answer
advertisement

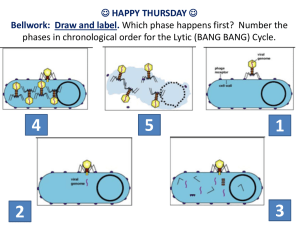
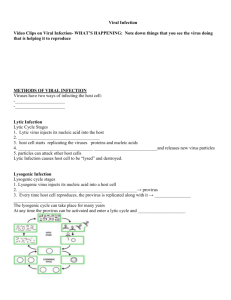
Viruses Name: Read each question, and write your answer in the space provided. 1. What is a virus? Infectious particles. 2. What properties of life does a virus lack? They cannot reproduce themselves and have no metabolism. They do not respond to stimulation nor are they made of cells. 3. How do viruses reproduce? Virus must infect a host and use the host’s biological machinery to reproduce. They basically hijack their host’s body. 4. List the 4 main shapes of viral structures. Helical Polyhedral Enveloped Other. 5. What is the function of the tail and tail fibers in a phage? They are docking mechanisms (tail fibers). The tail acts as a plunger for the genetic information to be delivered to the host through. Match the letter of the description that best defines the term or phrase. 6. 7. 8. 9. Capsid Envelope Glycoprotein Bacteriophage a. a protein with an attached carbohydrate molecule b. the protein coat of a virus c. a virus that infects bacteria d. a membrane that surrounds the capsid of some viruses Define the terms: 10. lytic cycle: A cycle of the virus’s existence characterized by Viral DNA being injected into host cell, the host cell replicates viral DNA and makes the viral capsids (protein coats), new viruses are assembled inside host cell, then finally, the cell bursts open releasing new viruses. This is usually when symptoms of viral infections are detectable. 11. lysogenic cycle: The dormant stage of a virus’s existence characterized by Viral DNA injected into the host cell, Viral DNA inserts itself into the host’s DNA where it remains inactive for days, months, or years. As the cell reproduces, more cells are produced that have the viral DNA in them. Eventually, when the conditions are favorable (like when your immune system is weakened) the virus will enter the lytic cycle. 12. Provirus: a virus that has integrated into a host’s genome and is replicated when the cell replicates its DNA. 13. Temperate virus: A virus that causes moderate symptoms. 14. HIV: human immunodeficiency virus. The enveloped virus that causes AIDS. 15. AIDS: Auto-immune disease caused by the HIV virus that continuously and unpredictably changes (mutates) its receptors so our immune system can never fully defend against it. 16. Prion: protein pathogens with no nucleic acids that cause other proteins to become misshapen in a chain reaction (mad cow disease) 17. Viroid: single-strained viral DNA with no capsid that cause disease (mostly in plants) Read the passage below. Then answer the questions that follow. Viruses lack the enzymes necessary for metabolism and have no structures for making proteins. Therefore, viruses must rely on living cells for reproduction. Before a virus can reproduce, it must first infect a living cell. In bacteriophages— bacterial viruses—the cycle of viral infection, reproduction, and cell destruction is called the lytic cycle. After the viral genetic material has entered the cell, it uses the host cell to replicate viral genes and to make viral proteins, such as capsids. The proteins are then assembled with the replicated viral genes to form complete viruses. The host cell breaks open and releases newly made viruses. During an infection, some viruses stay inside the cells but do not make new viruses. Instead of producing virus particles, the viral genetic material is inserted into the host chromosome and is called a provirus. Whenever the cell divides, the provirus also divides, resulting in two infected host cells. In this cycle, called the lysogenic cycle, the viral genome replicates without destroying the host cell. READING EFFECTIVELY: Read each question, and write your answer in the space provided. 18. Why must viruses rely on living cells for reproduction? How does this make them non-living? They cannot replicate themselves because they have no organelle that allows it. 19. What is the main idea of the second paragraph? Sometimes virus lay dormant and don’t’ go into a full-blown infection. SKILL: INTERPRETING GRAPHICS The figure below shows the lytic and lysogenic cycles. Circle and trace each. In the spaces provided, describe what is occurring in each numbered part of the figure. 20. Part 1: Virus attaches 21. Part 2: Virus enters either the either the lytic or lysogenic pathway. 22. Part 3: New viruses are made. 23. Part 4: The cell breaks open and releases new virus. (lytic pathway) 24. Part 5: The provirus may enter the lysogenic pathway. 25. Which stage is the dormant stage of the viral reproduction cycle? Lysogenic phase. 26. If you are showing signs of a viral infection, what stage of a virus’s reproduction is giving the symptoms? Lytic pathway.