useful, helpful Words that change to Nouns -er – meaning one who – farmer, teacher, worker -ess – meaning female – actress, goddess, waitress -ness – meaning state or condition of – kindness, sadness, darkness -ary – meaning quality of or relating to – dictionary, seminary -y – meaning characterized by – cheery, grouchy, jealousy, victory Words that change to Adverbs or Verbs -ly – meaning like or same – helpfully, actively, quickly, clearly -ize – meaning make – terrorize, idolize, privatize -ate – meaning cause or make – liquidate, liberate Comparative and Superlative Adverbs and Adjectives -er – Suffix used to compare two items. – wider, softer, happier, crazier, smaller, -est – Suffix used to compare more than two items – widest, softest, happiest, craziest, smallest Use more with words of two syllables or greater that end in –ful, -less, -ing, -ed, and -ous to compare two items – more hopeful, more painless, more boring, more worried, more famous Use most with words of two syllables or greater that end in –ful, -less, -ing, -ed, and -ous to compare more than two items – most hopeful, most painless, most boring, most worried, most famous Use more with words of three syllables or greater to compare two items – more essential, more fantastic, more wonderful, more interesting, more confident. Use most with words of three syllables or greater to compare more than two items – most essential, most fantastic, most wonderful, most interesting, most confident. , Third Grade 2014-15 *-Beginning in grade 3, these skills and understandings are particularly likely to require continued attention in higher grades as they are applied to increasingly sophisticated writing and speaking.